Research Area C - Publications 2008
29-Dec-2008
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article
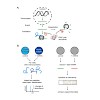
Inhibition or degradation? MicroRNAs have been considered primarily as inhibitors of translation, even though degradation of mRNAs also plays a role in their repressive potential. Two research groups have now quantified the extent to which each mechanism contributes to gene regulation by combining mass spectrometry with transcriptome profiling. The surprising ...
18-Dec-2008
Mol. Microbiol., 2009, 71(4), 989-1002, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06577.x published on 18.12.2008
Molecular Microbiology, online article
The general subunit of all three eukaryotic RNA polymerases, Rpb12, and subunit P of the archaeal enzyme show sequence similarities in their N-terminal zinc ribbon and some highly conserved residues in the C-terminus. We report here that archaeal subunit P under the control of a strong yeast promoter could complement the lethal phenotype of a RPB12 deletion ...
18-Dec-2008
Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., online article
Whereas mechanisms underlying the fidelity of DNA polymerases (DNAPs) have been investigated in detail, RNA polymerase (RNAP) fidelity mechanisms remained poorly understood. New functional and structural studies now suggest how RNAPs select the correct nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) substrate to prevent transcription errors, and how the enzymes detect and remove a ...
04-Dec-2008
The EMBO Journal, online article
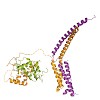
Mediator is a modular multiprotein complex required for regulated transcription by RNA polymerase (Pol) II. Here, we show that the middle module of the Mediator core contains a submodule of unique structure and function that comprises the N-terminal part of subunit Med7 (Med7N) and the highly conserved subunit Med31 (Soh1). The Med7N/31 submodule shows a ...
01-Dec-2008
Biophysical Journal, online article

We have studied the initial phase of cell adhesion as a function of the lateral organization of individual integrin molecules with single-cell force microscopy. Nanostructures, consisting of hexagonally ordered gold dots, were prepared with diblock-copolymer micelle lithography and functionalized with arginine- glycine-aspartate peptides, thus defining integrin ...
13-Nov-2008
Bioinformatics, online article
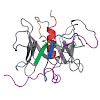
Motivation: Phospholipid scramblases (PLSCRs) constitute a family of cytoplasmic membrane-associated proteins that were identified based upon their capacity to mediate a Ca2+-dependent bidirectional movement of phospholipids across membrane bilayers, thereby collapsing the normally asymmetric distribution of such lipids in cell membranes. The exact function and ...
10-Nov-2008
The activation of well-defined numbers of integrin molecules in predefined areas by adhesion of tissue cells to biofunctionalized micro-nanopatterned surfaces was used to determine the minimum number of activated integrins necessary to stimulate focal adhesion formation. This was realized by combining micellar and conventional e-beam lithography, which enabled ...
05-Nov-2008
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
Structural investigations are frequently hindered by difficulties in obtaining diffracting crystals of the target protein. Here, we report the crystallization and structure solution of the U2AF homology motif (UHM) domain of splicing factor Puf60 fused to Escherichia coli thioredoxin A. Both modules make extensive crystallographic contacts, contributing to a ...
04-Nov-2008
Journal of Peptide Science online article
The incorporation of proline into cyclic peptides seems to be the most promising way to induce -turn structures. Recently, however, it was shown that N-methylated amino acids might be even better suited than proline for introducing turn structures. Another property of proline, the ability to effect cis-peptide bonds, has also been reported for N-methylated amino ...
01-Nov-2008
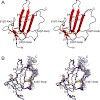
Viscotoxins are small cationic proteins found in European mistletoe Viscum album. They are highly toxic towards phytopathogenic fungi and cancer cells. Heterologous expression of viscotoxins would broaden the spectrum of methods to be applied for better understanding of their structure and function and satisfy possible biopharmaceutical needs. Here, we evaluated ...
29-Oct-2008
jbc, online article
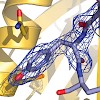
PUF60 is an essential splicing factor functionally related and homologous to U2AF65. Its C-terminal domain belongs to the family of U2AF (U2 auxiliary factor) homology motifs (UHM), a subgroup of RNA recognition motifs that bind to tryptophan-containing linear peptide motifs (UHM ligand motifs, ULMs) in several nuclear proteins. Here, we show that the Puf60 UHM ...
21-Oct-2008
The structure of the extracellular domain of BMP receptor IA was determined in solution by NMR spectroscopy and compared to its structure when bound to its ligand BMP-2. While most parts of the secondary structure are highly conserved between the bound and unbound forms, large conformational rearrangements can be observed in the b4b5 loop of BMPR-IA, which is in ...
17-Oct-2008
Protein Expression and Purification, online article
Viscotoxins are small cationic proteins found in European mistletoe Viscum album. They are highly toxic towards phytopathogenic fungi and cancer cells. Heterologous expression of viscotoxins would broaden the spectrum of methods to be applied for better understanding of their structure and function and satisfy possible biopharmaceutical needs. Here, we evaluated ...
17-Oct-2008
www.humboldt-foundation.de

We are very happy that Ulrike Gaul, professor of molecular biology at Rockefeller University New York, will join CIPSM at the Gene Center in 2009 as a newly established CIPSM full professor. This CIPSM professorship for molecular systems biology has been selected for the first Alexander von Humboldt professorship ever to be awarded and comes with an prize money ...
12-Oct-2008
Very often, the positions of flexible domains within macromolecules as well as within macromolecular complexes cannot be determined by standard structural biology methods. To overcome this problem, we developed a method that uses probabilistic data analysis to combine single-molecule measurements with X-ray crystallography data. The method determines not only the ...
06-Oct-2008
Perdeuterated poly(styrene) is introduced as an almost artefactfree and arbitrarily scalable alignment medium for measuring residual dipolar couplings and other anisotropic NMR parameters; the spectral quality achievable in this new medium is demonstrated for HSQC spectra leading to the conformational analysis of staurosporine and homonuclear TOCSY-type experiments.
30-Aug-2008

The oxazolidinones represent the first new class of antibiotics to enter into clinical usage within the past 30 years, but their binding site and mechanism of action has not been fully characterized. We have determined the crystal structure of the oxazolidinone linezolid bound to the Deinococcus radiodurans 50S ribosomal subunit. Linezolid binds in the A site ...
26-Aug-2008
Nature Reviews - Drug Disc, 2008, 7, 738-45 published on 26.08.2008
Nature Reviews - Drug discovery, online article
in the past decade, the potential of harnessing the ability of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMr) spectroscopy to monitor intermolecular interactions as a tool for drug discovery has been increasingly appreciated in academia and industry. in this Perspective, we highlight some of the major applications of NMR in drug discovery, focusing on hit and lead generation, ...
22-Aug-2008
http://www.eurpepsoc.com

CIPSM Coordinator Horst Kessler wins 2008 Joseph Rudinger Award of the European Peptide Society for his lifetime achievements in peptide chemistry! The Joseph Rudinger Award award is presented „in commemoration of Josef Rudinger’s role in the foundation of the European Peptide Symposia and of the diverse contributions he made to peptide chemistry.” We thank and ...
19-Aug-2008
ERC

CIPSM-Junior-Group Leader Katja Sträßer has done it! She received a grant of nearly one million Euros from the European Research Council for the next five years. She will explore the understanding of a new aspect of how genetic information is read out by a cell. Many of the individual steps examined separately in the past are coupled with each other to allow for ...
17-Aug-2008
Nature structural & molecular biology, online article
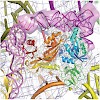
EF4 (LepA) is an almost universally conserved translational GTPase in eubacteria. It seems to be essential under environmental stress conditions and has previously been shown to back-translocate the tRNAs on the ribosome, thereby reverting the canonical translocation reaction. In the current work, EF4 was directly visualized in the process of back-translocating ...
01-Aug-2008
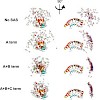
We present the implementation of a target function based on Small Angle Scattering data (Gabel et al. Eur Biophys J 35(4):313–327, 2006) into the Crystallography and NMR Systems (CNS) and demonstrate its utility in NMR structure calculations by simultaneous application of small angle scattering (SAS) and residual dipolar coupling (RDC) restraints. The efficiency ...
30-Jul-2008
jbc, online article

Yeast RNA polymerase (Pol) II consists of a 10-subunit core enzyme and the Rpb4/7 subcomplex, which is dispensable for catalytic activity and dissociates in vitro. To investigate whether Rpb4/7 is an integral part of DNA-associated Pol II in vivo, we used chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled to high resolution tiling microarray analysis. We show that the ...
22-Jul-2008

U2AF homology motifs (UHM) are protein domains that bind peptidic UHM ligand motifs (ULM) and thus form an intricate network of interactions involved in splicing regulation. Here, we report the backbone assignment of the UHM domain of the splicing factor Puf60 as well as 1H, 15N chemical shifts upon binding of the ULM peptides U2AF65 (85–112), SF1 (1–25), SF3b155 ...
18-Jul-2008
http://pubs.acs.org , online article
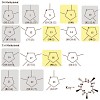
The potential of peptides as drug candidates is limited by their poor pharmacokinetic properties. Many peptides have a short half-life in vivo and a lack of oral availability. Inspired by the excellent pharmacokinetic profile of cyclosporine, a natural, multiply N-methylated cyclic peptide, we envisioned multiple N-methylation as a promising way to rationally ...
02-Jul-2008

Folding intermediates play a key role in defining protein folding and assembly pathways as well as those of misfolding and aggregation. Yet, due to their transient nature, they are poorly accessible to high-resolution techniques. Here, we made use of the intrinsically slow folding reaction of an antibody domain to characterize its major folding intermediate in ...
18-Jun-2008

Cell interactions with adhesive surfaces play a vital role in the regulation of cell proliferation, viability, and differentiation, and affect multiple biological processes. Since cell adhesion depends mainly on the nature and density of the adhesive ligand molecules, spatial molecular patterning, which enables the modulation of adhesion receptor clustering, ...
13-Jun-2008
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 2011, doi:10.1038/nsmb.1458, 811-818 published on 13.06.2008
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article

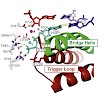
To study how RNA polymerase II translocates after nucleotide incorporation, we prepared elongation complex crystals in which pre- and post-translocation states interconvert. Crystal soaking with the inhibitor alpha-amanitin locked the elongation complex in a new state, which was refined at 3.4-Å resolution and identified as a possible translocation intermediate. ...
09-Jun-2008
ChemBioChem, 2008, 9, 1397-1407 published on 09.06.2008
ChemBioChem; online article

The inhibition of integrin function is a major challenge in medicinal chemistry. Potent ligands are currently in different stages of clinical trials for the antiangiogenic therapy of cancer and agerelated macula degeneration (AMD). The subtype a5b1has recently been drawn into the focus of research because of its genuine role in angiogenesis. In our previous work ...
09-May-2008
Acta Crystallographica, online article
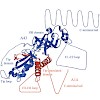
The removal of flexible protein regions is generally used to promote crystallization, but advanced strategies to quickly remove multiple flexible regions from proteins or protein complexes are lacking. Here, it is shown how a protein heterodimer with multiple flexibilities, the RNA polymerase I subcomplex A14/A43, could be crystallized with the use of an ...
The Role of 23S Ribosomal RNA Residue A2451 in Peptide Bond Synthesis Revealed by Atomic Mutagenesis
24-Apr-2008
Chemistry & Biology, 2008, Vol. 15, DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.03.014 published on 24.04.2008
Chemistry & Biology; online article
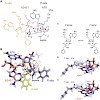
Peptide bond formation is a fundamental reaction in biology, catalyzed by the ribosomal peptidyl-transferase ribozyme. Although all active-site 23S ribosomal RNA nucleotides are universally conserved, atomic mutagenesis suggests that these nucleobases do not carry functional groups directly involved in peptide bond formation. Instead, a single ribose 20-hydroxyl ...
22-Apr-2008

With the advances made in surface patterning by micro- and nanotechnology, alternative methods to immobilize biomolecules for different purposes are highly desired. RGD peptides are commonly used to create cell-attractive surfaces for cell-biological and also medical applications. We have developed a fast, one-step method to bind RGD peptides covalently to ...
17-Apr-2008
Analytical Chemistry, online article

The multisubunit RNA polymerases (Pols) II and III synthesize mainly eukaryotic mRNAs and tRNAs, respectively. Pol II and Pol III are protein complexes consisting of 12 and 17 subunits. Here we analyzed both yeast Pol II and Pol III by multiplexed mass spectrometric analysis using various proteases and both collision induced and electron transfer dissociation. ...
16-Apr-2008
Nature, 2008, 452, 822-23 published on 16.04.2008
nature; online article

A few weeks ago, many of our friends suffered from ‘winter vomiting disease’, a form of gastroenteritis that swept epidemically across Germany. This unpleasant disease is caused by the highly contagious norovirus, a member of the Caliciviridae family of RNA viruses. Caliciviruses are unusual because they dock to sugar residues on the surfaces of cells to be ...
12-Apr-2008
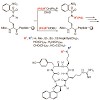
An optimized protocol for the mild and selective Fukuyama−Mitsunobu reaction was used for mono- and di-N-alkylation on solid support. Thereby, nonfunctionalized aliphatic and aromatic residues are quickly introduced into transiently protected, primary amines of a linear peptide. N-Alkylation can also be used to implement alkyl chains carrying (protected) ...
11-Apr-2008
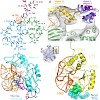
The thiopeptide class of antibiotics targets the GTPase-associated center (GAC) of the ribosome to inhibit translation factor function. Using X-ray crystallography, we have determined the binding sites of thiostrepton (Thio), nosiheptide (Nosi), and micrococcin (Micro), on the Deinococcus radiodurans large ribosomal subunit. The thiopeptides, by binding within a ...
28-Mar-2008
EH domains are protein–protein interaction domains that function in vesicular trafficking and endocytosis. Here, we report the NMR spectral assignments of the high-affinity complex between the second EH domain of Eps15 and a stonin 2 peptide—providing the basis for the characterization of a two-site binding mode.
21-Mar-2008
Journal of Magnetic Resonance, online article
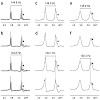
Heteronuclear residual dipolar one-bond couplings of organic molecules at natural abundance are most easily measured using t2 coupled HSQC spectra. However, inevitably mismatched transfer delays result in phase distortions due to residual dispersive antiphase coherences in such experiments. In this article, slightly modified t2 coupled HSQC experiments with clean ...
29-Feb-2008
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article

NMR spectroscopy is a well-established technique for the screening of compound libraries. One of the biggest advantages of NMR spectroscopy in relation to other methods is that it directly detects even weakinteractions between ligand and target molecules, which makes it ideally suited for fragment-based ligand design. In addition, the number of false-positive ...
26-Feb-2008
Angewandte Chemie, online article
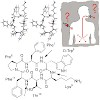
Full methyl jacket? A complete library of the N-methylated somatostatin cyclopeptidic analogue Veber–Hirschmann peptide cyclo(-PFwKTF-) is performed with the aim of improving its bioavailability. Several analogues from the library were found to bind to the somatostatin receptor in the nanomolar range and one of them shows a significant oral bioavailability of ...
22-Feb-2008
Journal of Biological Chemistry, online article

The Na+/solute symporter family comprises more than 400 members of pro- and eukaryotic origin. Using the Na+/proline transporter PutP of Escherichia coli as a model, the role of two conserved residues, Ser-340 and Thr-341, is investigated to obtain insights into the mechanism of transport catalyzed by members of this family. Substitution of these amino acids ...
15-Feb-2008
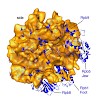
Related multisubunit RNA polymerases (RNAPs) carry out gene transcription in all kingdoms of life. Since structural information is limited to bacterial and eukaryotic RNAPs, we determined the cryo-electron microscopic structure of the RNAP from the thermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus at 13 Å resolution. Comparison with eukaryotic RNAP II reveals a conserved ...
08-Feb-2008
Chemistry a European Journal, online article
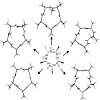
Systematic N-methylation of all peptide bonds in the cyclic pentapeptide cyclo(-d-Ala-Ala4-) has been performed yielding 30 different N-methylated derivatives, of which only seven displayed a single conformation on the NMR time scale. The conformation of these differentially N-methylated peptides was recently reported by us (J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 15 164–15 ...
07-Feb-2008
Biophysics, online article
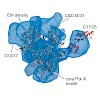
The eukaryotic RNA polymerases Pol I, Pol II, and Pol III are the central multiprotein machines that synthesize ribosomal, messenger, and transfer RNA, respectively. Here we provide a catalog of available structural information for these three enzymes. Most structural data have been accumulated for Pol II and its functional complexes. These studies have provided ...
06-Feb-2008
Cardiovascular Research, 2008, doi:10.1093/cvr/cvn033, 1-37 published on 06.02.2008
Cardiovascular Research, online article
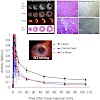
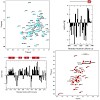
The purpose of this study was to determine the feasibility of a new positron emission tomography (PET) imaging approach using a 18F-labeled αvβ3 integrin antagonist (18F-Galacto-RGD) to monitor the integrin expression after myocardial infarction. METHODS: Male Wister rats were subjected to 20 min of transient left coronary artery occlusion followed by ...
01-Feb-2008
Nucleic Acids Research, online article

The active center clefts of RNA polymerase (RNAP) from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus (Pfu) and of yeast RNAP II are nearly identical, including four protruding loops, the lid, rudder, fork 1 and fork 2. Here we present a structure-function analysis of recombinant Pfu RNAP variants lacking these cleft loops, and analyze the function of each loop at different ...
01-Feb-2008
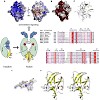
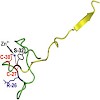
The ATPase RIG-I senses viral RNAs that contain 5`triphosphates in the cytoplasm. It initiates a signaling cascade that activates innate immune response by interferon and cytokine production, providing essential antiviral protection for the host. The mode of RNA 50-triphosphate sensing by RIG-I remains elusive. We show that the C-terminal regulatory domain RD of ...
01-Feb-2008
Genes & Development, online article
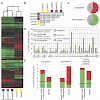
A combination of crystallography, biochemistry, and gene expression analysis identifies the coactivator subcomplex Med8C/18/20 as a functionally distinct submodule of the Mediator head module. Med8C forms a conserved α-helix that tethers Med18/20 to the Mediator. Deletion of Med8C in vivo results in dissociation of Med18/20 from Mediator and in loss of ...
17-Jan-2008
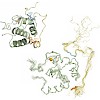
Eps15 homology (EH) domain-containing proteins play a key regulatory role in intracellular membrane trafficking and cell signalling. EH domains serve as interaction platforms for short peptide motifs comprising the residues NPF within natively unstructured regions of accessory proteins. The EH–NPF interactions described thus far are of very low affinity and ...
09-Jan-2008
Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, online article
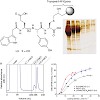
BACKGROUND: Hemophilia A is currently treated by infusions of the coagulation factor (F) VIII, of which production and purification remain a challenging task. Current purification procedures using immunoaffinity chromatography are cumbersome, expensive, and suffer from the instability of the applied antibody ligands, which elute along with the product and ...
08-Jan-2008

Single-pair fluorescence resonance energy transfer was used to track RNA exiting from RNA polymerase II (Pol II) in elongation complexes. Measuring the distance between the RNA 5´ end and three known locations within the elongation complex allows us determine its position by means of triangulation. RNA leaves the polymerase active center cleft via the previously ...