Research Area C - Publications 2016
16-Dec-2016
Nucl Acids Res, gkw1272., DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1272
Nucl Acids Res., online article

Ribosomes are the protein synthesizing machines of the cell. Recent advances in cryo-EM have led to the determination of structures from a variety of species, including bacterial 70S and eukaryotic 80S ribosomes as well as mitoribosomes from eukaryotic mitochondria, however, to date high resolution structures of plastid 70S ribosomes have been lacking. Here we ...
15-Dec-2016
J Nucl Med., doi:10.2967/jnumed.116.182824
J Nucl Med., online article
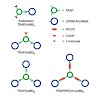
Expression of the cellular transmembrane receptor αvβ6 integrin is essentially restricted to malignant epithelial cells in carcinomas of a broad variety of lineages, while it is virtually absent in normal adult tissues. Thus, it is a highly attractive target for tumor imaging and therapy. Furthermore, αvβ6 integrin plays an important role for the ...
01-Dec-2016
Nature, doi:10.1038/nature20821
Nature, online article
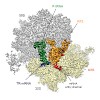
In bacteria, ribosomes stalled on truncated mRNAs lacking a stop codon are rescued by either the transfer-messenger RNA (tmRNA), alternative rescue factor A (ArfA) or ArfB rescue systems1. While tmRNA- and ArfB-ribosome structures have been elucidated2–7, structural insight into how ArfA recognizes the presence of truncated mRNAs and recruits the canonical ...
30-Nov-2016
Archaea, Volume 2016 (2016), Article ID 7316725, 14 pages, http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7316725
Archaea, online article

Translation initiation factor 5A (IF5A) is essential and highly conserved in Eukarya (eIF5A) and Archaea (aIF5A). The activity of IF5A requires hypusine, a posttranslational modification synthesized in Eukarya from the polyamine precursor spermidine. Intracellular polyamine analyses revealed that agmatine and cadaverine were the main polyamines produced in ...
29-Nov-2016
eLife; 5: e14707, DOI: 10.7554/eLife.14707
eLife, online article

The multi-domain splicing factor RBM5 regulates the balance between antagonistic isoforms of the apoptosis-control genes FAS/CD95, Caspase-2 and AID. An OCRE (OCtamer REpeat of aromatic residues) domain found in RBM5 is important for alternative splicing regulation and mediates interactions with components of the U4/U6.U5 tri-snRNP. We show that the RBM5 OCRE ...
31-Oct-2016
PNAS, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1605873113
PNAS, online article
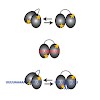
An essential early step in the assembly of human spliceosomes onto pre-mRNA involves the recognition of regulatory RNA cis elements in the 3′ splice site by the U2 auxiliary factor (U2AF). The large (U2AF65) and small (U2AF35) subunits of the U2AF heterodimer contact the polypyrimidine tract (Py-tract) and the AG-dinucleotide, respectively. The tandem RNA ...
18-Oct-2016
J. Med. Chem., 59 (22), pp 10190–10197, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01118
J. Med. Chem., online article
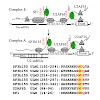
U2AF homology motifs (UHMs) are atypical RNA recognition motif domains that mediate critical protein–protein interactions during the regulation of alternative pre-mRNA splicing and other processes. The recognition of UHM domains by UHM ligand motif (ULM) peptide sequences plays important roles during early steps of spliceosome assembly. Splicing factor 45 kDa ...
12-Oct-2016
Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 20, Issue 4, p443–457, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2016.09.003
Cell Host & Microbe, online article
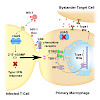
Upon sensing cytoplasmic retroviral DNA in infected cells, cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS) produces the cyclic dinucleotide cGAMP, which activates STING to trigger a type I interferon (IFN) response. We find that membrane fusion-inducing contact between donor cells expressing the HIV envelope (Env) and primary macrophages endogenously expressing the HIV ...
10-Oct-2016
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 23, 1020–1028, doi:10.1038/nsmb.3305
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
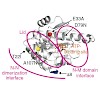
Hsp90 couples ATP hydrolysis to large conformational changes essential for activation of client proteins. The structural transitions involve dimerization of the N-terminal domains and formation of 'closed states' involving the N-terminal and middle domains. Here, we used Hsp90 mutants that modulate ATPase activity and biological function as probes to address the ...
09-Oct-2016
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, Volume 1863, Issue 5, Pages 804–813, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.09.034
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, online article
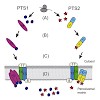
The peroxisomal proteins (peroxins) that mediate the import of peroxisomal matrix proteins have been identified. Recently, the purification of a functional peroxisomal translocon has been reported. However, the molecular details of the import pathways and the mechanisms by which the cargo is translocated into the lumen of the organelle are still poorly ...
06-Oct-2016
Scientific Reports, 6, Article number: 34525, doi:10.1038/srep34525
Scientific Reports, online article

Single strand annealing proteins (SSAPs) like Redβ initiate homologous recombination by annealing complementary DNA strands. We show that C-terminally truncated Redβ, whilst still able to promote annealing and nucleoprotein filament formation, is unable to mediate homologous recombination. Mutations of the C-terminal domain were evaluated using both single- and ...
13-Sep-2016
Front. Mol. Biosci., https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2016.00054
Front. Mol. Biosci., online article

Intrinsically disordered linkers provide multi-domain proteins with degrees of conformational freedom that are often essential for function. These highly dynamic assemblies represent a significant fraction of all proteomes, and deciphering the physical basis of their interactions represents a considerable challenge. Here we describe the difficulties associated ...
08-Sep-2016
Chem. Eur. J., Volume 22, Issue 43, Pages 15350–15359, DOI: 10.1002/chem.201602784
Chem. Eur. J., online article
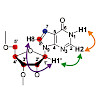
Structural features and internal dynamics of inosine-containing RNAs are poorly understood. NMR studies of such RNAs require 13C,15N-labeling, which cannot be achieved using in vitro transcription as inosine and guanosine are not distinguished by RNA polymerase. Herein, we report the synthesis of an inosine phosphoramidite with selective 13C8 and 15N7-isotope ...
08-Sep-2016
Chem. Eur. J., 22, 1 – 11, DOI: 10.1002/chem.201602784
Chem. Eur. J., online article
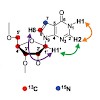
Structural features and internal dynamics of inosine-containing RNAs are poorly understood. NMR studies of such RNAs require 13C,15N-labeling, which cannot be achieved using in vitro transcription as inosine and guanosine are not distinguished by RNA polymerase. Herein, we report the synthesis of an inosine phosphoramidite with selective 13C8 and 15N7-isotope ...
01-Aug-2016
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med., doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a025361
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med., online article
Protein synthesis occurs on macromolecular machines, called ribosomes. Bacterial ribosomes and the translational machinery represent one of the major targets for antibiotics in the cell. Therefore, structural and biochemical investigations into ribosome-targeting antibiotics provide not only insight into the mechanism of action and resistance of antibiotics, but ...
06-Jul-2016
Nature Communications, 7, Article number: 12026, doi:10.1038/ncomms12026
Nature Communications, online article
Nascent polypeptides can induce ribosome stalling, regulating downstream genes. Stalling of ErmBL peptide translation in the presence of the macrolide antibiotic erythromycin leads to resistance in Streptococcus sanguis. To reveal this stalling mechanism we obtained 3.6-Å-resolution cryo-EM structures of ErmBL-stalled ribosomes with erythromycin. The nascent ...
29-Jun-2016
PNAS, vol. 113, no. 30, E4357–E4366, www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1523708113
PNAS, online article

Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) is a large, multidomain protein containing two catalytic domains: a Ras of complex proteins (Roc) G-domain and a kinase domain. Mutations associated with familial and sporadic Parkinson’s disease (PD) have been identified in both catalytic domains, as well as in several of its multiple putative regulatory domains. Several of ...
21-Jun-2016
PNAS, 1 of 6, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604790113
PNAS, online article

The ribosome is one of the major targets for therapeutic antibiotics; however, the rise in multidrug resistance is a growing threat to the utility of our current arsenal. The orthosomycin antibiotics evernimicin (EVN) and avilamycin (AVI) target the ribosome and do not display cross-resistance with any other classes of antibiotics, suggesting that they bind to a ...
16-Jun-2016
Nature Communications, 7, Article number: 11874, doi:10.1038/ncomms11874
Nature Communications, online article

Centrioles and cilia are microtubule-based structures, whose precise formation requires controlled cytoplasmic tubulin incorporation. How cytoplasmic tubulin is recognized for centriolar/ciliary-microtubule construction remains poorly understood. Centrosomal-P4.1-associated-protein (CPAP) binds tubulin via its PN2-3 domain. Here, we show that a C-terminal ...
13-Jun-2016
PNAS Early Edition, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604125113
PNAS, online article
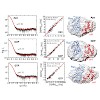
Heterotrimeric G proteins play a pivotal role in the signal-transduction pathways initiated by G-protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) activation. Agonist–receptor binding causes GDP-to-GTP exchange and dissociation of the Gα subunit from the heterotrimeric G protein, leading to downstream signaling. Here, we studied the internal mobility of a G-protein α subunit in ...
08-Jun-2016
Scientific Reports, volume 6, Article number: 27498 (2016), https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27498
Scientific Reports, online article
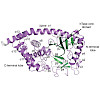
The exceptionally conserved metazoan MAB21 proteins are implicated in cell fate decisions and share considerable sequence homology with the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase. cGAS is the major innate immune sensor for cytosolic DNA and produces the second messenger 2′-5′, 3′-5′ cyclic GMP-AMP. Little is known about the structure and biochemical function of other proteins ...
26-May-2016
Scientific Reports, 6, Article number: 26707, doi:10.1038/srep26707
Scientific Reports, online article

p63 is a close homologue of p53 and, together with p73, is grouped into the p53 family of transcription factors. p63 is known to be involved in the induction of controlled apoptosis important for differentiation processes, germ line integrity and development. Despite its high homology to p53, especially within the DNA binding domain (DBD), p63-DBD does not show ...
25-May-2016
Trends in Microbiology, Volume 24, Issue 7, p517–519, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2016.05.001
Trends in Microbiology, online article

RIG-I-like receptors detect cytosolic viral RNA and activate an antiviral innate immune response. A new study employs the one STrEP-purification technique and next generation sequencing to characterize physiological ligands in an infected cell. The view of all three RLRs bound to viral RNAs shows specialization, collaboration and new binding sites.
25-May-2016
Nucleic Acids Research,1, doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw470
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
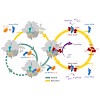
Under stress conditions, such as nutrient starvation, deacylated tRNAs bound within the ribosomal A-site are recognized by the stringent factor RelA, which converts ATP and GTP/GDP to (p)ppGpp. The signaling molecules (p)ppGpp globally rewire the cellular transcriptional program and general metabolism, leading to stress adaptation. Despite the additional ...
20-May-2016
Biopolymers, Volume 105, Issue 8, Pages 492–504, DOI 10.1002/bip.22843
Biopolymers, online article

ATP binding cassette (ABC) ATPases form chemo-mechanical engines and switches that function in a broad range of biological processes. Most prominently, a very large family of integral membrane NTPases—ABC transporters—catalyzes the import or export of a diverse molecules across membranes. ABC proteins are also important components of the chromosome segregation, ...
05-May-2016
THE JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE, Vol. 57, No. 10, 1618–1624, doi: 10.2967/jnumed.116.173948
J Nucl Med., online article
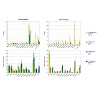
Ga-68-Aquibeprin and Ga-68-Avebetrin are tracers for selective in-vivo mapping of integrins α5β1 and αvβ3, respectively, by positron emission tomography (PET). As both tracers exhibit very high affinity to their respective targets, the aim of this study was to investigate the influence of the specific activity of preparations of both tracers on in vivo imaging ...
03-May-2016
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Volume 55, Issue 25, Pages 7048–7067, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201509782
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article
Engineering biomaterials with integrin-binding activity is a very powerful approach to promote cell adhesion, modulate cell behavior, and induce specific biological responses at the surface level. The aim of this Review is to illustrate the evolution of surface-coating molecules in this field: from peptides and proteins with relatively low integrin-binding ...
03-May-2016
mBio, Volume 7, Issue 3, e00598-16, doi: 10.1128/mBio.00598-16
mBio, online article
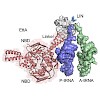
The increase in multidrug-resistant pathogenic bacteria is limiting the utility of our current arsenal of antimicrobial agents. Mechanistically understanding how bacteria obtain antibiotic resistance is a critical first step to the development of improved inhibitors. One common mechanism for bacteria to obtain antibiotic resistance is by employing ATP-binding ...
19-Apr-2016
Immunity, Volume 44, Issue 4, p739–754, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2016.04.002
Immunity, online article

Recognition of DNA and RNA by endosomal and cytosolic sensors constitutes a central element in the detection of microbial invaders by the innate immune system. However, the capacity of these sensors to discriminate between microbial and endogenous nucleic acids is limited. Over the past few years, evidence has accumulated to suggest that endogenous DNA or RNA ...
24-Mar-2016
Nature Communications, 7, Article number: 11032, doi:10.1038/ncomms11032
Nature Communications, online article

The RNA-binding protein Roquin is required to prevent autoimmunity. Roquin controls T-helper cell activation and differentiation by limiting the induced expression of costimulatory receptors such as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily 4 (Tnfrs4 or Ox40). A constitutive decay element (CDE) with a characteristic triloop hairpin was previously shown to be ...
15-Mar-2016
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, Volumes 76–77, Pages 7–14, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ssnmr.2016.03.005
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, online article

In recent years, MAS solid-state NMR has emerged as a technique for the investigation of soluble protein complexes. It was found that high molecular weight complexes do not need to be crystallized in order to obtain an immobilized sample for solid-state NMR investigations. Sedimentation induced by sample rotation impairs rotational diffusion of proteins and ...
10-Mar-2016
Oncotarget, Vol. 7, No. 16, DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.8022
Oncotarget, online article
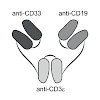
Simultaneous targeting of multiple tumor-associated antigens (TAAs) in cancer immunotherapy is presumed to enhance tumor cell selectivity and to reduce immune escape.
The combination of B lymphoid marker CD19 and myeloid marker CD33 is exclusively present on biphenotypic B/myeloid leukemia cells. Triplebody 33-3-19 binds specifically to both of these TAAs and ...
02-Mar-2016
Scientific Reports, 6, Article number: 22540, doi:10.1038/srep22540
Scientific Reports, online article
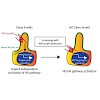
Trafficking of the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) Smoothened (Smo) to the primary cilium (PC) is a potential target to inhibit oncogenic Hh pathway activation in a large number of tumors. One drawback is the appearance of Smo mutations that resist drug treatment, which is a common reason for cancer treatment failure. Here, we undertook a high content screen ...
22-Feb-2016
PLOS ONE, DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0149477
PLOS ONE, online article
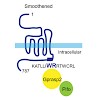
The seven-transmembrane receptor Smoothened (Smo) activates all Hedgehog (Hh) signaling by translocation into the primary cilia (PC), but how this is regulated is not well understood. Here we show that Pitchfork (Pifo) and the G protein-coupled receptor associated sorting protein 2 (Gprasp2) are essential components of an Hh induced ciliary targeting complex able ...
22-Feb-2016
Biochemistry, 55 (12), pp 1839–1849, DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01272
Biochemistry, online article

Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by deposition of the amyloid β-peptide (Aβ) in brain tissue of affected individuals. In recent years, many potential lead structures have been suggested that can potentially be used for diagnosis and therapy. However, the mode of action of these compounds is so far not understood. Among these small molecules, the nonsteroidal ...
19-Feb-2016
The EMBO Journal, Volume 35, Issue 7, Pages 759–772, DOI: 10.15252/embj.201592934
The EMBO Journal, online article
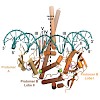
The Mre11–Rad50–Nbs1 (MRN) complex is a central factor in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). The ATP-dependent mechanisms of how MRN detects and endonucleolytically processes DNA ends for the repair by microhomology-mediated end-joining or further resection in homologous recombination are still unclear. Here, we report the crystal structures of the ...
07-Feb-2016
Current Opinion in Structural Biology, Volume 37, Pages 123–133, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2016.01.008
Current Opinion in Structural Biology, online article

As the nascent polypeptide chain is being synthesized, it passes through a tunnel within the large ribosomal subunit. Interaction between the nascent polypeptide chain and the ribosomal tunnel can modulate the translation rate and induce translational stalling to regulate gene expression. In this article, we highlight recent structural insights into how the ...
29-Jan-2016
Journal of Molecular Biology, Volume 428, Issue 6, Pages 1315–1332, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2016.01.015
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article
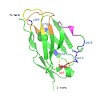
The aggregation of mostly antibody light chain variable (VL) domains into amyloid fibrils in various tissues is the main cause of death in systemic amyloid light chain amyloidosis. Point mutations within the domain are important to shift the VL into the fibrillar pathway, but why and how only some site-specific mutations achieve this still remains elusive. We ...
21-Jan-2016
Genes & Dev., 30: 337-354, doi: 10.1101/gad.273813.115
Genes & Dev., online article

Little is known about how cells ensure DNA replication in the face of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII)-mediated transcription, especially under conditions of replicative stress. Here we present genetic and proteomic analyses from budding yeast that uncover links between the DNA replication checkpoint sensor Mec1–Ddc2 (ATR–ATRIP), the chromatin remodeling complex INO80C ...
20-Jan-2016
Nucl. Acids Res., doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1545
Nucl. Acids Res., online article

Proline-rich antimicrobial peptides (PrAMPs) produced as part of the innate immune response of animals, insects and plants represent a vast, untapped resource for the treatment of multidrug-resistant bacterial infections. PrAMPs such as oncocin or bactenecin-7 (Bac7) interact with the bacterial ribosome to inhibit translation, but their supposed specificity as ...
13-Jan-2016
Nature Communications, 7, Article number: 10355, doi:10.1038/ncomms10355
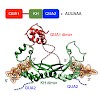
Sam68 and T-STAR are members of the STAR family of proteins that directly link signal transduction with post-transcriptional gene regulation. Sam68 controls the alternative splicing of many oncogenic proteins. T-STAR is a tissue-specific paralogue that regulates the alternative splicing of neuronal pre-mRNAs. STAR proteins differ from most splicing factors, in ...
13-Jan-2016
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 138 (5), pp 1601–1610, DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5b11598
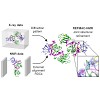
Integrated experimental approaches play an increasingly important role in structural biology, taking advantage of the complementary information provided by different techniques. In particular, the combination of NMR data with X-ray diffraction patterns may provide accurate and precise information about local conformations not available from average-resolution ...
07-Jan-2016
Scientific Reports, 6, Article number: 18934, doi:10.1038/srep18934
The IκB kinase (IKK) complex acts as the gatekeeper of canonical NF-κB signaling, thereby regulating immunity, inflammation and cancer. It consists of the catalytic subunits IKKα and IKKβ and the regulatory subunit NEMO/IKKγ. Here, we show that the ubiquitin binding domain (UBAN) in NEMO is essential for IKK/NF-κB activation in response to TNFα, but not IL-1β ...
WIREs RNA, 7, 455–469, doi: 10.1002/wrna.1333
WIREs RNA, online article
Posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression plays a central role in the initiation of innate and adaptive immune responses. This is exemplified by the protein Roquin, which has attracted great interest during the past decade owing to its ability to prevent autoimmunity. Roquin controls T‐cell activation and T helper cell differentiation by limiting the ...










