Research Area D - Publications 2017
19-Dec-2017
Immunity, Volume 47, Issue 6, p1067–1082.e12, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2017.11.008
Immunity, online article
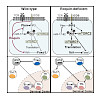
Roquin proteins preclude spontaneous T cell activation and aberrant differentiation of T follicular helper (Tfh) or T helper 17 (Th17) cells. Here we showed that deletion of Roquin-encoding alleles specifically in regulatory T (Treg) cells also caused the activation of conventional T cells. Roquin-deficient Treg cells downregulated CD25, acquired a follicular ...
08-Dec-2017
Journal of Molecular Biology, Volume 429, Issue 24, Pages 3814-3824, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2017.10.014
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article

Ubiquitination is a multifunctional posttranslational modification controlling the activity, subcellular localization and stability of proteins. The E3 ubiquitin ligase ubiquitin-like PHD and RING finger domain-containing protein 1 (UHRF1) is an essential epigenetic factor that recognizes repressive histone marks as well as hemi-methylated DNA and recruits DNA ...
07-Dec-2017
Molecular Cell, Volume 68, Issue 5, p860–871.e7, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.11.019
Molecular Cell, online article
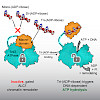
DNA damage triggers chromatin remodeling by mechanisms that are poorly understood. The oncogene and chromatin remodeler ALC1/CHD1L massively decompacts chromatin in vivo yet is inactive prior to DNA-damage-mediated PARP1 induction. We show that the interaction of the ALC1 macrodomain with the ATPase module mediates auto-inhibition. PARP1 activation suppresses ...
21-Nov-2017
Cell Reports, 21, Issue 8, 2048–2057, p2048–2057, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.092
Cell Reports, online article

HP1 is a structural component of heterochromatin. Mammalian HP1 isoforms HP1α, HP1β, and HP1γ play different roles in genome stability, but their precise role in heterochromatin structure is unclear. Analysis of Hp1α−/−, Hp1β−/−, and Hp1γ−/− MEFs show that HP1 proteins have both redundant and unique functions within pericentric heterochromatin (PCH) and also act ...
17-Nov-2017
PNAS, vol. 114, no. 49,12994–12999, https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1705165114
PNAS, online article

IL-22 has been identified as a cancer-promoting cytokine that is secreted by infiltrating immune cells in several cancer models. We hypothesized that IL-22 regulation would occur at the interface between cancer cells and immune cells. Breast and lung cancer cells of murine and human origin induced IL-22 production from memory CD4+ T cells. In the present study, ...
23-Oct-2017
J. Bacteriol., vol. 200, no. 2 e00599-17, doi: 10.1128/JB.00599-17
J. Bacteriol., online article

The peptide transporter carbon starvation (CstA) family (transporter classification [TC] 2.A.114) belongs to the second largest superfamily of secondary transporters, the amino acid/polyamine/organocation (APC) superfamily. No representative of the CstA family has previously been characterized either biochemically or structurally, but we have now identified the ...
16-Oct-2017
J. Bacteriol., vol. 200 no. 1 e00536-17, doi: 10.1128/JB.00536-17
J. Bacteriol., online article

Fluctuating environments and individual physiological diversity force bacteria to constantly adapt and optimize the uptake of substrates. We focus here on two very similar two-component systems (TCSs) of Escherichia coli belonging to the LytS/LytTR family: BtsS/BtsR (formerly YehU/YehT) and YpdA/YpdB. Both TCSs respond to extracellular pyruvate, albeit with ...
10-Oct-2017
eLife 2017;6:e29736, doi: 10.7554/eLife.29736
eLife, online article

Gene transcription can be activated by decreasing the duration of RNA polymerase II pausing in the promoter-proximal region, but how this is achieved remains unclear. Here we use a 'multi-omics' approach to demonstrate that the duration of polymerase pausing generally limits the productive frequency of transcription initiation in human cells ('pause-initiation ...
09-Oct-2017
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, volume 24, 902–910, doi:10.1038/nsmb.3481
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article

Histone variants are structural components of eukaryotic chromatin that can replace replication-coupled histones in the nucleosome. The histone variant macroH2A1.1 contains a macrodomain capable of binding NAD+-derived metabolites. Here we report that macroH2A1.1 is rapidly induced during myogenic differentiation through a switch in alternative splicing, and that ...
26-Sep-2017
mBio, vol. 8, no. 5 e01412-17, doi: 10.1128/mBio.01412-17
mBio, online article

Glycosylation is a universal strategy to posttranslationally modify proteins. The recently discovered arginine rhamnosylation activates the polyproline-specific bacterial translation elongation factor EF-P. EF-P is rhamnosylated on arginine 32 by the glycosyltransferase EarP. However, the enzymatic mechanism remains elusive. In the present study, we solved the ...
18-Sep-2017
PNAS, vol. 114, no. 40, www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1705972114
PNAS, online article

Successful pathogens use complex signaling mechanisms to monitor their environment and reprogram global gene expression during specific stages of infection. Group A Streptococcus (GAS) is a major human pathogen that causes significant disease burden worldwide. A secreted cysteine protease known as streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin B (SpeB) is a key virulence ...
13-Sep-2017
Nature, 549, 394–398, doi:10.1038/nature23890
Nature, online article

Cytosolic DNA arising from intracellular pathogens triggers a powerful innate immune response. It is sensed by cyclic GMP–AMP synthase (cGAS), which elicits the production of type I interferons by generating the second messenger 2′3′-cyclic-GMP–AMP (cGAMP). Endogenous nuclear or mitochondrial DNA can also be sensed by cGAS under certain conditions, resulting in ...
30-Aug-2017
Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 45, Issue 20, Pages 11700–11710, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx775
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
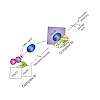
Newly synthesized histones H3 and H4 undergo a cascade of maturation steps to achieve proper folding and to establish post-translational modifications prior to chromatin deposition. Acetylation of H4 on lysines 5 and 12 by the HAT1 acetyltransferase is observed late in the histone maturation cascade. A key question is to understand how to establish and regulate ...
17-Aug-2017
Molecular Cell, Volume 67, Issue 4, p550–565.e5, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.07.012
Molecular Cell, online article
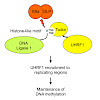
DNA methylation is an essential epigenetic mark in mammals that has to be re-established after each round of DNA replication. The protein UHRF1 is essential for this process; it has been proposed that the protein targets newly replicated DNA by cooperatively binding hemi-methylated DNA and H3K9me2/3, but this model leaves a number of questions unanswered. Here, ...
10-Aug-2017
PLoS ONE, 12(8): e0182993, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0182993
PLoS ONE, online article

Bacterial histidine kinase/response regulator systems operate at the interface between environmental cues and physiological states. Escherichia coli contains two LytS/LytTR-type histidine kinase/response regulator systems, BtsS/BtsR (formerly YehU/YehT) and YpdA/YpdB, which have been identified as pyruvate-responsive two-component systems. Since they exhibit ...
09-Aug-2017
EMBO reports, Volume 18, Issue 10, https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201744292
EMBO reports, online article

X chromosome dosage compensation in Drosophila requires chromosome‐wide coordination of gene activation. The male‐specific lethal dosage compensation complex (DCC) identifies and binds to X‐chromosomal high‐affinity sites (HAS) from which it boosts transcription. A sub‐class of HAS, PionX sites, represent first contacts on the X. Here, we explored the chromosomal ...
31-Jul-2017
Molecular Microbiology, Volume 106, Issue 1, Pages 54–73, DOI: 10.1111/mmi.13751
Molecular Microbiology, online article
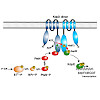
The two-component system KdpD/KdpE governs K+ homeostasis by controlling synthesis of the high affinity K+ transporter KdpFABC. When sensing low environmental K+ concentrations, the dimeric kinase KdpD autophosphorylates in trans and transfers the phosphoryl-group to the response regulator KdpE, which subsequently activates kdpFABC transcription. In Escherichia ...
17-Jul-2017
Nature Chemistry, doi:10.1038/nchem.2811
Nature Chemistry, online article
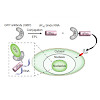
Functional antibody delivery in living cells would enable the labelling and manipulation of intracellular antigens, which constitutes a long-thought goal in cell biology and medicine. Here we present a modular strategy to create functional cell-permeable nanobodies capable of targeted labelling and manipulation of intracellular antigens in living cells. The ...
23-Jun-2017
The EMBO Journal, DOI 10.15252/embj.201695757
The EMBO Journal, online article
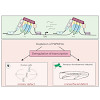
Replacement of canonical histones with specialized histone variants promotes altering of chromatin structure and function. The essential histone variant H2A.Z affects various DNA-based processes via poorly understood mechanisms. Here, we determine the comprehensive interactome of H2A.Z and identify PWWP2A as a novel H2A.Z-nucleosome binder. PWWP2A is a ...
12-Jun-2017
Nature Communications, 8, Article number: 15760, doi:10.1038/ncomms15760
Nature Communications, online article

Histone H2AX phosphorylation is an early signalling event triggered by DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). To elucidate the elementary units of phospho-H2AX-labelled chromatin, we integrate super-resolution microscopy of phospho-H2AX during DNA repair in human cells with genome-wide sequencing analyses. Here we identify phospho-H2AX chromatin domains in the ...
22-May-2017
American Association for Cancer Research, Print ISSN 0008-5472, DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1922
American Association for Cancer Research, online article
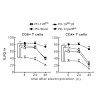
Inherent intermediate-to-low affinity T cell receptors (TCR) that develop during the natural course of immune responses may not allow sufficient activation for tumor elimination, making the majority of T cells suboptimal for adoptive T cell therapy (ATT). TCR affinity enhancement has been implemented to provide stronger T cell activity but carries the risk of ...
16-May-2017
PLoS ONE 12(5): e0177408. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0177408
PLOS ONE, online article
The nuclear acetyltransferase MOF (KAT8 in mammals) is a subunit of at least two multi-component complexes involved in transcription regulation. In the context of complexes of the ‘Non-Specific-Lethal’ (NSL) type it controls transcription initiation of many nuclear housekeeping genes and of mitochondrial genes. While this function is conserved in metazoans, MOF ...
10-May-2017
Scientific Reports, 7, Article number: 1684, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-01943-6
Scientific Reports, online article

The bromodomain protein Brd4 is an epigenetic reader and plays a critical role in the development and maintenance of leukemia. Brd4 binds to acetylated histone tails and activates transcription by recruiting the positive elongation factor P-TEFb. Small molecule inhibitor JQ1 competitively binds the bromodomains of Brd4 and displaces the protein from acetylated ...
03-May-2017
Scientific Reports, 7, Article number: 1388, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-01410-2
Scientific Reports, online article

Two-component systems are crucial for signal perception and modulation of bacterial behavior. Nevertheless, to date, very few ligands have been identified that directly interact with histidine kinases. The histidine kinase/response regulator system YehU/YehT of Escherichia coli is part of a nutrient-sensing network. Here we demonstrate that this system senses the ...
02-May-2017
PNAS, vol. 114 no. 20, E3944-E3953, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1700128114
PNAS, online article

The carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) orchestrates dynamic recruitment of specific cellular machines during different stages of transcription. Signature phosphorylation patterns of Y1S2P3T4S5P6S7 heptapeptide repeats of the CTD engage specific “readers.” Whereas phospho-Ser5 and phospho-Ser2 marks are ubiquitous, ...
01-May-2017
J Cell Sci., 2017 130: 1570-1582; doi: 10.1242/jcs.199216
J Cell Sci., online article

Genetic loss-of-function studies on development, cancer and somatic cell reprogramming have suggested that the group of macroH2A histone variants might function through stabilizing the differentiated state by a yet unknown mechanism. Here, we present results demonstrating that macroH2A variants have a major function in maintaining nuclear organization and ...
21-Apr-2017
Scientific Reports, 7, Article number: 1051, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-01031-9
Scientific Reports, online article
The transmembrane DNA-binding protein CadC of E. coli, a representative of the ToxR-like receptor family, combines input and effector domains for signal sensing and transcriptional activation, respectively, in a single protein, thus representing one of the simplest signalling systems. At acidic pH in a lysine-rich environment, CadC activates the transcription of ...
18-Apr-2017
Front. Microbiol., Volume 8, Article 634, doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00634
Front. Microbiol., online article
Quorum sensing (QS) is a process enabling a bacterial population to communicate via small molecules called autoinducers (AIs). This intercellular communication process allows single cells to synchronize their behavior within a population. The marine bacterium Vibrio harveyi ATCC BAA-1116 channels the information of three AI signals into one QS cascade. Three ...
13-Apr-2017
Nature Protocols, 12, 1011–1028, doi:10.1038/nprot.2017.020
Nature Protocols, online article

3D structured illumination microscopy (3D-SIM) is the super-resolution technique of choice for multicolor volumetric imaging. Here we provide a validated sample preparation protocol for labeling nuclei of cultured mammalian cells, image acquisition and registration practices, and downstream image analysis of nuclear structures and epigenetic marks. Using ...
06-Apr-2017
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 24, 341–343, doi:10.1038/nsmb.3394
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article

Chromatin-remodeling enzymes perform the formidable task of reorganizing the structure of a stable macromolecular assembly, the nucleosome. Recently published work demonstrates that the SNF2H chromatin remodeler distorts the histone octamer structure upon binding to the nucleosome, then taps into this induced plasticity to productively achieve nucleosome sliding.
03-Apr-2017
Molecular Plant, Volume 10, Issue 4, p575–589, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.12.012
Molecular Plant, online article
The translocon on the outer membrane of mitochondria (TOM) facilitates the import of nuclear-encoded proteins. The principal machinery of mitochondrial protein transport seems conserved in eukaryotes; however, divergence in the composition and structure of TOM components has been observed between mammals, yeast, and plants. TOM9, the plant homolog of yeast Tom22, ...
20-Mar-2017
Chem. Sci., 8, 3471, DOI: 10.1039/c7sc00574a
Chem. Sci., online article
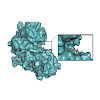
The broad substrate tolerance of tubulin tyrosine ligase is the basic rationale behind its wide applicability for chemoenzymatic protein functionalization. In this context, we report that the wild-type enzyme enables ligation of various unnatural amino acids that are substantially bigger than and structurally unrelated to the natural substrate, tyrosine, without ...
13-Mar-2017
Circulation Research, 2017;120:1305-1317, https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.309631
Circulation Research, online article
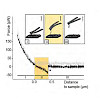
Rationale: The sympathetic nervous system is a major mediator of heart function. Intercalated discs composed of desmosomes, adherens junctions, and gap junctions provide the structural backbone for coordinated contraction of cardiac myocytes.
Objective: Gap junctions dynamically remodel to adapt to sympathetic signaling. However, it is unknown whether such rapid ...
03-Mar-2017
Hum Mol Genet., 26 (8): 1522-1534; DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddx057
Hum Mol Genet., online article

DNMT1 is recruited to substrate sites by PCNA and UHRF1 to maintain DNA methylation after replication. The cell cycle dependent recruitment of DNMT1 is mediated by the PCNA-binding domain (PBD) and the targeting sequence (TS) within the N-terminal regulatory domain. The TS domain was found to be mutated in patients suffering from hereditary sensory and autonomic ...
16-Feb-2017
PLoS ONE, 12(2): e0171798, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0171798
PLoS ONE, online article

Hybrid incompatibility between Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans is caused by a lethal interaction of the proteins encoded by the Hmr and Lhr genes. In D. melanogaster the loss of HMR results in mitotic defects, an increase in transcription of transposable elements and a deregulation of heterochromatic genes. To better understand the molecular mechanisms ...
10-Feb-2017
ACS Synth. Biol., 6 (5), pp 826–836, DOI: 10.1021/acssynbio.6b00323
ACS Synth. Biol., online article

Natural and synthetic scaffolds support enzyme organization in complexes, and they regulate their function and activity. Here we report that CipA and CipB, two small proteins that form protein crystalline inclusions (PCIs) in the cytoplasm of Photorhabdus luminescens, can be utilized as scaffolds to efficiently incorporate exogenous proteins into PCIs. We ...
09-Feb-2017
Molecular Cell, Volume 65, Issue 4, p631–643.e4, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.01.023
Molecular Cell, online article

Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) offers new possibilities to address biological and medical questions. However, systematic comparisons of the performance of diverse scRNA-seq protocols are lacking. We generated data from 583 mouse embryonic stem cells to evaluate six prominent scRNA-seq methods: CEL-seq2, Drop-seq, MARS-seq, SCRB-seq, Smart-seq, and ...
03-Feb-2017
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, June 2017, Volume 74, Issue 11, pp 2055–2065, DOI 10.1007/s00018-017-2454-8
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, online article
Endogenous retroviruses (ERV) are an abundant class of repetitive elements in mammalian genomes. To ensure genomic stability, ERVs are largely transcriptionally silent. However, these elements also feature physiological roles in distinct developmental contexts, under which silencing needs to be partially relieved. ERV silencing is mediated through a ...
31-Jan-2017
Nature Chemical Biology, doi:10.1038/nchembio.2282
Nature Chemical Biology, online article

Protein lysine methyltransferases (PKMTs) regulate diverse physiological processes including transcription and the maintenance of genomic integrity. Genetic studies suggest that the PKMTs SUV420H1 and SUV420H2 facilitate proficient nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ)-directed DNA repair by catalyzing the di- and trimethylation (me2 and me3, respectively) of lysine ...
27-Jan-2017
Molecular Microbiology, 104(1), 16–31 , doi:10.1111/mmi.13597
Molecular Microbiology, online article
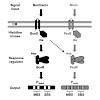
BceRS and PsdRS are paralogous two-component systems in Bacillus subtilis controlling the response to antimicrobial peptides. In the presence of extracellular bacitracin and nisin, respectively, the two response regulators (RRs) bind their target promoters, PbceA or PpsdA, resulting in a strong up-regulation of target gene expression and ultimately antibiotic ...
17-Jan-0207
MicrobiologyOpen, Volume 6, Issue 3, e00438, DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.438
MicrobiologyOpen, online article
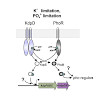
Two-component signal transduction constitutes the predominant strategy used by bacteria to adapt to fluctuating environments. The KdpD/KdpE system is one of the most widespread, and is crucial for K+ homeostasis. In Escherichia coli, the histidine kinase KdpD senses K+ availability, whereas the response regulator KdpE activates synthesis of the high-affinity K+ ...










