Research Area D - Publications 2011
13-Dec-2011
Current Opinion in Microbiology, online article
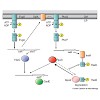
Two-component systems, composed of a histidine kinase (HK) and a response regulator (RR), are the major signal transduction devices in bacteria. Originally it was thought that these two components function as linear, phosphorylationdriven stimulus–response system. Here, we will review how accessory proteins are employed by HKs and RRs to mediate signal ...
13-Dec-2011
Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, online article

We present a strategy for rapidly gaining structural information about a protein from crosslinks formed by genetically encoded unnatural amino acids. We applied it to ISWI, a chromatin remodeling enzyme involved in chromatin assembly, DNA replication and transcription. ISWI is part of the vast Snf2 family of helicase-related proteins, many of which constitute the ...
01-Dec-2011
Science Direct, online article
The rapid and ongoing discovery of new disease related biomarkers leads to a dramatic paradigm change in human healthcare and constitutes the basis for a truly personalized medicine. Molecular imaging enables early detection and classification of human diseases and provides valuable data for optimized, target-oriented therapies. By now, the biochemical and ...
17-Nov-2011
Histopathology, online article
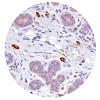
In breast cancer, a high ratio of tumour-infiltrating intraepithelial CD8+ to FoxP3+ cells is characteristic for the medullary subtype.
15-Nov-2011
International Journal of Cancer, online article
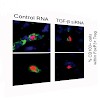
Regulatory T cells (Treg) mediate tolerance towards self-antigens by suppression of innate and adaptive immunity. In cancer patients, tumor-infiltrating FoxP3+ Treg suppress local anti-tumor immune responses and are often associated with poor prognosis. Markers that are selectively expressed on tumor-infiltrating Treg may serve as targets for immunotherapy of ...
03-Nov-2011
Nucl. Acids Res., online article

Histone post-translational modifications play an important role in regulating chromatin structure and gene expression in vivo. Extensive studies investigated the post-translational modifications of the core histones H3 and H4 or the linker histone H1. Much less is known on the regulation of H2A and H2B modifications. Here, we show that a major modification of H2B ...
01-Nov-2011
Journal of Cell Science, online article
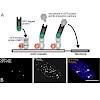
Telomerase-negative tumor cells use an alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT) pathway that involves DNA recombination and repair to maintain their proliferative potential. The cytological hallmark of this process is the accumulation of promyelocytic leukemia (PML) nuclear1 protein at telomeric DNA to form ALT-associated PML bodies (APBs). Here, the de novo ...
27-Oct-2011
Nucleic Acids Research, online article

The MOF (males absent on the first)-containing NSL (non-specific lethal) complex binds to a subset of active promoters in Drosophila melanogaster and is thought to contribute to proper gene expression. The determinants that target NSL to specific pro- moters and the circumstances in which the complex engages in regulating transcription are currently unknown. ...
21-Oct-2011
Nature Cell Biology, online article

Kinases and phosphatases regulate messenger RNA synthesis through post-translational modification of the carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (ref. 1). In yeast, the phosphatase Cdc14 is required for mitotic exit2,3 and for segregation of repetitive regions4. Cdc14 is also a subunit of the silencing complex RENT (refs 5,6), ...
12-Oct-2011
Plos, online article
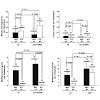
Reprogramming of adult differentiated cells to induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS) cells has been achieved by over-expression of specific transcription factors. Nuclear reprogramming induces a series of profound changes at the telomeres of the parental differentiated cells, including a telomerase-dependent telomere elongation and the remodeling of telomeric ...
30-Sep-2011
Nucleus, online article
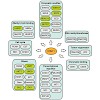
DNA methylation plays a central role in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression during development and disease. Remarkably, the complex and changing patterns of genomic DNA methylation are established and maintained by only three DNA methyltransferases. Here we focus on DNMT1, the major and ubiquitously expressed DNA methyltransferase in vertebrates, to ...
14-Sep-2011
PLoS ONE, online article

Chromatin proteins provide a scaffold for DNA packaging and a basis for epigenetic regulation and genomic maintenance. Despite understanding its functional roles, mapping the chromatin proteome (i.e. the ‘‘Chromatome’’) is still a continuing process. Here, we assess the biological specificity and proteomic extent of three distinct chromatin preparations by ...
08-Sep-2011
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
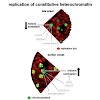
The replication of the genome is a spatio-temporally highly organized process. Yet, its flexibility throughout development suggests that this process is not genetically regulated. However, the mechanisms and chromatin modifications controlling replication timing are still unclear. We made use of the prominent structure and defined heterochromatic landscape of ...
23-Aug-2011
Cancer Research, online article

The estrogen receptor-alpha (ERa) determines the phenotype of breast cancers where it serves as a positive prognostic indicator. ERa is a well-established target for breast cancer therapy, but strategies to target its function remain of interest to address therapeutic resistance and further improve treatment. Recent findings indicate that proteasome inhibition ...
18-Aug-2011
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, online article
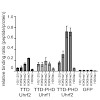
Gene expression is regulated by DNA as well as histone modifications but the crosstalk and mechanistic link between these epigenetic signals are still poorly understood. Here we investigate the multi-domain protein Uhrf2 that is similar to Uhrf1, an essential cofactor of maintenance DNA methylation. Binding assays demonstrate a cooperative interplay of Uhrf2 ...
24-Jul-2011
Nature Structual & Molecular Biology, online article
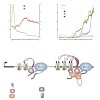
Several lines of recent evidence support a role for chromatin in splicing regulation. Here, we show that splicing can also contribute to histone modification, which implies bidirectional communication between epigenetic mechanisms and RNA processing. Genome-wide analysis of histone methylation in human cell lines and mouse primary T cells reveals that ...
22-Jul-2011
PLoS ONE, online article

Vertebrate embryos are derived from a transitory pool of pluripotent cells. By the process of embryonic induction, these precursor cells are assigned to specific fates and differentiation programs. Histone post-translational modifications are thought to play a key role in the establishment and maintenance of stable gene expression patterns underlying these ...
21-Jul-2011
Cell Death and Disease, online article

The wogonin-containing herb Scutellaria baicalensis has successfully been used for curing various diseases in traditional Chinese medicine. Wogonin has been shown to induce apoptosis in different cancer cells and to suppress growth of human cancer xenografts in vivo. However, its direct targets remain unknown. In this study, we demonstrate for the first time that ...
18-Jul-2011
Nature Chemical Biology, online article
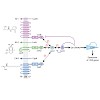
Bacteria communicate by sending and receiving chemical cues in a process termed ‘quorum sensing’. New research shows how five feedback loops of the Vibrio harveyi quorum sensing cascade ensure signal integration and transmission fidelity, with one loop controlling signal sensitivity by regulating receptor ratios.
17-Jul-2011
Nature Structual & Molecular Biology, online article

Recent work has shown that RNA polymerase (Pol) II can be recruited to and transcribe distal regulatory regions. Here we analyzed transcription initiation and elongation through genome-wide localization of Pol II, general transcription factors (GTFs) and active chromatin in developing T cells. We show that Pol II and GTFs are recruited to known T cell–specific ...
11-Jul-2011
Nucleic Acids Research, online article

Active chromatin remodelling is integral to the DNA damage response in eukaryotes, as damage sensors, signalling molecules and repair enzymes gain access to lesions. A variety of nucleosome remodel- ling complexes is known to promote different stages of DNA repair. The nucleosome sliding factors CHRAC/ACF of Drosophila are involved in chromatin organization ...
22-Jun-2011
PLoS ONE, online article
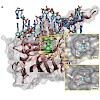
Recent discovery of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) in genomic DNA raises the question how this sixth base is recognized by cellular proteins. In contrast to the methyl-CpG binding domain (MBD) of MeCP2, we found that the SRA domain of Uhrf1, an essential factor in DNA maintenance methylation, binds 5hmC and 5-methylcytosine containing substrates with similar ...
22-Jun-2011
Cancer Research, online article

Topical application of small molecule Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) agonists is highly effective for the treatment of skin tumors, whereas their systemic application has been largely unsuccessful for cancer therapy. One reason may be that repeated systemic application of TLR ligands can induce a state of immune unresponsiveness, termed TLR tolerance. We show here ...
02-Jun-2011
PLoS ONE, online article
Gene expression is highly dynamic and many genes show a wide range in expression over several orders of magnitude. This regulation is often mediated by sequence specific transcription factors. In addition, the tight packaging of DNA into chromatin can provide an additional layer of control resulting in a dynamic range of gene expression covering several orders of ...
31-May-2011
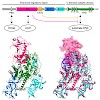
DNA methylation, the postreplicative transfer of a methyl group to the C5 position of cytosine bases, was the first epigenetic modification identified and has been intensively studied for more than half a century. By now it is clear that Dnmt1, the major eukaryotic DNA methyltransferase, faithfully maintains genome-wide methylation patterns and plays an essential ...
20-Apr-2011
Click here to read the german press article

The DFG will fund the program of emphasis on inidividuality of bacteria which is coordinated by CIPSM's Kirsten Jung. In this program scientists from a range of disciplines are trying to show whether or not bacteria of a population which are genetically identical and have the same phenotype show the same properties and behave in the same manner or not. The DFG ...
12-Apr-2011
BMC Microbiology, online article
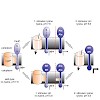
Background: In an acidic and lysine-rich environment Escherichia coli induces expression of the cadBA operon which encodes CadA, the lysine decarboxylase, and CadB, the lysine/cadaverine antiporter. cadBA expression is dependent on CadC, a membrane-integrated transcriptional activator which belongs to the ToxR-like protein family. Activation of CadC requires two ...
05-Apr-2011
Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology, online article
We studied the nuclear topography of RNA transcription and DNA replication in mammalian cell types with super-resolution fluorescence microscopy, which offers a resolution beyond the classical Abbe/Raleigh limit. Three-dimensional structured illumination microscopy (3D-SIM) demonstrated a network of channels and wider lacunas, called the interchromatin ...
01-Apr-2011
Science, online article

The carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) in mammals undergoes extensive posttranslational modification, which is essential for transcriptional initiation and elongation. Here, we show that the CTD of RNAPII is methylated at a single arginine (R1810) by the coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1 (CARM1). Although methylation at ...
31-Mar-2011
PLOS Genetics, online article
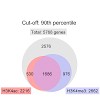
Methylation of histone H3 lysine 4 (H3K4me) is an evolutionarily conserved modification whose role in the regulation of gene expression has been extensively studied. In contrast, the function of H3K4 acetylation (H3K4ac) has received little attention because of a lack of tools to separate its function from that of H3K4me. Here we show that, in addition to being ...
29-Mar-2011

Much progress has been made concerning histone function in the nucleus; however, following their synthesis, how their marking andsubcellular trafficking are regulated remains tobeexplored.To gainaninsight into these issues, wefocusedonsoluble histonesand analyzed endogenous and tagged H3 histones in parallel. We distinguished six complexes that we could place to ...
14-Mar-2011
The Journal of Bacteriology, online article
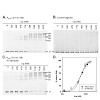
Expression of lysP, which encodes the lysine-specific transporter LysP in Escherichia coli, is regulated by the concentration of exogenous available lysine. In this study, the LysR-type transcriptional regulator ArgP was identified as the activator of lysP expression. At lysine concentrations higher than 25 µM, lysP expression was shut off and phenocopied an argP ...
11-Mar-2011
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
Post-translational poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation has diverse essential functions in the cellular response to DNA damage as it contributes to avid DNA damage detection and assembly of the cellular repair machinery but extensive modification eventually also induces cell death. While there are 17 human poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) genes, there is only one ...
10-Mar-2011
PLOSGenetics, online article
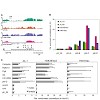
The ubiquitous tandem kinase JIL-1 is essential for Drosophila development. Its role in defining decondensed domains of larval polytene chromosomes is well established, but its involvement in transcription regulation has remained controversial. For a first comprehensive molecular characterisation of JIL-1, we generated a high-resolution, chromosome-wide ...
08-Mar-2011
Click here to read the interview on Laborjournal.de
04-Mar-2011
Nucl. Acids Res., online article

In mammalian genomes a sixth base, 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (hmC), is generated by enzymatic oxidation of 5-methylcytosine (mC). This discovery has raised fundamental questions about the functional relevance of hmC in mammalian genomes. Due to their very similar chemical structure, discrimination of the rare hmC against the far more abundant mC is technically ...
01-Mar-2011
Nature Communications, online article
In mammals, dosage compensation between male and female cells is achieved by inactivating one female X chromosome (Xi). Late replication of Xi was proposed to be involved in the maintenance of its silenced state. Here, we show a highly synchronous replication of the Xi within 1 to 2 h during early-mid S-phase by following DNA replication in living mammalian cells ...
11-Feb-2011
Science Direct, online article

Dosage compensation processes in flies and worms provide a unique opportunity to study common regulatory principles of thousands of genes.Technological advancement in the recent years has allowed for the comprehensive description of key aspects such as the targeting of the regulatory factors,the emerging chromatin structure changes and the ensuing subtle ...
11-Feb-2011
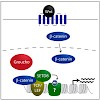
Growth factor signaling pathways regulate a broad spectrum of cellular processes ranging from proliferation to differentiation and tissue homeostasis. Activation of a signaling pathway ultimately leads to transcriptional changes in specific target genes. Although the molecular identities of many signaling pathway components have been revealed over the last years, ...
10-Feb-2011
Science, online article
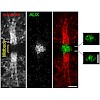
Following partitioning of cytoplasmic contents by cleavage furrow ingression, animal cells remain connected by an intercellular bridge, which subsequently splits by abscission. Here, we examined intermediate stages of abscission in human cells, using live imaging, three-dimensional structured illumination microscopy, and electron tomography. We identified helices ...
04-Feb-2011
La Crosse encephalitis virus (LACV) is a mosquito-borne member of the negative-strand RNA virus family Bunyaviridae. We have previously shown that the virulence factor NSs of LACV is an efficient inhibitor of the antiviral type I interferon system. A recombinant virus unable to express NSs (rLACVdelNSs) strongly induced interferon transcription, whereas the ...
02-Feb-2011
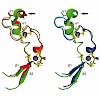
Several mammalian proteins involved in chromatin and DNA modification contain CXXC zinc finger domains. We compared the structure and function of the CXXC domains in the DNA methyltransferase Dnmt1 and the methylcytosine dioxygenase Tet1. Sequence alignment showed that both CXXC domains have a very similar framework but differ in the central tip region. Based on ...
25-Jan-2011
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, online article

In mammals Dnmt1 is the DNA methyltransferase chiefly responsible for maintaining genomic methylation patterns through DNA replication cycles, but how its maintenance activity is controlled is still not well understood. Interestingly, Uhrf1, a crucial cofactor for maintenance of DNA methylation by Dnmt1, is endowed with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. Here, we show ...
24-Jan-2011
Protein Science, online article
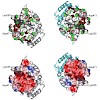
The membrane-integral transcriptional activator CadC comprises sensory and transcriptional regulatory functions within one polypeptide chain. Its C-terminal periplasmic domain, CadCpd, is responsible for sensing of environmental pH as well as for binding of the feedback inhibitor cadaverine. Here we describe the crystal structure of CadCpd (residues 188–512) ...
20-Jan-2011
Chromosome Research, online article
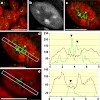
We used chicken retinospheroids (RS) to study the nuclear architecture of vertebrate cells in a three-dimensional (3D) cell culture system. The results showed that the different neuronal cell types of RS displayed an extreme form of radial nuclear organization. Chromatin was arranged into distinct radial zones which became already visible after DAPI staining. The ...
13-Jan-2011
Clinical Cancer Research, online article
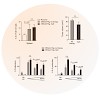
Purpose: The Toll-like receptor (TLR) 9 ligand CpG has been used successfully for the immunotherapy of cancer. Chronic CpG application in tumor-free hosts leads, however, to the expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC), which can cause T-cell suppression and may thus hamper the development of an effective immune response. Here, we investigated the ...
07-Jan-2011
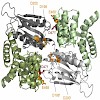
The membrane-integrated transcriptional regulator CadC of Escherichia coli activates expression of the cadBA operon at low external pH with concomitantly available lysine, providing adaptation to mild acidic stress. CadC is a representative of the ToxR-like proteins that combine sensory, signal transduction, and DNA-binding activities within a single polypeptide. ...
30-Nov--0001












