Research Area E - Publications 2017
26-Dec-2017
Cell Reports, Volume 21, Issue 13, p3846–3859, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.12.018
Cell Reports, online article

Inflammasomes activate the protease caspase-1, which cleaves interleukin-1β and interleukin-18 to generate the mature cytokines and controls their secretion and a form of inflammatory cell death called pyroptosis. By generating mice expressing enzymatically inactive caspase-1C284A, we provide genetic evidence that caspase-1 protease activity is required for ...
15-Dec-2017
Org. Lett., 20 (1), pp 232–235, DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b03574
Org. Lett., online article

A very short, high yielding, and convergent synthesis with broad substrate scope, enabling access to a very diverse range of hemithioindigos with 4-fold substituted double-bonds, is presented. With this method, carbon as well as nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur based substituents can easily be introduced, delivering a wide array of novel structural motifs. Irradiation ...
04-Dec-2017
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Volume56, Issue49, Pages 15746-15750, https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201708454
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article

The Staphylococcus aureus ClpXP protease is an important regulator of cell homeostasis and virulence. We utilized a high‐throughput screen against the ClpXP complex and identified a specific inhibitor of the ClpX chaperone that disrupts its oligomeric state. Synthesis of 34 derivatives revealed that the molecular scaffold is restrictive for diversification, with ...
01-Dec-2017
Science, Vol. 358, Issue 6367, eaan4368, DOI: 10.1126/science.aan4368
Science, online article
Kinase inhibitors are an important class of drugs that block certain enzymes involved in diseases such as cancer and inflammatory disorders. There are hundreds of kinases within the human body, so knowing the kinase “target” of each drug is essential for developing successful treatment strategies. Sometimes clinical trials can fail because drugs bind more than ...
27-Nov-2017
Nature Chemical Biology, volume 14, pages 72–78, doi:10.1038/nchembio.2531
Nature Chemical Biology, online article

Tet enzymes oxidize 5-methyl-deoxycytidine (mdC) to 5-hydroxymethyl-dC (hmdC), 5-formyl-dC (fdC) and 5-carboxy-dC (cadC) in DNA. It was proposed that fdC and cadC deformylate and decarboxylate, respectively, to dC over the course of an active demethylation process. This would re-install canonical dC bases at previously methylated sites. However, whether such ...
13-Nov-2017
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Volume 56, Issue 46, Pages 14536–14539, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201708178
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article
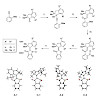
Hemithioindigo molecular motors undergo very fast unidirectional rotation upon irradiation with visible light, which has prevented a complete analysis of their working mechanism. In this work, we have considerably slowed down their motion by using a new synthesis for sterically hindered motor derivatives. This method allowed the first observation of all four ...
08-Nov-2017
Chem. Commun., 2017, 53, 12818--12821, DOI: 10.1039/c7cc04990k
Chem. Commun., online article

The spongiolactones are marine natural products with an unusual rearranged spongiane skeleton and a fused β-lactone ring. These compounds have potential anticancer properties but their mode of action has yet to be explored. Here we employ activity-based protein profiling to identify the targets of a more potent spongiolactone derivative in live cancer cells, and ...
03-Nov-2017
Molecular Systems Biology, Volume13, Issue11, https://doi.org/10.15252/msb.20177701
Molecular Systems Biology, online article

Most molecular cancer therapies act on protein targets but data on the proteome status of patients and cellular models for proteome‐guided pre‐clinical drug sensitivity studies are only beginning to emerge. Here, we profiled the proteomes of 65 colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines to a depth of > 10,000 proteins using mass spectrometry. Integration with proteomes ...
16-Oct-2017
Chem. Commun., 2017, 53, 11929--11932 , DOI: 10.1039/C7CC07001B
Chem. Commun., online article
A method for identifying probe modification of proteins via tandem mass spectrometry was developed. Azide bearing molecules are immobilized on functionalised sepharose beads via copper catalysed Huisgen-type click chemistry and selectively released under acidic conditions by chemical cleavage of the triazene linkage. We applied this method to identify the ...
26-Sep-2017
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Volume56, Issue44, Pages 13570-13572, https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201708456
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article
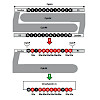
The N‐methylation of backbone amide bonds in peptide natural products was thought to be exclusive to non‐ribosomal peptides. A newly discovered methylation mechanism now brings this structural feature into the world of ribosomal peptides, thereby significantly expanding the structural diversity of ribosomally synthesized and post‐translationally modified peptides ...
26-Sep-2017
mBio, vol. 8, no. 5 e01412-17, doi: 10.1128/mBio.01412-17
mBio, online article

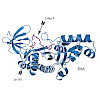
Glycosylation is a universal strategy to posttranslationally modify proteins. The recently discovered arginine rhamnosylation activates the polyproline-specific bacterial translation elongation factor EF-P. EF-P is rhamnosylated on arginine 32 by the glycosyltransferase EarP. However, the enzymatic mechanism remains elusive. In the present study, we solved the ...
25-Sep-2017
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 139 (42), pp 15060–15067, DOI: 10.1021/jacs.7b07531
J. Am. Chem. Soc., online article
Hemiindigo is a long known chromophore that absorbs in the blue part of the spectrum but has almost completely been ignored as potential photoswitch. Herein we show how the absorption of hemiindigo is shifted to the red part of the visible spectrum and how nearly perfect photoswitching can be achieved using blue or green and red light. Five derivatives were ...
22-Sep-2017
ACS Synth. Biol., 2017, 6 (12), pp 2241–2247, DOI: 10.1021/acssynbio.7b00199
ACS Synth. Biol., online article

The molecular recognition of carbohydrates plays a fundamental role in many biological processes. However, the development of carbohydrate-binding reagents for biomedical research and use poses a challenge due to the generally poor affinity of proteins toward sugars in aqueous solution. Here, we describe the effective molecular recognition of pyranose ...
12-Sep-2017
Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, Volume 40, October 2017, Pages 102-110, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2017.08.007
Current Opinion in Chemical Biology, online article
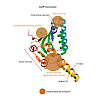
Maintaining the cellular protein homeostasis means managing life on the brink of death. This balance is largely based on precise fine-tuning of enzyme activities. For instance, the ClpP protease possesses several conformational switches which are fundamental to regulating its activity. Efforts have focused on revealing the structural basis of ClpP's ...
05-Sep-2017
Proteomics, Volume17, Issue21, Pages 1700263, https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201700263
Proteomics, online article
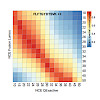
Beyond specific applications, such as the relative or absolute quantification of peptides in targeted proteomic experiments, synthetic spike‐in peptides are not yet systematically used as internal standards in bottom‐up proteomics. A number of retention time standards have been reported that enable chromatographic aligning of multiple LC–MS/MS experiments. ...
01-Sep-2017
J. Proteome Res., 2017, 16 (10), pp 3816–3829, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00474
J. Proteome Res., online article
Lactic acid bacteria are broadly employed as starter cultures in the manufacture of foods. Upon technological preparation, they are confronted with drying stress that amalgamates numerous stress conditions resulting in losses of fitness and survival. To better understand and differentiate physiological stress responses, discover general and specific markers for ...
28-Aug-2017
J. Biol. Chem., (2017) 292(41), 17073–17083, DOI 10.1074/jbc.M117.797829
J. Biol. Chem., online article

The eukaryotic Hsp90 chaperone machinery comprises many co-chaperones and regulates the conformation of hundreds of cytosolic client proteins. Therefore, it is not surprising that the Hsp90 machinery has become an attractive therapeutic target for diseases such as cancer. The compounds used so far to target this machinery affect the entire Hsp90 system. However, ...
21-Aug-2017
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Volume56, Issue35, Pages 10592-10597, https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201703893
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article
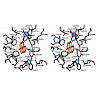
Benzo[a]pyrene, which is produced during the incomplete combustion of organic material, is an abundant noxious pollutant because of its carcinogenic metabolic degradation products. The high‐affinity (KD≈3 nm) monoclonal antibody 22F12 allows facile bioanalytical quantification of benzo[a]pyrene even in complex matrices. We report the functional and X‐ray ...
17-Aug-2017
Molecular Cell, Volume 67, Issue 4, p711–723.e7, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.07.019
Molecular Cell, online article

The mitochondrial calcium uniporter complex is essential for calcium (Ca2+) uptake into mitochondria of all mammalian tissues, where it regulates bioenergetics, cell death, and Ca2+ signal transduction. Despite its involvement in several human diseases, we currently lack pharmacological agents for targeting uniporter activity. Here we introduce a high-throughput ...
03-Aug-2017
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Volume 56, Issue 42, Pages 12888-12891, https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201705976
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article
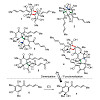
Natural products are a virtually inexhaustible source of small molecules with spectacular molecular architectures and biomedical potential. Their structural complexity generates formidable challenges to total synthesis but often also precludes time‐ and resource‐efficient, stereoselective synthetic access. Biosynthetically, nature frequently uses dimerization and ...
01-Aug-2017
Anal. Chem., 2017, 89 (17), pp 8884–8891, DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01356
Anal. Chem., online article
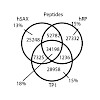
Offline two-dimensional chromatography is a common means to achieve deep proteome coverage. To reduce sample complexity and dynamic range and to utilize mass spectrometer (MS) time efficiently, high chromatographic resolution of and good orthogonality between the two dimensions are needed. Ion exchange and high pH reversed phase chromatography are often used for ...
24-Jul-2017
ChemBioChem, DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201700209
ChemBioChem, oline article
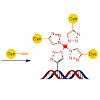
The in vivo incorporation of alkyne-modified bases into the genome of cells is today the basis for the efficient detection of cell proliferation. Cells are grown in the presence of ethinyl-dU (EdU), fixed and permeabilised. The incorporated alkynes are then efficiently detected by using azide-containing fluorophores and the CuI-catalysed alkyne–azide click ...
17-Jul-2017
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 139 (30), pp 10359–10364, DOI: 10.1021/jacs.7b04131
J. Am. Chem. Soc., online article
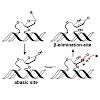
5-Formyl-dC (fdC) and 5-carboxy-dC (cadC) are newly discovered bases in the mammalian genome that are supposed to be substrates for base excision repair (BER) in the framework of active demethylation. The bases are recognized by the monofunctional thymine DNA glycosylase (Tdg), which cleaves the glycosidic bond of the bases to give potentially harmful abasic ...
02-Jul-2017
2015, published on 31.08.2015

Das Institut für chemische Epigenetik (ICEM) mit einer Nutzfläche von 3.430 m² und einer Fördersumme von 38,73 Millionen Euro hat eine Förderempfehlung von Seiten des Wissenschaftsrates erhalten.
Das ICEM basiert auf dem CIPSM und wird den Forschungsschwerpunkt der chemischen Epigenetik erforschen.
Der Forschungsbau wird auf dem HighTech Campus ...
23-Jun-2017
The EMBO Journal, DOI 10.15252/embj.201695757
The EMBO Journal, online article
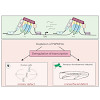
Replacement of canonical histones with specialized histone variants promotes altering of chromatin structure and function. The essential histone variant H2A.Z affects various DNA-based processes via poorly understood mechanisms. Here, we determine the comprehensive interactome of H2A.Z and identify PWWP2A as a novel H2A.Z-nucleosome binder. PWWP2A is a ...
21-Jun-2017
ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 999 – 1011, DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201700217
ChemMedChem., online article

The receptor tyrosine kinase EPHA2 has gained attention as a therapeutic drug target for cancer and infectious diseases. However, EPHA2 research and EPHA2‐based therapies have been hampered by the lack of selective small‐molecule inhibitors. Herein we report the synthesis and evaluation of dedicated EPHA2 inhibitors based on the clinical BCR‐ABL/SRC inhibitor ...
19-Jun-2017
J. Proteome Res., 2017, 16 (8), pp 2887–2898, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00184
J. Proteome Res., online article

The pig is one of the earliest domesticated animals in the history of human civilization and represents one of the most important livestock animals. The recent sequencing of the Sus scrofa genome was a major step toward the comprehensive understanding of porcine biology, evolution, and its utility as a promising large animal model for biomedical and ...
30-May-2017
ChemBioChem, Volume 18, Issue 14, Pages 1379–1382, DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201700169
ChemBioChem, online article
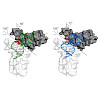
Aromatic amines are strongly carcinogenic. They are activated in the liver to give reactive nitrenium ions that react with nucleobases within the DNA duplex. The reaction occurs predominantly at the C8 position of the dG base, thereby giving C8-acetyl-aryl- or C8-aryl-dG adducts in an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. Alternatively, reaction with the ...
19-May-2017
ACS Chem. Biol., 2017, 12 (7), pp 1874–1882, DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.6b00847
ACS Chem. Biol., online aticle
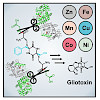
The formation of glutathione (GSH) conjugates, best known from the detoxification of xenobiotics, is a widespread strategy to incorporate sulfur into biomolecules. The biosynthesis of gliotoxin, a virulence factor of the human pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus, involves attachment of two GSH molecules and their sequential decomposition to yield two reactive ...
04-May-2017
PLoS ONE, 12(5):e0176450., https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176450
PLoS ONE, online article
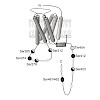
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) undergo phosphorylation at several intracellular residues by G protein-coupled receptor kinases. The resulting phosphorylation pattern triggers arrestin recruitment and receptor desensitization. The exact sites of phosphorylation and their function remained largely unknown for the human β1-adrenoceptor (ADRB1), a key GPCR in ...
25-Apr-2017
npj Biofilms and Microbiomes, volume 3, Article number: 11 (2017), doi:10.1038/s41522-017-0018-1
npj Biofilms and Microbiomes, online article

The colonization of surfaces by bacterial biofilms constitutes a huge problem in healthcare and industry. When attempting biofilm inactivation or removal, it is crucial to sufficiently wet the biofilm surface with antibacterial agents; however, certain biofilms efficiently resist wetting, and the origin of this behavior remains to date unclear. Here, we ...
30-Mar-2017
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Volume 56, Issue 37, Pages 11268–11271, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201700424
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article
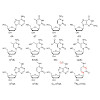
Until recently, it was believed that the genomes of higher organisms contain, in addition to the four canonical DNA bases, only 5-methyl-dC (m5dC) as a modified base to control epigenetic processes. In recent years, this view has changed dramatically with the discovery of 5-hydroxymethyl-dC (hmdC), 5-formyl-dC (fdC), and 5-carboxy-dC (cadC) in DNA from stem cells ...
29-Mar-2017
Bioconjugate Chem., 2017, 28 (4), pp 913–917, DOI: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.7b00110
Bioconjugate Chem., online article
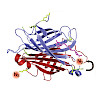
In chemical biology, azides are used to chemically manipulate target structures in a bioorthogonal manner for a plethora of applications ranging from target identification to the synthesis of homogeneously modified protein conjugates. While a variety of methods have been established to introduce the azido group into recombinant proteins, a method that directly ...
28-Mar-2017
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139 (17), pp 6152–6159, DOI: 10.1021/jacs.7b01072
J. Am. Chem. Soc., online article
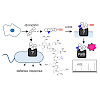
Host–microbe communication via small molecule signals is important for both symbiotic and pathogenic relationships, but is often poorly understood at the molecular level. Under conditions of host stress, levels of the human opioid peptide dynorphin are elevated, triggering virulence in the opportunistic pathogenic bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa via an unknown ...
24-Mar-2017
Chem. Eur. J., Volume 23, Issue 26, Pages 6237–6243, DOI: 10.1002/chem.201700826
Chem. Eur. J., online article
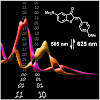
Photoswitches reacting to visible light instead of harmful UV irradiation are of very high interest due to the mild and broadly compatible conditions of their operation. Shifting the absorption into the red region of the electromagnetic spectrum usually comes at the cost of losing thermal stability of the metastable state—the switch switches off by itself. Only ...
17-Mar-2017
J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2017, 8 (7), pp 1585–1592, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b00371
J. Phys. Chem. Lett., online article

Twisted intramolecular charge transfer (TICT) formation in hemithioindigo photoswitches has recently been reported and constitutes a second deexcitation pathway complementary to photoisomerization. Typically, this behavior is not found for this type of photoswitches, and it takes special geometric and electronic conditions to realize it. Here we present a ...
01-Mar-2017
The Prostate, Volume77, Issue7, Pages 749-764, https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.23311
The Prostate, online article

BACKGROUND
Prostate‐specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is a validated target for the imaging and therapy of prostate cancer. Here, we report the detailed characterization of four novel murine monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) recognizing human PSMA as well as PSMA orthologs from different species.
METHODS
Performance of purified mAbs was assayed using a comprehensive ...
27-Feb-2017
Nature Materials, volume 16, pages 664–670 (2017), doi:10.1038/nmat4863
Nature Materials, online article
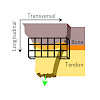
The exceptional mechanical properties of the load-bearing connection of tendon to bone rely on an intricate interplay of its biomolecular composition, microstructure and micromechanics. Here we identify that the Achilles tendon–bone insertion is characterized by an interface region of ∼500 μm with a distinct fibre organization and biomolecular composition. Within ...
16-Feb-2017
American Association for Cancer Research, Volume 77, Issue 8, pp. 1842-1853 , DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2976
American Association for Cancer Research, online article

HER2/ERBB2–overexpressing breast cancers targeted effectively by the small-molecule kinase inhibitor lapatinib frequently acquire resistance to this drug. In this study, we employed explorative mass spectrometry to profile proteome, kinome, and phosphoproteome changes in an established model of lapatinib resistance to systematically investigate initial inhibitor ...
10-Feb-2017
J. Proteome Res., 2017, 16 (3), pp 1180–1192, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00705
J. Proteome Res., online article

β-Lactones have recently been introduced as the first selective ClpP inhibitors that attenuate virulence of both sensitive Staphylococcus aureus and multiresistant strains (MRSA). Although previous knockout studies showed that ClpP is essential for S. aureus alpha-toxin production, a link between β-lactone inhibition and molecular virulence mechanisms has been ...
30-Jan-2017
Nature Methods, volume 14, pages 259–262, doi:10.1038/nmeth.4153
Nature Methods, online article
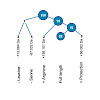
We describe ProteomeTools, a project building molecular and digital tools from the human proteome to facilitate biomedical research. Here we report the generation and multimodal liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry analysis of >330,000 synthetic tryptic peptides representing essentially all canonical human gene products, and we exemplify the utility of ...
27-Jan-2017
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1 – 6, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201611063
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article
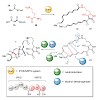
Nature provides an inexhaustible diversity of small organic molecules with beautiful molecular architectures that have strong and selective inhibitory activities. However, this tremendous biomedical potential often remains inaccessible, as the structural complexity of natural products can render their synthetic preparation extremely challenging. This problem is ...










