Research Area E - Publications 2011
16-Dec-2011

Photochromic channel blockers provide a conceptually simple and convenient way to modulate neuronal activity with light. We have recently described a family of azobenzenes that function as tonic blockers of Kv channels but require UV-A light to unblock and need to be actively switched by toggling between two different wavelengths. We now introduce red-shifted ...
02-Dec-2011

5-Formylcytosine (fC or 5-CHOdC) and 5-carboxylcytosine (caC or 5-COOHdC) have recently been identified as constituents of mammalian DNA. The nucleosides are formed from 5-methylcytosine (mC or 5-MedC) via 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (hmC or 5-HOMedC) and are possible intermediates of an active DNA demethylation process. Here we show efficient syntheses of ...
11-Nov-2011
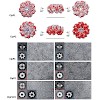
Nature provides a rich source of bioactive compounds comprising a diverse set of electrophilic core structures that are poised to react with corresponding nucleophilic residues such as serine and cysteine in enzyme active sites.These residues are usually relevant for catalysis and therefore display fine-tuned reactivity towards their dedicated substrates.We and ...
08-Nov-2011
Molecular Systems Biology, online article
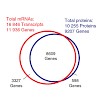
While the number and identity of proteins expressed in a single human cell type is currently unknown, this fundamental question can be addressed by advanced mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics. Online liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution MS and MS/MS yielded 166 420 peptides with unique amino-acid sequence from HeLa cells. These peptides ...
07-Oct-2011

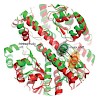
RIG-I detects cytosolic viral dsRNA with 5′ triphosphates (5′-ppp-dsRNA), thereby initiating an antiviral innate immune response. Here we report the crystal structure of superfamily 2 (SF2) ATPase domain of RIG-I in complex with a nucleotide analogue. RIG-I SF2 comprises two RecA-like domains 1A and 2A and a helical insertion domain 2B, which together form a ...
04-Oct-2011

The genetic system contains several levels of information. Firstly, the sequence of the canonical bases A, C, G, and T/U in DNA and RNA encodes amino acids through specific base triplets. Secondly, the methylation status of the cytosine base in DNA imprints epigenetic information into the genetic system, thereby contributing to the division of genes into active ...
22-Sep-2011

Thanks to everyone of the 360 people who attended the „Scientific Oktoberfest 2011“! We were able to experience amazing science combined with a awesome spirit. Thank you! Here you can see some impressions.
15-Sep-2011

The „Scientific Oktoberfest“ will be this years meeting point for some of the internationally most distinguished researchers in the field of Chemical Biology. The so-called „CIPSM Fest of Chemical Biology“ will be held from the 15th to the 16th of September in the Department of Chemistry of the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität (LMU) München. At the two-day ...
12-Sep-2011
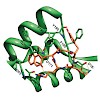
The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is a critical regulator of inflammation and immune surveillance, and it is specifically implicated in cancer metastasis and HIV-1 infection. On the basis of the observation that several of the known antagonists remarkably share a C2 symmetry element, we constructed symmetric dimers with excellent antagonistic activity using a ...
28-Aug-2011
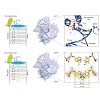
The universal genetic code relies on two hydrogen-bonded Watson–Crick base pairs that can form 64 triplet codons. This places a limit on the number of amino acids that can be encoded, which has motivated efforts to create synthetic base pairs that are orthogonal to the natural ones. An additional base pair would result in another 61 triplet codons. Artificial ...
25-Jul-2011

Cellular development requires the silencing and activation of specific gene sequences in a well-orchestrated fashion. Transcriptional gene silencing is associated with the clustered methylation of cytosine bases (C) in CpG units of promoters. The methylation occurs at position C5 of cytosine to give 5- methylcytosine (mC) with the help of special DNA ...
20-Jul-2011
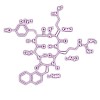
Nowadays, personalized medicine is considered to be of utmost importance to target the different causes of identical phenotypes. For example, cancer of the same type can significantly differ in its biochemical phenotypes and thus its molecular profile between patients. The disease-specific characterization of malignant cells at the molecular level is a ...
11-Jul-2011
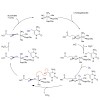
5-Hydroxymethylcytosine (hmC) was recently discovered as a new constituent of mammalian DNA. Besides 5-methylcytosine (mC), it is the only other modified base in higher organisms. The discovery is of enormous importance because it shows that the methylation of cytosines to imprint epigenetic information is not a final chemical step that leads to gene silencing ...
07-Jul-2011
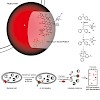
Vancomycin is a potent glycopeptide antibiotic that has evolved to specifically bind to the D-Ala-D-Ala dipeptide termini of nascent peptidoglycans. Although this mode of action is well established, several studies indicate that vancomycin and analogues exploit noncanonical target sites. In order to address all vancomycin targets in clinically relevant ...
Evaluation of α-Pyrones and Pyrimidones as Photoaffinity Probes for Affinity-Based Protein Profiling
05-Jul-2011
α-Pyrones and pyrimidones are common structural motifs in natural products and bioactive compounds. They also display photochemistry that generates high-energy intermediates that may be capable of protein reactivity. A library of pyrones and pyrimidones was synthesized, and their potential to act as photoaffinity probes for nondirected affinity-based protein ...
22-Jun-2011
PLoS ONE, online article
Recent discovery of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) in genomic DNA raises the question how this sixth base is recognized by cellular proteins. In contrast to the methyl-CpG binding domain (MBD) of MeCP2, we found that the SRA domain of Uhrf1, an essential factor in DNA maintenance methylation, binds 5hmC and 5-methylcytosine containing substrates with similar ...
19-Jun-2011
Nature Chemistry, online article
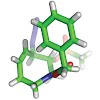
Loline is a small alkaloid that, in spite of its simple-looking structure, has posed surprising challenges to synthetic chemists. It has been known for more than a century and has been the subject of extensive biological investigations, but only two total syntheses have been achieved to date. Here, we report an asymmetric total synthesis of loline that, with less ...
09-Jun-2011

Photochromic channel blockers provide a conceptually simple and convenient way to modulate neuronal activity with light. We have recently described a family of azobenzenes that function as tonic blockers of Kv channels but require UV-A light to unblock and need to be actively switched by toggling between two different wavelengths. We now introduce red-shifted ...
17-May-2011
Nucl. Acids Res., online article

There are only few reports on protein products originating from overlapping mammalian genes even though computational predictions suggest that an appreciable fraction of mammalian genes could potentially overlap. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics has now acquired the tools to probe proteins in an unbiased manner, providing direct evidence of the output of the ...
04-May-2011
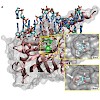
The barrel-shaped serine protease ClpP degrades misfolded, damaged, and regulatory proteins. Substrate proteins enter the ClpP barrel through the two axial pores, but it is unclear how the peptide products exit the barrel. Here we report the structure of ClpP from Staphylococcus aureus, which reveals a previously unobserved compressed state of the barrel. A ...
28-Apr-2011
J. Proteome Res, online article
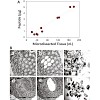
Proteomic analysis of samples isolated by laser capture microdissection from clinical specimens requires sample preparation and fractionation methods suitable for small amounts of protein. Here we describe a streamlined filter-aided sample preparation (FASP) workflow that allows efficient analysis of lysates from low numbers of cells. Addition of carrier ...
26-Mar-2011
American Society for Mass Spectrometry, online article

The modification of serine and threonine residues in proteins by a single N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) residue is an emerging post-translational modification (PTM) with broad biological implications. However, the systematic or large-scale analysis of this PTM is hampered by several factors, including low stoichiometry and the lability of the O-glycosidic bond ...
22-Mar-2011
UV irradiation of cellular DNA leads to the formation of a number of defined mutagenic DNA lesions. Here we report the discovery of new intrastrand C(4−8)G and G(8−4)C cross-link lesions in which the C(4) amino group of the cytosine base is covalently linked to the C(8) position of an adjacent dG base. The structure of the novel lesions was clarified by ...
12-Mar-2011
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, online article
Activity-based probes (ABPs) have found increasing use in functional proteomics studies. Recently, ABPs that can be employed in combination with click chemistry gained particular attention due to their flexible application in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, there is a continuous need for new ABPs that target small subsets of enzymes. We here report novel clickable ...
03-Mar-2011
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, online article
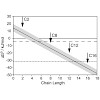
The fusion of biological membranes is mediated by integral membrane proteins with Alpha-helical transmembrane segments. Additionally, those proteins are often modified by the covalent attachment of hydrocarbon chains. Previously, a series of de novo designed Alpha-helical peptides with mixed Leu/Val sequences was presented, mimicking fusiogenically active ...
22-Feb-2011
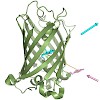
A novel kind of fluorescent protein relying on the intramolecular interplay between two different fluorophores, one of chemical origin and one of biological origin, was developed. The fluorescent non-natural amino acid L-(7-hydroxycoumarin-4-yl)ethylglycine was site-specifically incorporated into the recombinant enhanced cyan fluorescent protein (eCFP) at a ...
16-Feb-2011
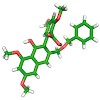
A potentially biomimetic approach toward the complex polyketide A-74528 is described. It is based on highly substituted biaryl compounds, synthesized using advanced cross-coupling and condensation methodologies.
07-Feb-2011

Speculations on the biosynthetic origin of natural products continue to inspire synthetic chemists and have led to many elegant and efficient total syntheses. Many of these involve cascade reactions, where a high-energy substrate is formed and then spontaneously reacts further to create increasingly more complex products. As such, biomimetic strategies do not ...
24-Jan-2011
Protein Science, online article
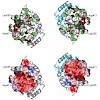
The membrane-integral transcriptional activator CadC comprises sensory and transcriptional regulatory functions within one polypeptide chain. Its C-terminal periplasmic domain, CadCpd, is responsible for sensing of environmental pH as well as for binding of the feedback inhibitor cadaverine. Here we describe the crystal structure of CadCpd (residues 188–512) ...
10-Jan-2011
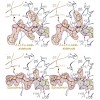
The proteasome's participation in essential biological processes such as stress response, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and antigen presentation has been well established.[1] It is, therefore, not surprising that academia and the pharmaceutical industry have made efforts to develop a range of small synthetic inhibitors against this proteolytic molecular machine ...
07-Jan-2011
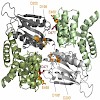
The membrane-integrated transcriptional regulator CadC of Escherichia coli activates expression of the cadBA operon at low external pH with concomitantly available lysine, providing adaptation to mild acidic stress. CadC is a representative of the ToxR-like proteins that combine sensory, signal transduction, and DNA-binding activities within a single polypeptide. ...
01-Jan-2011
Chemical Communications, 2011, DOI: 10.1039/C0CC02238A, Communication, 385-387 published on 01.01.2011
Chemical Communications, online article
The preparation of a Syringolin A/Glidobactin A hybrid (SylA–GlbA) consisting of a SylA macrocycle connected to the GlbA side chain and its potent proteasome targeting of all three proteasomal subsites is reported. The influence of the syrbactin macrocycle moiety on subsite selectivity is demonstrated.











