Research Area D - Publications 2009
21-Dec-2009
NAR, 2009, doi:10.1093/nar/gkp1152, published on 21.12.2009
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
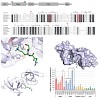
DNA methylation and histone modifications play a central role in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression and cell differentiation. Recently, Np95 (also known as UHRF1 or ICBP90) has been found to interact with Dnmt1 and to bind hemimethylated DNA, indicating together with genetic studies a central role in the maintenance of DNA methylation. Using in vitro ...
13-Dec-2009
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
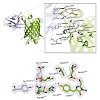
Protein conformation is critically linked to function and often controlled by interactions with regulatory factors. Here we report the selection of camelid-derived single-domain antibodies (nanobodies) that modulate the conformation and spectral properties of the green fluorescent protein (GFP). One nanobody could reversibly reduce GFP fluorescence by a factor of ...
11-Dec-2009
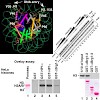
The heterochromatin-enriched HP1 proteins play a critical role in regulation of transcription. These proteins contain two related domains known as the chromo- and the chromoshadow-domain. The chromo-domain binds histone H3 tails methylated on lysine 9. However, in vivo and in vitro experiments have shown that the affinity of HP1 proteins to native methylated ...
01-Dec-2009
Infection and Immunity, online article
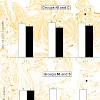
Preexisting antivector immunity can severely compromise the ability of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium live vaccines to induce protective CD8 T-cell frequencies after type III secretion system-mediated heterologous protein translocation in orally immunized mice. To circumvent this problem, we injected CpG DNA admixed to the immunodominant p60217-225 ...
15-Nov-2009
The Journal of Immunology, online article
RNA oligonucleotides containing immune-activating sequences promote the development of cytotoxic T cell and B cell responses to Ag. In this study, we show for the first time that immunostimulatory RNA oligonucleotides induce a NK cell response that prevents growth of NK-sensitive tumors. Treatment of mice with immunostimulatory RNA oligonucleotides activates NK ...
15-Nov-2009
Nature Immunology, online article

Interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta) is a potent proinflammatory factor during viral infection. Its production is tightly controlled by transcription of Il1b dependent on the transcription factor NF-κB and subsequent processing of pro-IL-1betaby an inflammasome. However, the sensors and mechanisms that facilitate RNA virus–induced production of IL-1beta are not well ...
10-Nov-2009
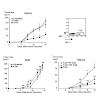
Histidine protein kinases and serine, threonine, or tyrosine protein kinases play essential roles in signal transduction in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. A third type of protein kinase, an arginine protein kinase, has been identified. McsB of Bacillus subtilis hosphorylates the heat shock transcriptional regulator CtsR and can be regarded as the founding member of ...
09-Nov-2009
JBC, 2009, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.046565 published on 09.11.2009
JBC, online article

The largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) carboxy-terminal heptarepeat domain (CTD) is subject to phosphorylation during initiation and elongation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Here we study the molecular mechanisms leading to phosphorylation of serine-7 (ser-7) in the human enzyme. Ser-7 becomes phosphorylated before initiation of transcription ...
Measurement of replication structures at the nanometer scale using super-resolution light microscopy
28-Oct-2009
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
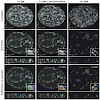
DNA replication, similar to other cellular processes, occurs within dynamic macromolecular structures. Any comprehensive understanding ultimately requires quantitative data to establish and test models of genome duplication. We used two different super-resolution light microscopy techniques to directly measure and compare the size and numbers of replication foci ...
05-Oct-2009
German Academy of Sciences Leopoldina

CIPSM is very proud Thomas Cremer was honored by the prestigious Schleiden Medal of the German Academy of Sciences Leopoldina for his outstanding scientific work on the topograhy of chromosomes in the nucleus of Eucaryota. German press release: Die Deutsche Akademie der Naturforscher Leopoldina - Nationale Akademie der Wissenschaften würdigt die ...
02-Oct-2009
EMBO reports, online article
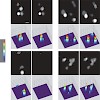
Recent studies have indicated that nuclear protein of 95 kDa (Np95) is essential for maintaining genomic methylation by recruiting DNA methyltransferase (Dnmt) 1 to hemi-methylated sites. Here, we show that Np95 interacts more strongly with regulatory domains of the de novo methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b. To investigate possible functions, we developed an ...
01-Oct-2009
The cooperation "Experimental and theoretical methods for dissecting the dynamics of epigenetic gene silencing in living cells" between Prof. Heinrich Leonhardt's and Prof. Gunnar Schotta's CIPSM groups and scientists from the University of Heidelberg will be supported for the next three years by the "New methods in systembiology" program of the BMBF financially. ...
17-Sep-2009
Chomosome Research, online article

The nuclear architecture is considered an important contributor to genome function. Although the fine structural features of the cell nucleus have been investigated extensively by means of ultrastructural cytochemistry, mainly on ultrathin sections in two dimensions (2D), there was a of lack routine methods for a rapid reconstruction of three-dimensional (3D) ...
11-Sep-2009

Yeah, the CIPSM football team won the 2009 ScieKickIn football tournament. We thank its members around Prof. Axel Imhof for their excellent performance and passion. german press release
27-Aug-2009
Molecular Microbiology, 2009, 73(6), 982–991, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06847.x published on 27.08.2009
Molecular Microbiology, online article
Bacteria sense environmental stimuli and transduce this information to cytoplasmic components of the signal transduction machinery to cope with and to adapt to ever changing conditions. Hence, bacteria are equipped with numerous membrane-integrated proteins responsible for sensing such as histidine kinases, chemoreceptors and ToxR-like proteins. There is ...
26-Aug-2009
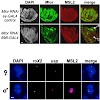
The dosage compensation complex (DCC) in Drosophila globally increases transcription from the X chromosome in males to compensate for its monosomy.We discovered a male-specific conformation of the X chromosome that depends on the associations of high-affinity binding sites (HAS) of the DCC. The core DCC subunits MSL1–MSL2 are responsible for this male-specific ...
25-Aug-2009
Cytogenetic and Genome Research, online article

Quantum dots (Qdots) are semiconductor nanocrystals, which are photo-stable, show bright fluorescence with narrow, symmetric emission spectra and are available in multiple resolvable colors. We established a FISH protocol for the simultaneous visualization of up to 6 different DNA probes differentially labeled with Qdots and with conventional organic ...
21-Aug-2009
J. Mol. Biol., online article

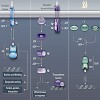
The analysis of stress response systems in microorganisms can reveal molecular strategies for regulatory control and adaptation. In this study, we focused on the Cad module, a subsystem of Escherichia coli’s response to acidic stress that is conditionally activated at low pH only when lysine is available. When expressed, the Cad system counteracts the elevated H+ ...
18-Aug-2009

Acetylation is a well-studied posttranslational modification that has been associated with a broad spectrum of biological processes, notably gene regulation. Many studies have contributed to our knowledge of the enzymology underlying acetylation, including efforts to understand the molecular mechanism of substrate recognition by several acetyltransferases, but ...
03-Aug-2009
The Journal of Clinical Investigation, online article
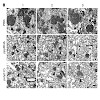
The retinoic acid–inducible gene I (RIG-I) and melanoma differentiation–associated antigen 5 (MDA-5) helicases sense viral RNA in infected cells and initiate antiviral responses such as the production of type I IFNs. Here we have shown that RIG-I and MDA-5 also initiate a proapoptotic signaling pathway that is independent of type I IFNs. In human melanoma cells, ...
23-Jul-2009
Molecular Microbiology, online article
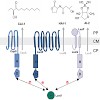
Quorum sensing (QS) refers to the ability of bacterial populations to read out the local environment for cell density and to collectively activate gene expression. Vibrio harveyi, one of the best characterized model organisms in QS, was used to address the question how single cells behave within a QS-activated community in a homogeneous environment. Analysis of ...
15-Jul-2009
Experimental Cell Research, online article
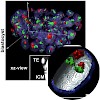
Gene-dense chromosome territories (CTs) are typically located more interior, gene-poor CTs more peripheral in mammalian cell nuclei. Here, we show that this gene-density correlated CT positioning holds for the most gene-rich and gene-poor bovine chromosomes 19 and 20, respectively, in bovine fibroblast and lymphocyte nuclei. In order to determine the period at ...
09-Jul-2009
BMC Microbiology, 2009, 9(133), doi:10.1186/1471-2180-9-133 published on 09.07.2009
BMC Microbiology, online article

The KdpD/KdpE two-component system of Escherichia coli regulates expression of the kdpFABC operon encoding the high affinity K+ transport system KdpFABC. The input domain of KdpD comprises a domain that belongs to the family of universal stress proteins (Usp). It has been previously demonstrated that UspC binds to this domain, resulting in KdpD/KdpE scaffolding ...
03-Jul-2009
EMBO reports, online article

Post-translational histone modifications have essential roles in controlling nuclear processes; however, the specific mechanisms regulating these modifications and their combinatorial activities remain elusive. Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9) regulates gene expression by phosphorylating transcriptional regulatory proteins, including the RNA polymerase II ...
02-Jul-2009

The ATPase retinoid acid-inducible gene (RIG)-I senses viral RNA in the cytoplasm of infected cells and subsequently activates cellular antiviral defense mechanisms. RIG-I recognizes molecular structures that discriminate viral from host RNA. Here, we show that RIG-I ligands require base-paired structures in conjunction with a free 5′-triphosphate to trigger ...
29-Jun-2009
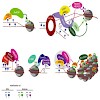
During differentiation and development cells undergo dramatic morphological, and functional changes without any change in the DNA sequence. The underlying changes of gene expression patterns are established and maintained by epigenetic processes. Early mechanistic insights came from the observation that gene activity and repression states correlate with the DNA ...
19-Jun-2009
European Biophysics Journal, online article

Chromosome shattering has been described as a special form of mitotic catastrophe, which occurs in cells with unrepaired DNA damage. The shattered chromosome phenotype was detected after application of a methanol/acetic acid (MAA) fixation protocol routinely used for the preparation of metaphase spreads. The corresponding phenotype in the living cell and the ...
18-Jun-2009
Nucleic Acids Research, online article

Every cell has to duplicate its entire genome during S-phase of the cell cycle. After replication, the newly synthesized DNA is rapidly assembled into chromatin. The newly assembled chromatin ‘matures’ and adopts a variety of different conformations. This differential packaging of DNA plays an important role for the maintenance of gene expression patterns and has ...
05-Jun-2009
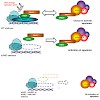
Loss of the of the maintenance methyltransferase xDNMT1 during Xenopus development results in premature transcription and activation of a p53-dependent apoptotic program that accounts for embryo lethality. Here, we show that activation of the apoptotic response is signalled through the methyl-CpG binding protein xMBD4 and the mismatch repair pathway protein ...
05-Jun-2009
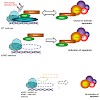
Loss of the of the maintenance methyltransferase xDNMT1 during Xenopus development results in premature transcription and activation of a p53-dependent apoptotic program that accounts for embryo lethality. Here, we show that activation of the apoptotic response is signalled through the methyl-CpG binding protein xMBD4 and the mismatch repair pathway protein ...
05-Jun-2009
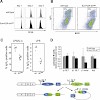
H4K20 methylation is a broad chromatin modification that has been linked with diverse epigenetic functions. Several enzymes target H4K20 methylation, consistent with distinct mono-, di-, and trimethylation states controlling different biological outputs. To analyze the roles of H4K20 methylation states, we generated conditional null alleles for the two Suv4-20h ...
15-May-2009
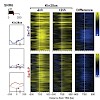
Posttranslational modifications of the carboxyterminal domain (CTD) of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) specify a molecular recognition code that is deciphered by proteins involved in RNA biogenesis. The CTD is comprised of a repeating heptapeptide (Y1S2P3T4S5P6S7). Recently, phosphorylation of serine 7 was shown to be important for ...
29-Apr-2009
Molecular Microbiology, online article

Proteins EINtr, NPr and IIANtr form a phosphoryl group transfer chain (Ntr-PTS) working in parallel to the phosphoenolpyruvate:carbohydrate phosphotransferase system (transport-PTS) in Escherichia coli. Recently, it was shown that dephosphorylated IIANtr binds and inhibits TrkA, a low-affinity potassium transporter. Here we report that the Ntr-PTS also regulates ...
23-Apr-2009
Journal of Anatomy, online article

Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC) are a heterogeneous cell population, which is reflected in varying morphological and biological properties. Three subpopulations with intrinsic characteristics can be distinguished: small rapidly self-renewing cells, spindle-shaped cells and large, flattened cells. Unfortunately, it has neither been possible to morphologically ...
20-Apr-2009
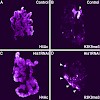
Although tremendous progress has been made toward identifying factors that regulate nucleosome structure and positioning, the mechanisms that regulate higher-order chromatin structure remain poorly understood. Recent studies suggest that the ISWI chromatin-remodeling factor plays a key role in this process by promoting the assembly of chromatin containing histone ...
17-Apr-2009
The Cell, 2008, 137, 356-68 published on 17.04.2009
The Cell, online article
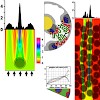
We show that the nuclear architecture of rod photoreceptor cells differs fundamentally in nocturnal and diurnal mammals. The rods of diurnal retinas possess the conventional architecture found in nearly all eukaryotic cells, with most heterochromatin situated at the nuclear periphery and euchromatin residing toward the nuclear interior. The rods of nocturnal ...
07-Apr-2009

HP1 is a major component of chromatin and regulates gene expression through its binding to methylated histone H3. Most eukaryotes express at least three isoforms of HP1 with similar domain architecture. However, despite the common specificity for methylated histone H3, the three HP1 isoforms bind to different regions of the genome. Most of the studies so far ...
03-Apr-2009
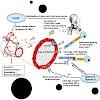
Ischemic cardiomyopathy is one of the main causes of death, which may be prevented by stem cell-based therapies. SDF-1a is the major chemokine attracting stem cells to the heart. Since SDF-1a is cleaved and inactivated by CD26/dipeptidylpeptidase IV (DPP-IV), we established a therapeutic concept— applicable to ischemic disorders in general—by combining genetic ...
19-Feb-2009

For the compact Drosophila genome, several factors mediating insulator function, such as su(Hw) and dCTCF, have been identified. Recent analyses showed that both these insulator-binding factors are functionally dependent on the same cofactor, CP190. Here we analysed genome-wide binding of CP190 and dCTCF. CP190 binding was detected at CTCF, su(Hw) and GAF sites ...
08-Feb-2009

In order to adapt to ever changing environmental conditions, bacteria sense environmental stimuli, and convert them into signals that are transduced intracellularly. Several mechanisms have evolved by which receptors transmit signals across the cytoplasmic membrane. Stimulus perception may trigger receptor dimerization and/or conformational changes. Another ...
02-Feb-2009
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 2009, 104, 1562–1569 published on 02.02.2009
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, online article
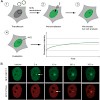
Mammalian cells are constantly threatened by multiple types ofDNAlesions arising from various sources like irradiation, environmental agents, replication errors or by-products of the normal cellular metabolism. If not readily detected and repaired these lesions can lead to cell death or to the transformation of cells giving rise to life-threatening diseases like ...
27-Jan-2009
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, online article
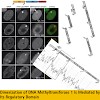
DNA methylation is a major epigenetic modification and plays a crucial role in the regulation of gene expression. Within the family of DNA methyltransferases (Dnmts), Dnmt3a and 3b establish methylation marks during early development, while Dnmt1 maintains methylation patterns after DNA replication. The maintenance function of Dnmt1 is regulated by its large ...
15-Jan-2009

The backbone structure is determined by site-directed spin labeling, double electron electron resonance measurements of distances, and modeling in terms of a helix-loop-helix construct for a transmembrane domain that is supposed to line the translocation pathway in the 54.3 kDa Naþ/proline symporter PutP of Escherichia coli. The conformational distribution of the ...
07-Jan-2009
Nucleic Acids Research , online article
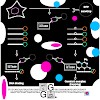
We present a simple, non-radioactive assay for DNA methyltransferase activity and DNA binding. As most proteins are studied as GFP fusions in living cells, we used a GFP binding nanobody coupled to agarose beads (GFP nanotrap) for rapid one-step purification. Immobilized GFP fusion proteins were subsequently incubated with different fluorescently labeled DNA ...
22-Oct-2008

Histone modifications play an important role in shaping chromatin structure. Here, we describe the use of an in vitro chromatin assembly system from Drosophila embryo extracts to investigate the dynamic changes of histone modifications subsequent to histone deposition. In accordance with what has been observed in vivo, we find a deacetylation of the initially ...










