News 2014
31-Dec-2014

Recognition of mRNA transcripts by RNA binding proteins plays essential roles at various steps of gene expression, including splicing, translation, stability and general mRNA metabolism. Also the biogenesis and activity of non-coding RNAs (miRNAs, siRNAs, lncRNAs) and other regulatory RNA molecules depends on protein interactions. Cis elements, i.e. short RNA ...
29-Dec-2014
Quantitative proteome research is greatly promoted by high-resolution parallel format assays. A characterization of protein complexes based on binding forces offers an unparalleled dynamic range and allows for the effective discrimination of non-specific interactions. Here we present a DNA-based Molecular Force Assay to quantify protein-protein interactions, ...
Spin Component-Scaled Second-Order Møller−Plesset Perturbation Theory for Calculating NMR Shieldings
22-Dec-2014
Spin component-scaled and scaled opposite-spin second-order Møller–Plesset perturbation approaches (SCS-MP2 and SOS-MP2) are introduced for calculating NMR chemical shifts in analogy to the well-established scaled approaches for MP2 energies. Gauge-including atomic orbitals (GIAO) are employed throughout this work. The GIAO-SCS-MP2 and GIAO-SOS-MP2 methods ...
20-Dec-2014

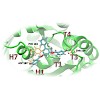
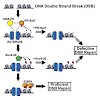
DNA double-strand breaks can be repaired by homologous recombination, during which the DNA ends are long-range resected by helicase–nuclease systems to generate 3′ single strand tails. In archaea, this requires the Mre11–Rad50 complex and the ATP-dependent helicase–nuclease complex HerA–NurA. We report the cryo-EM structure of Sulfolobus solfataricus HerA–NurA at ...
19-Dec-2014
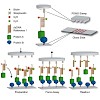
DNA replication, transcription and repair involve the recruitment of protein complexes that change their composition as they progress along the genome in a directed or strand‐specific manner. Chromatin immunoprecipitation in conjunction with hidden Markov models (HMMs) has been instrumental in understanding these processes, as they segment the genome into ...
19-Dec-2014
Heterologous enzymes and binding proteins were secreted by the moss Physcomitrella patens or anchored extracellularly on its cell membrane in order to functionalize the apoplast as a biochemical reaction compartment. This modular membrane anchoring system utilizes the signal peptide and the transmembrane segment of the somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase ...
18-Dec-2014
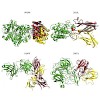
Protein-protein interactions are abundant in the cell but to date structural data for a large number of complexes is lacking. Computational docking methods can complement experiments by providing structural models of complexes based on structures of the individual partners. A major caveat for docking success is accounting for protein flexibility. Especially, ...
17-Dec-2014
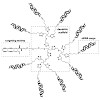
We report the development of dendritic siRNA nanostructures that are able to penetrate even difficult to transfect cells such as neurons with the help of a special receptor ligand. The nanoparticles elicit strong siRNA responses, despite the dendritic structure. An siRNA dendrimer directed against the crucial rabies virus (RABV) nucleoprotein (N protein) and ...
17-Dec-2014

CIPSM wishing you and your family a wonderful holiday season and a healthy & peaceful New Year 2015!
16-Dec-2014
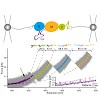
The heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is a dimeric molecular chaperone essential in numerous cellular processes. Its three domains (N, M, and C) are connected via linkers that allow the rearrangement of domains during Hsp90’s chaperone cycle. A unique linker, called charged linker (CL), connects the N- and M-domain of Hsp90. We used an integrated approach, combining ...
16-Dec-2014

Therapeutic strategies for spinal cord injury (SCI) commonly focus on regenerating disconnected axons. An alternative approach would be to maintain continuity of damaged axons, especially after contusion. The viability of such neuropreservative strategies depends on the degree to which initially injured axons can recover. Here we use morphological and molecular ...
16-Dec-2014
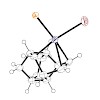
A synthetic strategy toward the intriguing hydrocarbon nanorod polytwistane is outlined. Our approach aims toward the polymerization of acetylene starting from precursors that would provide a helical bias for the formation of polytwistane. Both transition-metal-catalyzed and radical polymerizations were investigated. Two potential initiator molecules were ...
12-Dec-2014
NMR spectroscopy is a powerful tool to study the structure and dynamics of nucleic acids. In this unit, we give an overview of important experiments to determine and characterize hydrogen bonds in nucleic acids and provide detailed instructions for setting up recently developed sensitivity-improved NMR pulse sequences, i.e., BEST selective long-range HNN-COSY, ...
12-Dec-2014

In eukaryotes, the molecular chaperones Hsp90 and Hsp70 are connected via the co-chaperone Sti1/Hop, which allows transfer of clients. Here, we show that the basic functions of yeast Sti1 and human Hop are conserved. These include the simultaneous binding of Hsp90 and Hsp70, the inhibition of the ATPase activity of Hsp90, and the ability to support client ...
08-Dec-2014
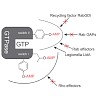
Essential cell division protein FtsZ is considered an attractive target in the search for antibacterials with novel mechanisms of action to overcome the resistance problem. FtsZ undergoes GTP-dependent assembly at midcell to form the Z-ring, a dynamic structure that evolves until final constriction of the cell. Therefore, molecules able to inhibit its activity ...
08-Dec-2014
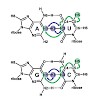
In the cell, proteins are frequently modified covalently at specific amino acids with post-translational modifications, leading to a diversification of protein functions and activities. Since the introduction of high-resolution mass spectrometry, new post-translational modifications are constantly being discovered. One particular modification is the adenylylation ...
04-Dec-2014

In Escherichia coli, detoxification of methylglyoxal (MG) requires glyoxalases I and II. Glyoxalase I (gloA/GlxI) isomerizes the hemithioacetal, formed spontaneously from MG and glutathione (GSH) to S-lactoylglutathione (SLG), which is hydrolyzed by glyoxalase II (gloB/GlxII) to lactate and GSH. YcbL from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is an unusual type ...
04-Dec-2014
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) defines a group of inherited degenerative retinal diseases causing progressive loss of photoreceptors. To this day, RP is still untreatable and rational treatment development will require a thorough understanding of the underlying cell death mechanisms. Methylation of the DNA base cytosine by DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) is an ...
01-Dec-2014
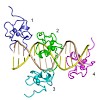
The male-specific lethal dosage compensation complex (MSL-DCC) selectively assembles on the X chromosome in Drosophila males and activates gene transcription by twofold through histone acetylation. An MSL recognition element (MRE) sequence motif nucleates the initial MSL association, but how it is recognized remains unknown. Here, we identified the CXC domain of ...
26-Nov-2014

Despite the importance of superoxide dismutases (SODs) in the plant antioxidant defence system little is known about their regulation by post-translational modifications. Here, we investigated the in vitro effects of nitric oxide derivatives on the seven SOD isoforms of Arabidopsis thaliana. S-nitrosoglutathione, which causes S-nitrosylation of cysteine residues, ...
24-Nov-2014

We searched for genetic alterations in human B cell lymphoma that affect the ubiquitin-proteasome system. This approach identified FBXO25 within a minimal common region of frequent deletion in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). FBXO25 encodes an orphan F-box protein that determines the substrate specificity of the SCF (SKP1–CUL1–F-box)FBXO25 ubiquitin ligase complex. An ...
21-Nov-2014

Although antigen-binding fragments (Fabs) of antibodies constitute established tracers for in vivo radiodiagnostics, their functionality is hampered by a very short circulation half-life. PASylation, the genetic fusion with a long, conformationally disordered amino acid chain comprising Pro, Ala and Ser, provides a convenient way to expand protein size and, ...
19-Nov-2014
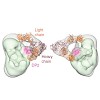
In eukarya, chaperones Hsp70 and Hsp90 act coordinately in the folding and maturation of a range of key proteins with the help of several co-chaperones, especially Hop. Although biochemical data define the Hop-mediated Hsp70–Hsp90 substrate transfer mechanism, the intrinsic flexibility of these proteins and the dynamic nature of their complexes have limited ...
18-Nov-2014

Visualizing neuronal mitochondria in a living, intact mammalian organism is a challenge that can be overcome in zebrafish larvae, which are highly accessible for optical imaging and genetic manipulation. Here, we detail an approach to visualize neuronal mitochondria in sensory Rohon–Beard axons, which allows quantitatively measuring mitochondrial shape, dynamics, ...
17-Nov-2014
Fluorine-containing natural products are extremely rare. The recent report on the isolation and biological activity of the bacterial secondary metabolite 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-fluorophenyl)propionic acid was thus highly remarkable. The compound contained the first aromatic fluorine substituent known to date in any natural product. The promise to discover an ...
17-Nov-2014
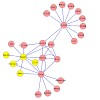
In vitro, assembly of box C/D small nucleolar ribonucleoproteins (snoRNPs) involves the sequential recruitment of core proteins to snoRNAs. In vivo, however, assembly factors are required (NUFIP, BCD1, and the HSP90–R2TP complex), and it is unknown whether a similar sequential scheme applies. In this paper, we describe systematic quantitative stable isotope ...
13-Nov-2014
Advances in phosphopeptide enrichment methods enable the identification of thousands of phosphopeptides from complex samples. Current offline enrichment approaches using TiO2, Ti, and Fe immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography (IMAC) material in batch or microtip format are widely used, but they suffer from irreproducibility and compromised selectivity. To ...
12-Nov-2014

DOT1 enzymes are conserved methyltransferases that catalyse the methylation of lysine 79 on histone H3 (H3K79). Most eukaryotes contain one DOT1 enzyme, whereas African trypanosomes have two homologues, DOT1A and DOT1B, with different enzymatic activities. DOT1A mediates mono- and dimethylation of H3K76, the homologue of H3K79 in other organisms, whereas ...
06-Nov-2014

An astounding property of the nervous system is its cellular diversity. This diversity, which was initially realized by morphological and electrophysiological differences, is ultimately produced by variations in gene-expression programs. In most cases, these variations are determined by external cues. However, a growing number of neuronal types have been ...
05-Nov-2014

The human histone macroH2A.1.1 recruits activated PARP1 enzyme to chromatin through its poly(ADP-ribose)-binding macrodomain. New work shows that PARP1 and CBP can be displaced from chromatin in cancer cells that have lost macroH2A.1.1, thus leading to changes in histone H2B acetylation at cancer-relevant genes.
01-Nov-2014
In Caenorhabditis elegans, germline apoptosis is promoted by egl-1 and ced-13 in response to meiotic checkpoint activation. We report that the requirement for these two factors depends on which checkpoints are active. We also identify a regulatory region of egl-1 required to inhibit germline apoptosis in response to DNA damage incurred during meiotic recombination.
28-Oct-2014

Die LMU vereinbart bislang umfangreichsten Lizenzvertrag im Bereich der Proteinforschung: BASF kauft aussichtsreiche Patente für innovative Entwicklungen in der Biomedizin. Die LMU hat mit dem Unternehmen BASF SE einen Lizenzvertrag im Bereich neuer chemischer Methoden zur Modifizierung von Biomolekülen geschlossen, die am Exzellenzcluster Center for integrated ...
27-Oct-2014

The Mre11–Rad50 nuclease–ATPase is an evolutionarily conserved multifunctional DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair factor. Mre11–Rad50's mechanism in the processing, tethering, and signaling of DSBs is unclear, in part because we lack a structural framework for its interaction with DNA in different functional states. We determined the crystal structure of ...
26-Oct-2014
Vertebrate vision relies on two types of photoreceptors, rods and cones, which signal increments in light intensity with graded hyperpolarizations. Rods operate in the lower range of light intensities while cones operate at brighter intensities. The receptive fields of both photoreceptors exhibit antagonistic center-surround organization. Here we show that at ...
24-Oct-2014
UV excitation of the DNA single strand (dT)18 leads to electronically excited states that are potential gateways to DNA photolesions. Using time-resolved infrared spectroscopy we characterized a species with a lifetime of [similar]100 ps and identified it as a charge separated excited state between two thymine bases..
20-Oct-2014
Hemithioindigo (HTI) photoswitches have a tremendous potential for biological and supramolecular applications due to their absorptions in the visible-light region in conjunction with ultrafast photoisomerization and high thermal bistability. Rational tailoring of the photophysical properties for a specific application is the key to exploit the full potential of ...
16-Oct-2014
Aneuploidy is a hallmark of cancer and is associated with malignancy and poor prognosis. Recent studies have revealed that aneuploidy inhibits proliferation, causes distinct alterations in the transcriptome and proteome and disturbs cellular proteostasis. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the changes in gene expression and the impairment of ...
13-Oct-2014
Excited-state dynamics are essential to understanding the formation of DNA lesions induced by UV light. By using femtosecond IR spectroscopy, it was possible to determine the lifetimes of the excited states of all four bases in the double-stranded environment of natural DNA. After UV excitation of the DNA duplex, we detected a concerted decay of base pairs ...
09-Oct-2014

Bacterial ribosomes stall on polyproline stretches and require the elongation factor P (EF-P) to relieve the arrest. Yet it remains unclear why evolution has favored the development of EF-P rather than selecting against the occurrence of polyproline stretches in proteins. We have discovered that only a single polyproline stretch is invariant across all domains of ...
08-Oct-2014

During protein synthesis, nascent polypeptide chains within the ribosomal tunnel can act in cis to induce ribosome stalling and regulate expression of downstream genes. The Staphylococcus aureus ErmCL leader peptide induces stalling in the presence of clinically important macrolide antibiotics, such as erythromycin, leading to the induction of the downstream ...
06-Oct-2014

Alpha-synuclein (αlphaS) misfolding is associated with Parkinson's disease (PD) but little is known about the mechanisms underlying αS toxicity. Increasing evidence suggests that defects in membrane transport play an important role in neuronal dysfunction. Here we demonstrate that the GTPase Rab8a interacts with αS in rodent brain. NMR spectroscopy reveals that ...
26-Sep-2014
Throughout their life, bacteria need to sense and respond to environmental stress. Thus, such stress responses can require dramatic cellular reprogramming, both at the transcriptional as well as the translational level. This review focuses on the protein factors that interact with the bacterial translational apparatus to respond to and cope with different types ...
26-Sep-2014
Throughout their life, bacteria need to sense and respond to environmental stress. Thus, such stress responses can require dramatic cellular reprogramming, both at the transcriptional as well as the translational level. This review focuses on the protein factors that interact with the bacterial translational apparatus to respond to and cope with different types ...
25-Sep-2014

Mass spectrometers equipped with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI-MS) require frequent multipoint calibration to obtain good mass accuracy over a wide mass range and across large numbers of samples. In this study, we introduce a new synthetic peptide mass calibration standard termed PAS-cal tailored for MALDI-MS based bottom-up proteomics. This ...
22-Sep-2014
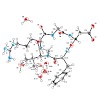
The X-ray crystal and NMR spectroscopic structures of the peptide drug candidate Cilengitide (cyclo(RGDf(NMe)Val)) in various solvents are obtained and compared in addition to the integrin receptor bound conformation. The NMR-based solution structures exhibit conformations closely resembling the X-ray structure of Cilengitide bound to the head group of integrin ...
22-Sep-2014
The concept of proteasome inhibition ranks among the latest achievements in the treatment of blood cancer and represents a promising strategy for modulating autoimmune diseases. In this study, we describe peptidic sulfonyl fluoride inhibitors that selectively block the catalytic β5 subunit of the immunoproteasome by inducing only marginal cytotoxic effects. ...
22-Sep-2014
The molecular chaperone Hsp90 undergoes an ATP-driven cycle of conformational changes in which large structural rearrangements precede ATP hydrolysis. Well-established small-molecule inhibitors of Hsp90 compete with ATP-binding. We wondered whether compounds exist that can accelerate the conformational cycle. In a FRET-based screen reporting on conformational ...
19-Sep-2014

The radical SAM enzyme, spore photoproduct lyase, requires an H-atom transfer (HAT) pathway to catalyze DNA repair. By rational engineering, we demonstrate that it is possible to rewire its HAT pathway, a first step toward the development of novel catalysts based on the radical SAM enzyme scaffold.
16-Sep-2014
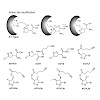
Acivicin is a natural product with diverse biological activities. Several decades ago its clinical application in cancer treatment was explored but failed due to unacceptable toxicity. The causes behind the desired and undesired biological effects have never been elucidated and only limited information about acivicin-specific targets is available. In order to ...
12-Sep-2014
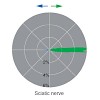
Microtubule dynamics in neurons play critical roles in physiology, injury and disease and determine microtubule orientation, the cell biological correlate of neurite polarization. Several microtubule binding proteins, including end-binding protein 3 (EB3), specifically bind to the growing plus tip of microtubules. In the past, fluorescently tagged end-binding ...
11-Sep-2014
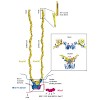
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are one of the most deleterious forms of DNA damage and can result in cell inviability or chromosomal aberrations. The Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 (MRN) ATPase-nuclease complex is a central player in the cellular response to DSBs and is implicated in the sensing and nucleolytic processing of DSBs, as well as in DSB signaling by activating the ...
09-Sep-2014
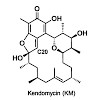
Natural products are a valuable source for novel lead structures in drug discovery, but for the majority of isolated bioactive compounds, the cellular targets are unknown. The structurally unique ansa-polyketide kendomycin (KM) was reported to exert its potent cytotoxic effects via impairment of the ubiquitin proteasome system, but the exact mode of action ...
07-Sep-2014
Genetic equality between males and females is established by chromosome-wide dosage-compensation mechanisms. In the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster, the dosage-compensation complex promotes twofold hypertranscription of the single male X-chromosome and is silenced in females by inhibition of the translation of msl2, which codes for the limiting component of the ...
05-Sep-2014

IFNβ is a common therapeutic option to treat multiple sclerosis (MS). It is unique amongst the family of type I IFNs in that it binds to the interferon receptors with high affinity, conferring exceptional biological properties. We have previously reported the generation of an interferon superagonist (dubbed YNSα8) that is built on the backbone of a low affinity ...
04-Sep-2014

Biogenesis of eukaryotic messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes (mRNPs) involves the synthesis, splicing, and 3′ processing of pre-mRNA, and the assembly of mature mRNPs for nuclear export. We mapped 23 mRNP biogenesis factors onto the yeast transcriptome, providing 104–106 high-confidence RNA interaction sites per factor. The data reveal how mRNP biogenesis ...
03-Sep-2014
INTRODUCTION: Natively folded proteins generally have a significant number of hydrophobic residues that cluster together to form a hydrophobic core. However, during the vectorial synthesis on the ribosome and subsequent folding, these hydrophobic residues are exposed. Because folding occurs in a highly crowded environment, exposed residues can lead to undesired ...
28-Aug-2014
A short total synthesis of the published structure of racemic trichodermatide A is reported. Our synthesis involves a Knoevenagel condensation/Michael addition sequence, followed by the formation of tricyclic hexahydroxanthene-dione and a diastereoselective bis-hydroxylation. The final product, the structure of which was confirmed by X-ray crystallography, has ...
27-Aug-2014

Dosage compensation is a regulatory process that balances the expression of X-chromosomal genes between males (XY) and females (XX). In Drosophila, this requires non-coding RNAs and RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) whose specific functions remain elusive. Here we show that the Drosophila RBP UNR promotes the targeting of the activating male-specific-lethal complex to ...
26-Aug-2014

The retention and splicing (RES) complex is a conserved spliceosome-associated module that was shown to enhance splicing of a subset of transcripts and promote the nuclear retention of unspliced pre-mRNAs in yeast. The heterotrimeric RES complex is organized around the Snu17p protein that binds to both the Bud13p and Pml1p subunits. Snu17p exhibits an RRM domain ...
21-Aug-2014
Endolysosomal organelles play a key role in trafficking, breakdown and receptor-mediated recycling of different macromolecules such as low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol, epithelial growth factor (EGF) or transferrin. Here we examine the role of two-pore channel (TPC) 2, an endolysosomal cation channel, in these processes. Embryonic mouse fibroblasts ...
20-Aug-2014
Fluorescence fluctuation imaging is a powerful means to investigate dynamics, interactions, and stoichiometry of proteins inside living cells. Pulsed interleaved excitation (PIE) is the method of nanosecond alternating excitation with time-resolved detection and allows accurate, independent, and quasi-simultaneous determination of fluorescence intensities and ...
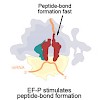
20-Aug-2014
The polymerization of amino acids into proteins occurs on ribosomes, with the rate influenced by the amino acids being polymerized. The imino acid proline is a poor donor and acceptor for peptide-bond formation, such that translational stalling occurs when three or more consecutive prolines (PPP) are encountered by the ribosome. In bacteria, stalling at PPP ...
18-Aug-2014
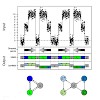
The cell establishes heritable patterns of active and silenced chromatin via interacting factors that set, remove, and read epigenetic marks. To understand how the underlying networks operate, we have dissected transcriptional silencing in pericentric heterochromatin (PCH) of mouse fibroblasts. We assembled a quantitative map for the abundance and interactions of ...
15-Aug-2014
The potential contribution of protein aggregates to the unwanted immunogenicity of protein pharmaceuticals is a major concern. In the present study a murine monoclonal antibody was utilized to study the immunogenicity of different types of aggregates in mice. Samples containing defined types of aggregates were prepared by processes such as stirring, agitation, ...
15-Aug-2014
Mucolipidosis type IV (MLIV) is caused by loss of function mutations in the TRPML1 ion channel. We previously reported that tissue zinc levels in MLIV were abnormally elevated; however, the mechanism behind this pathologic accumulation remains unknown. Here, we identify transmembrane (TMEM)-163 protein, a putative zinc transporter, as a novel interacting partner ...
14-Aug-2014
Mucolipidosis type IV (MLIV) is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder often characterized by severe neurodevelopmental abnormalities and neuro-retinal degeneration. Mutations in the TRPML1 gene are causative for MLIV. We used lead optimization strategies to identify—and MLIV patient fibroblasts to test—small-molecule activators for their potential to ...
08-Aug-2014
One of the limiting factors in determining the sensitivity of tandem mass spectrometry using hybrid quadrupole orthogonal acceleration time-of-flight instruments is the duty cycle of the orthogonal ion injection system. As a consequence, only a fraction of the generated fragment ion beam is collected by the time-of-flight analyzer. Here we describe a method ...
07-Aug-2014
The Nrd1-Nab3-Sen1 (NNS) complex is essential for controlling pervasive transcription and generating sn/snoRNAs in S. cerevisiae. The NNS complex terminates transcription of noncoding RNA genes and promotes exosome-dependent processing/degradation of the released transcripts. The Trf4-Air2-Mtr4 (TRAMP) complex polyadenylates NNS target RNAs and favors their ...
07-Aug-2014
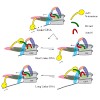
ISWI family chromatin remodeling enzymes generate regularly spaced nucleosome arrays. In a recent Nature report, Hwang et al. (2014) describe how ACF gauges the length of linker DNA when deciding to accelerate nucleosome sliding or to put on the brakes.
06-Aug-2014
We present a low-prefactor, cubically scaling scaled-opposite-spin second-order Møller-Plesset perturbation theory (SOS-MP2) method which is highly suitable for massively parallel architectures like graphics processing units (GPU). The scaling is reduced from O(N5) to O(N3) by a reformulation of the MP2-expression in the atomic orbital basis via Laplace ...
05-Aug-2014
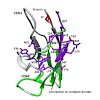
Variable (V) domains of antibodies are essential for antigen recognition by our adaptive immune system. However, some variants of the light chain V domains (VL) form pathogenic amyloid fibrils in patients. It is so far unclear which residues play a key role in governing these processes. Here, we show that the conserved residue 2 of VL domains is crucial for ...
05-Aug-2014
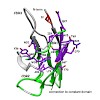
Variable (V) domains of antibodies are essential for antigen recognition by our adaptive immune system. However, some variants of the light chain V domains (VL) form pathogenic amyloid fibrils in patients. It is so far unclear which residues play a key role in governing these processes. Here, we show that the conserved residue 2 of VL domains is crucial for ...
04-Aug-2014

The development of methods to assemble nucleosomes from recombinant histones decades ago has transformed chromatin research. Nevertheless, nucleosome reconstitution remains time consuming to this day, not least because the four individual histones must be purified first. Here, we present a streamlined purification protocol of recombinant histones from bacteria. ...
03-Aug-2014
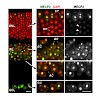
Methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MECP2) is a protein that specifically binds methylated DNA, thus regulating transcription and chromatin organization. Mutations in the gene have been identified as the principal cause of Rett syndrome, a severe neurological disorder. Although the role of MECP2 has been extensively studied in nervous tissues, still very little is ...
01-Aug-2014
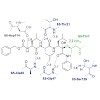
The major challenge for proteasome inhibitor design lies in achieving high selectivity for, and activity against, the target, which requires specific interactions with the active site. Novel ligands aim to overcome off-target-related side effects such as peripheral neuropathy, which is frequently observed in cancer patients treated with the FDA-approved ...
31-Jul-2014
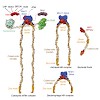
DNA double-strand breaks are repaired by two major pathways, homologous recombination or nonhomologous end joining. The commitment to one or the other pathway proceeds via different steps of resection of the DNA ends, which is controlled and executed by a set of DNA double-strand break sensors, endo- and exonucleases, helicases, and DNA damage response factors. ...
28-Jul-2014
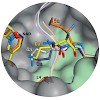
The dehydrogenase PylD catalyzes the ultimate step of the pyrrolysine pathway by converting the isopeptide L-lysine-Nε-3R-methyl-D-ornithine to the 22nd proteinogenic amino acid. In this study, we demonstrate how PylD can be harnessed to oxidize various isopeptides to novel amino acids by combining chemical synthesis with enzyme kinetics and X-ray ...
25-Jul-2014
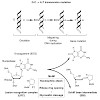
Living organisms protect the genome against external influences by recognizing and repairing damaged DNA. A common source of gene mutation is the oxidized guanine, which undergoes base excision repair through cleavage of the glycosidic bond between the ribose and the nucleobase of the lesion. We unravel the repair mechanism utilized by bacterial glycosylase, ...
24-Jul-2014
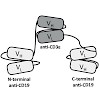
Although selective binding of 53BP1 to dimethylated histone H4 lysine 20 (H4K20me2) at DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) is a necessary and pivotal determinant of nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ)-directed repair, the enzymes that generate H4K20me2 at DSBs were unclear. Here, we determined that the PR-Set7 monomethyltransferase (H4K20me1) regulates de novo H4K20 ...
23-Jul-2014
Triplebody 19-3-19, an antibody-derived protein, carries three single chain fragment variable domains in tandem in a single polypeptide chain. 19-3-19 binds CD19-bearing lymphoid cells via its two distal domains and primary T cells via its CD3-targeting central domain in an antigen-specific manner. Here, malignant B-lymphoid cell lines and primary cells from ...
18-Jul-2014
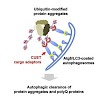
Selective ubiquitin-dependent autophagy plays a pivotal role in the elimination of protein aggregates, assemblies, or organelles and counteracts the cytotoxicity of proteins linked to neurodegenerative diseases. Following substrate ubiquitylation, the cargo is delivered to autophagosomes involving adaptors like human p62 that bind ubiquitin and the autophagosomal ...
18-Jul-2014
Recent discoveries in the field of innate immunity have highlighted the existence of a family of nucleic acid-sensing proteins that have similar structural and functional properties. These include the well-known oligoadenylate synthase (OAS) family proteins and the recently identified OAS homologue cyclic GMP–AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS). The OAS proteins and cGAS ...
14-Jul-2014

DNA structure functions as an overlapping code to the DNA sequence. Rapid progress in understanding the role of DNA structure in gene regulation, DNA damage recognition and genome stability has been made. The three dimensional structure of both proteins and DNA plays a crucial role for their specific interaction, and proteins can recognise the chemical signature ...
14-Jul-2014

Legionella spp. cause the severe pneumonia Legionnaires' disease. The environmental bacteria replicate intracellularly in free-living amoebae and human alveolar macrophages within a distinct, endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-derived compartment termed the Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV). LCV formation requires the bacterial Icm/Dot type IV secretion system (T4SS) ...
14-Jul-2014
Centromeres are chromosomal regions crucial for correct chromosome segregation during mitosis and meiosis. They are epigenetically defined by centromeric proteins such as the centromere-specific histone H3-variant centromere protein A (CENP-A). In humans, 16 additional proteins have been described to be constitutively associated with centromeres throughout the ...
13-Jul-2014
Roquin function in T cells is essential for the prevention of autoimmune disease. Roquin interacts with the 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs) of co-stimulatory receptors and controls T-cell activation and differentiation. Here we show that the N-terminal ROQ domain from mouse roquin adopts an extended winged-helix (WH) fold, which is sufficient for binding to the ...
09-Jul-2014

The catalytic and selective construction of carbon–carbon bonds for the generation of complex molecules is one of the most important tasks in organic chemistry. This was clearly highlighted by the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, which was awarded for the development of Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. The underlying concept of cross-linking building blocks ...
09-Jul-2014

Das Exzellenzcluster „Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich (CIPSM)“ der LMU startet am 9. Juli gemeinsam mit dem Feodor-Lynen-Gymnasium in Planegg im Landkreis München ein Projekt in dem Forscher/innen Schülern/innen der Klassenstufe 8 wissenschaftliche Zusammenhänge anschaulich und spannend vermitteln um sie frühzeitig für die Natur und ihre ...
09-Jul-2014

Mammalian genomes encode seven catalytic proteasome subunits, namely, β1c, β2c, β5c (assembled into constitutive 20S proteasome core particles), β1i, β2i, β5i (incorporated into immunoproteasomes), and the thymoproteasome-specific subunit β5t. Extensive research in the past decades has yielded numerous potent proteasome inhibitors including compounds currently ...
08-Jul-2014
Repeat proteins consisting of helical segments seem to fold by a matrix-assisted mechanism in which folded segments induce structure in intrinsically disordered parts of the protein, as shown by Watson and colleagues in this issue of Structure for an Armadillo repeat protein and previously by the Balbach group for an Ankyrin repeat protein.
08-Jul-2014
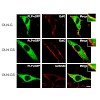
In the central nervous system, lipid-protein interactions are pivotal for myelin maintenance, as these interactions regulate protein transport to the myelin membrane as well as the molecular organization within the sheath. To improve our understanding of the fundamental properties of myelin, we focused here on the lateral membrane organization and dynamics of ...
07-Jul-2014

NMR spectroscopy is a key method for studying the structure and dynamics of (large) multidomain proteins and complexes in solution. It plays a unique role in integrated structural biology approaches as especially information about conformational dynamics can be readily obtained at residue resolution. Here, we review NMR techniques for such studies focusing on ...
06-Jul-2014

Idiopathic achalasia is characterized by a failure of the lower esophageal sphincter to relax due to a loss of neurons in the myenteric plexu. This ultimately leads to massive dilatation and an irreversibly impaired megaesophagus. We performed a genetic association study in 1,068 achalasia cases and 4,242 controls and fine-mapped a strong MHC association signal ...
03-Jul-2014

Toxic DNA-protein crosslinks (DPCs) arise by ionizing irradiation and UV light, are particularly caused by endogenously produced reactive compounds such as formaldehyde, and also occur during compromised topoisomerase action. Although nucleotide excision repair and homologous recombination contribute to cell survival upon DPCs, hardly anything is known about ...
03-Jul-2014
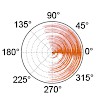
Relaxation parameters such as longitudinal relaxation are susceptible to artifacts such as spin diffusion, and can be affected by paramagnetic impurities as e.g. oxygen, which make a quantitative interpretation difficult. We present here the site-specific measurement of [1H]13C and [1H]15N heteronuclear rates in an immobilized protein. For methyls, a strong ...
02-Jul-2014
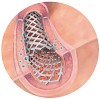
The use of highly active and selective integrin ligands in combination with stent implantation is emerging as a promising alternative to the release of classical immunosuppressive drugs by current drug-eluting stents (DES), which has been associated with delayed vascular healing and late stent thrombosis. Herein we present the development and biological ...
01-Jul-2014
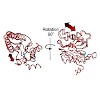
Two clusters of configurations of the main proteolytic subunit β5 were identified by principal component analysis of crystal structures of the yeast proteasome core particle (yCP). The apo-cluster encompasses unliganded species and complexes with nonpeptidic ligands, and the pep-cluster comprises complexes with peptidic ligands. The murine constitutive CP ...
A Modular View of the Diversity of Cell-Density-Encoding Schemes in Bacterial Quorum-Sensing Systems
01-Jul-2014
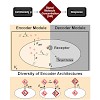
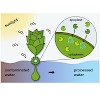
Certain environmental parameters are accessible to cells only indirectly and require an encoding step for cells to retrieve the relevant information. A prominent example is the phenomenon of quorum sensing by microorganisms, where information about cell density is encoded by means of secreted signaling molecules. The mapping of cell density to signal molecule ...
01-Jul-2014

Patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) frequently harbor mutations in genes involved in the DNA (hydroxy)methylation pathway (DNMT3A, TET2, IDH1 and IDH2). In this study, we measured 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC) levels in 206 clinically and molecularly well-characterized younger adult AML patients (≤60 years) included in the EORTC/GIMEMA AML-12 06991 ...
24-Jun-2014
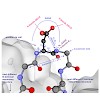
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and proteins containing antibody domains are the most prevalent class of biotherapeutics in diverse indication areas. Today, established techniques such as immunization or phage display allow for an efficient generation of new mAbs. Besides functional properties, the stability of future therapeutic mAbs is a key selection criterion ...
24-Jun-2014
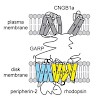
Outer segments (OS) of rod photoreceptors are cellular compartments specialized in the conversion of light into electrical signals. This process relies on the light-triggered change in the intracellular levels of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), which in turn controls the activity of cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channels in the rod OS plasma membrane. The ...
20-Jun-2014

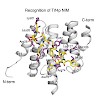
Integrins moderate diverse important functions in the human body and are promising targets in cancer therapy. Hence, the selective inhibition of specific integrins is of great medicinal interest. Here, we report the optimization of a grafted lasso peptide, yielding MccJ25(RGDF), which is a highly potent and selective αvβ3 integrin inhibitor. Furthermore, its NMR ...
19-Jun-2014

Hydroamination reactions involving the addition of an amine to an inactivated alkene are entropically prohibited and require strong chemical catalysts. While this synthetic process is efficient at generating substituted amines, there is no equivalent in small molecule-mediated enzyme inhibition. We report an unusual mechanism of proteasome inhibition that ...
19-Jun-2014

Many neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease, can be directly correlated with the deregulation in neuronal signaling. Hence, it is indispensable for therapy development to understand the participating signaling processes. Because the activity of the involved protein kinases is of major interest for the investigation of these signaling processes, ...
19-Jun-2014
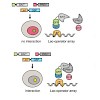
The discovery of hydroxymethyl-, formyl- and carboxylcytosine, generated through oxidation of methylcytosine by TET dioxygenases, raised the question how these modifications contribute to epigenetic regulation. As they are subjected to complex regulation in vivo, we dissected links to gene expression with in vitro modified reporter constructs. We used an Oct4 ...
13-Jun-2014

Antibodies are uniquely suited to serve essential roles in the human immune defense as they combine several specific functions in one hetero-oligomeric protein. Their constant regions activate effector functions and their variable domains provide a stable framework that allows incorporation of highly diverse loop sequences. The combination of non-germline DNA ...
13-Jun-2014
Our recently developed QQR-type integral screening is introduced in our Cholesky-decomposed pseudo-densities Møller-Plesset perturbation theory of second order (CDD-MP2) method. We use the resolution-of-the-identity (RI) approximation in combination with efficient integral transformations employing sparse matrix multiplications. The RI-CDD-MP2 method shows an ...
06-Jun-2014
Modulation of the function of small GTPases that regulate vesicular trafficking is a strategy employed by several human pathogens. Legionella pneumophila infects lung macrophages and injects a plethora of different proteins into its host cell. Among these is DrrA/SidM, which catalyzes stable adenylylation of Rab1b, a regulator of endoplasmatic reticulum to Golgi ...
The structural analysis of shark IgNAR antibodies reveals evolutionary principles of immunoglobulins
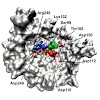
03-Jun-2014
Sharks and other cartilaginous fish are the phylogenetically oldest living organisms that rely on antibodies as part of their adaptive immune system. They produce the immunoglobulin new antigen receptor (IgNAR), a homodimeric heavy chain-only antibody, as a major part of their humoral adaptive immune response. Here, we report the atomic resolution structure of ...
30-May-2014
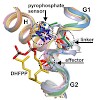
We present crystallographic and functional data of selina-4(15),7(11)-diene synthase (SdS) from Streptomyces pristinaespiralis in its open and closed (ligand-bound) conformation. We could identify an induced-fit mechanism by elucidating a rearrangement of the G1/2 helix-break motif upon substrate binding. This rearrangement highlights a novel effector triad ...
29-May-2014

To leverage the potential of multi-omics studies, exploratory data analysis methods that provide systematic integration and comparison of multiple layers of omics information are required. We describe multiple co-inertia analysis (MCIA), an exploratory data analysis method that identifies co-relationships between multiple high dimensional datasets. Based on a ...
29-May-2014
Lack of permissive mechanisms and abundance of inhibitory molecules in the lesioned central nervous system of adult mammals contribute to the failure of functional recovery, which leads to severe disabilities in motor functions or pain. Previous studies have indicated that the neural cell adhesion molecule L1 constitutes a viable target to promote regeneration. ...
28-May-2014

We describe the design, preparation, and mass-spectrometric characterization of a new recombinant peptide calibration standard with uniform biophysical and ionization characteristics for mass spectrometry. “PAS-cal” is an artificial polypeptide concatamer of peptide cassettes with varying lengths, each composed of the three small, chemically stable amino acids ...
28-May-2014

Proteomes are characterized by large protein-abundance differences, cell-type- and time-dependent expression patterns and post-translational modifications, all of which carry biological information that is not accessible by genomics or transcriptomics. Here we present a mass-spectrometry-based draft of the human proteome and a public, high-performance, in-memory ...
28-May-2014

Although the role of noxious α-synuclein (α-SYN) in the degeneration of midbrain dopaminergic neurons and associated motor deficits of Parkinson’s disease is recognized, its impact on non-motor brain circuits and related symptoms remains elusive. Through combining in vivo two-photon imaging with time-coded labelling of neurons in the olfactory bulb of A30P α-SYN ...
22-May-2014
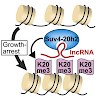
A complex network of regulatory pathways links transcription to cell growth and proliferation. Here we show that cellular quiescence alters chromatin structure by promoting trimethylation of histone H4 at lysine 20 (H4K20me3). In contrast to pericentric or telomeric regions, recruitment of the H4K20 methyltransferase Suv4-20h2 to rRNA genes and IAP elements ...
21-May-2014
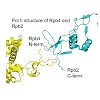
RNA polymerase II (Pol II) is the central enzyme that carries out eukaryotic mRNA transcription and consists of a 10-subunit catalytic core and a subcomplex of subunits Rpb4 and Rpb7 (Rpb4/7). Rpb4/7 has been proposed to dissociate from Pol II, enter the cytoplasm, and function there in mRNA translation and degradation. Here we provide evidence that Rpb4 mainly ...
18-May-2014
Ten eleven translocation (Tet) enzymes oxidize the epigenetically important DNA base 5-methylcytosine (mC) stepwise to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (hmC), 5-formylcytosine and 5-carboxycytosine. It is currently unknown whether Tet-induced oxidation is limited to cytosine-derived nucleobases or whether other nucleobases are oxidized as well. We synthesized isotopologs ...
09-May-2014

In mammals, the carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase (Pol) II consists of 52 conserved heptapeptide repeats containing the consensus sequence Tyr1-Ser2-Pro3-Thr4-Ser5-Pro6-Ser7. Post-translational modifications of the CTD coordinate the transcription cycle and various steps of mRNA maturation. Here we describe Tyr1 phosphorylation (Tyr1P) as a hallmark ...
09-May-2014
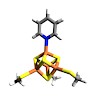
(E)-1-Hydroxy-2-methylbut-2-enyl 4-diphosphate reductase (IspH) is a [Fe4S4] cluster-containing enzyme involved in isoprenoid biosynthesis in many bacteria as well as in malaria parasites and is an important drug target. Several inhibitors including amino and thiol substrate analogues, as well as acetylene and pyridine diphosphates, have been reported. Here, we ...
09-May-2014
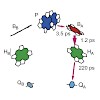
The primary dynamics of reaction centers from Rhodobacter sphaeroides at room temperature are studied at low excitation intensities and low excitation rates. Analysis based on singular value decomposition yields three time constants in the picosecond range (ca. 1.2 ps, 3.5 ps and 220 ps). The spectral and temporal signatures are fully consistent with the ...
08-May-2014

The GroEL/ES chaperonin system functions as a protein folding cage. Many obligate substrates of GroEL share the (βα)8 TIM-barrel fold, but how the chaperonin promotes folding of these proteins is not known. Here, we analyzed the folding of DapA at peptide resolution using hydrogen/deuterium exchange and mass spectrometry. During spontaneous folding, all elements ...
07-May-2014
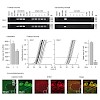
In central mammalian neurons, activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor type1 (mGluR1) evokes a complex synaptic response consisting of IP3 receptor-dependent Ca2+ release from internal Ca2+ stores and a slow depolarizing potential involving TRPC3 channels. It is largely unclear how mGluR1 is linked to its downstream effectors. Here, we explored the role of ...
01-May-2014
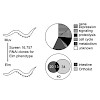
The development and homeostasis of multicellular animals requires precise coordination of cell division and differentiation. We performed a genome-wide RNA interference screen in Caenorhabditis elegans to reveal the components of a regulatory network that promotes developmentally programmed cell-cycle quiescence. The 107 identified genes are predicted to ...
29-Apr-2014
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1, also known as ARTD1) is an abundant nuclear enzyme that plays important roles in DNA repair, gene transcription and differentiation through the modulation of chromatin structure and function. In this work we identify a physical and functional poly(ADP-ribose) mediated interaction of PARP1 with the E3 ubiquitin ligase UHRF1 ...
29-Apr-2014
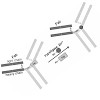
Bioconjugates, such as antibody–drug conjugates, have gained recent attention because of their increasing use in therapeutic and diagnostic applications. Commonly used conjugation reactions based upon chemoselective reagents exhibit a number of drawbacks: most of these reactions lack regio- and stereospecificity, thus resulting in loss of protein functionality ...
28-Apr-2014

Double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) in the cytoplasm triggers the production of interleukin 1β (IL-1β) as an antiviral host response, and deregulation of the pathways involved can promote inflammatory disease. Here we report a direct cytosolic interaction between the DNA-damage sensor Rad50 and the innate immune system adaptor CARD9. Transfection of dendritic cells with ...
28-Apr-2014

Native chemical ligation (NCL) was established for the conversion of sequence-defined oligomers of different topologies into targeted and PEG shielded pDNA and siRNA carriers. From an existing library of non-targeted oligoethanamino amides, six oligomers containing N-terminal cysteines were selected as cationic cores, to which monodisperse polyethylene glycol ...
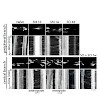
25-Apr-2014
During the cell cycle, the levels of hundreds of mRNAs change in a periodic manner, but how this is achieved by alterations in the rates of mRNA synthesis and degradation has not been studied systematically. Here, we used metabolic RNA labeling and comparative dynamic transcriptome analysis (cDTA) to derive mRNA synthesis and degradation rates every 5 min during ...
24-Apr-2014

Chromatin reorganization and the incorporation of specific histone modifications during DNA damage response are essential steps for the successful repair of any DNA lesion. Here, we show that the histone-fold protein CHRAC14 plays an essential role in response to DNA damage in Drosophila. Chrac14 mutants are hypersensitive to genotoxic stress and do not activate ...
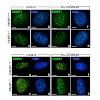
23-Apr-2014
Despite the inability of CNS axons to regenerate, an increased regenerative capacity can be elicited following conditioning lesion to the peripheral branch of dorsal root ganglia neurons (DRGs). By in vivo radiolabeling of rat DRGs, coupled to mass spectrometry and kinesin immunoprecipitation of spinal cord extracts, we determined that the anterograde transport ...
23-Apr-2014

Posttranslational modifications (PTMs) of proteins determine their structure-function relationships, interaction partners, as well as their fate in the cell and are crucial for many cellular key processes. For instance chromatin structure and hence gene expression is epigenetically regulated by acetylation or methylation of lysine residues in histones, a ...
20-Apr-2014
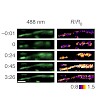
Mitochondrial redox signals have a central role in neuronal physiology and disease. Here we describe a new optical approach to measure fast redox signals with single-organelle resolution in living mice that express genetically encoded redox biosensors in their neuronal mitochondria. Moreover, we demonstrate how parallel measurements with several biosensors can ...
20-Apr-2014
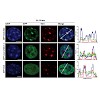
Histone variants play an important role in shaping the mammalian epigenome and their aberrant expression is frequently observed in several types of cancer. However, the mechanisms that mediate their function and the composition of the variant-containing chromatin are still largely unknown. A proteomic interrogation of chromatin containing the different H2A ...
17-Apr-2014
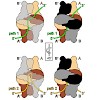
Instead of a classical single-stranded deoxyribonuleic acid (DNA)-binding protein (SSB), some hyperthermophilic crenarchaea harbor a non-canonical SSB termed ThermoDBP. Two related but poorly characterized groups of proteins, which share the ThermoDBP N-terminal DNA-binding domain, have a broader phylogenetic distribution and co-exist with ThermoDBPs and/or other ...
17-Apr-2014
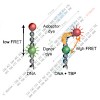
During transcription initiation, the promoter DNA is recognized and bent by the basal transcription factor TATA-binding protein (TBP). Subsequent association of transcription factor B (TFB) with the TBP–DNA complex is followed by the recruitment of the ribonucleic acid polymerase resulting in the formation of the pre-initiation complex. TBP and TFB/TF(II)B are ...
17-Apr-2014
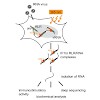
RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs: RIG-I, MDA5 and LGP2) play a major role in the innate immune response against viral infections and detect patterns on viral RNA molecules that are typically absent from host RNA. Upon RNA binding, RLRs trigger a complex downstream signaling cascade resulting in the expression of type I interferons and proinflammatory cytokines. In the ...
17-Apr-2014
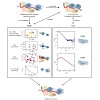
Structural biology provides essential information for elucidating molecular mechanisms that underlie biological function. Advances in hardware, sample preparation, experimental methods, and computational approaches now enable structural analysis of protein complexes with increasing complexity that more closely represent biologically entities in the cellular ...
16-Apr-2014
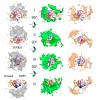
Multidomain proteins containing intrinsically disordered linkers exhibit large-scale dynamic modes that play key roles in a multitude of molecular recognition and signaling processes. Here, we determine the conformational space sampled by the multidomain splicing factor U2AF65 using complementary nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and small-angle scattering ...
15-Apr-2014
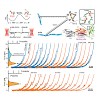
Proline switches, controlled by cis–trans isomerization, have emerged as a particularly effective regulatory mechanism in a wide range of biological processes. In this study, we use single-molecule mechanical measurements to develop a full kinetic and energetic description of a highly conserved proline switch in the force-sensing domain 20 of human filamin and ...
15-Apr-2014

The 26S proteasome is a 2.5 MDa molecular machine that executes the degradation of substrates of the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. The molecular architecture of the 26S proteasome was recently established by cryo-EM approaches. For a detailed understanding of the sequence of events from the initial binding of polyubiquitylated substrates to the translocation into ...
15-Apr-2014
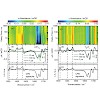
The decay of triplet states and the formation of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) after UV excitation of the all-thymine oligomer (dT)18 and the locked dinucleotide TLpTL were studied by nanosecond IR spectroscopy. IR marker bands characteristic for the CPD lesion and the triplet state were observed from 1 ns (time resolution of the setup) onward. The ...
13-Apr-2014
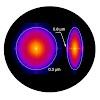
Using a descanned, laser-induced guide star and direct wavefront sensing, we demonstrate adaptive correction of complex optical aberrations at high numerical aperture (NA) and a 14-ms update rate. This correction permits us to compensate for the rapid spatial variation in aberration often encountered in biological specimens and to recover diffraction-limited ...
09-Apr-2014
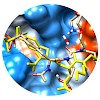
Many human diseases are correlated with the dysregulation of signal transduction processes. One of the most important protein interaction domains in the context of signal transduction is the Src homology 2 (SH2) domain that binds phosphotyrosine residues. Hence, appropriate methods for the investigation of SH2 proteins are indispensable in diagnostics and ...
09-Apr-2014

Solid tumors are dependent for growth on nutrients and the supply of oxygen, which they often acquire via neoangiogenesis. Vascular endothelial growth factors and the corresponding receptors (VEGFRs) play central roles in this process, and consequently, the blockade of this pathway is one therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment. A number of small molecules ...
03-Apr-2014
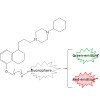
Despite the promising potentials of σ2 receptors in cancer therapy and diagnosis, there are still ambiguities related to the nature and physiological role of the σ2 protein. With the aim of providing potent and reliable tools to be used in σ2 receptor research, we developed a novel series of fluorescent σ2 ligands on the basis of our previous work, where ...
01-Apr-2014

Regarding its many roles for lead optimization and drug development, fluorine will definitely continue to be of major importance in medicinal chemistry. With safe and selective fluorinating agents at hands, the use of fluorinated compounds has become routine in pharmaceutical and material sciences and many of the well-appreciated organofluorine inductive effects ...
31-Mar-2014
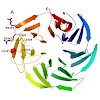
Mutations in the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 gene (LRRK2) are associated with familial and sporadic Parkinson's disease (PD). LRRK2 is a complex protein that consists of multiple domains, including predicted C-terminal WD40 repeats. In this study, we analyzed functional and molecular features conferred by the WD40 domain. Electron microscopic analysis of the ...
26-Mar-2014
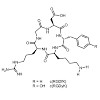
The αvβ3-integrin addressing cyclic pentapeptide cyclo(RGDfK) was conjugated to NOPO, 1,4,7-triazacyclononane 1,4-bis[methylene(hydroxymethyl)phosphinic acid]-7-[methylene(2-carboxyethyl)phosphinic acid], a bifunctional chelator with exceptional gallium-68 labeling properties. NOPO–c(RGDfK) and its Ga(III) and Cu(II) complexes showed high affinity to αvβ3 ...
25-Mar-2014

Alternative pre-messenger ribonucleic acid (pre-mRNA) splicing is an essential process in eukaryotic gene regulation. The T-cell intracellular antigen-1 (TIA-1) is an apoptosis-promoting factor that modulates alternative splicing of transcripts, including the pre-mRNA encoding the membrane receptor Fas. TIA-1 is a multi-domain ribonucleic acid (RNA) binding ...
24-Mar-2014
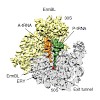
In bacteria, ribosome stalling during translation of ErmBL leader peptide occurs in the presence of the antibiotic erythromycin and leads to induction of expression of the downstream macrolide resistance methyltransferase ErmB. The lack of structures of drug-dependent stalled ribosome complexes (SRCs) has limited our mechanistic understanding of this regulatory ...
24-Mar-2014
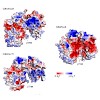
Phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain (CTD) by cyclin-dependent kinases is important for productive transcription. Here we determine the crystal structure of Cdk12/CycK and analyse its requirements for substrate recognition. Active Cdk12/CycK is arranged in an open conformation similar to that of Cdk9/CycT but different from those of cell ...
Pharmacophoric Modifications Lead to Superpotent αvβ3 Integrin Ligands with Suppressed α5β1 Activity
23-Mar-2014
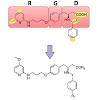
The selective targeting of the αvβ3 integrin subtype without affecting the structurally closely related receptor α5β1 is crucial for understanding the details of their biological and pathological functions and thus of great relevance for diagnostic and therapeutic approaches in cancer treatment. Here, we present the synthesis of highly active RGD peptidomimetics ...
21-Mar-2014

When carbon sources become limiting for growth, bacteria must choose which of the remaining nutrients should be used first. We have identified a nutrient-sensing signaling network in Escherichia coli that is activated at the transition to stationary phase. The network is composed of the two histidine kinase/response regulator systems YehU/YehT and YpdA/YpdB and ...
20-Mar-2014
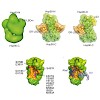
Hsp90 is the most abundant molecular chaperone in the eukaryotic cell. One of the most stringent clients is the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), whose in vivo function strictly depends on the interaction with the Hsp90 machinery. However, the molecular mechanism of this interaction has been elusive. Here we have reconstituted the interaction of Hsp90 with ...
19-Mar-2014
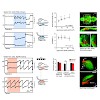
Animals respond to whole-field visual motion with compensatory eye and body movements in order to stabilize both their gaze and position with respect to their surroundings. In zebrafish, rotational stimuli need to be distinguished from translational stimuli to drive the optokinetic and the optomotor responses, respectively. Here, we systematically characterize ...
18-Mar-2014

Many transmembrane helices contain serine and/or threonine residues whose side chains form intrahelical H-bonds with upstream carbonyl oxygens. Here, we investigated the impact of threonine side-chain/main-chain backbonding on the backbone dynamics of the amyloid precursor protein transmembrane helix. This helix consists of a N-terminal dimerization region and a ...
12-Mar-2014

Ultra-high-field NMR spectroscopy requires an increased bandwidth for heteronuclear decoupling, especially in biomolecular NMR applications. Composite pulse decoupling cannot provide sufficient bandwidth at practical power levels, and adiabatic pulse decoupling with sufficient bandwidth is compromised by sideband artifacts. A novel low-power, broadband ...
12-Mar-2014
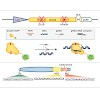
Labeling and tracing of specific sequences in living cells has been a major challenge in studying the spatiotemporal dynamics of native chromatin. Here we repurposed the prokaryotic CRISPR/Cas adaptive immunity system to specifically detect endogenous genomic loci in mouse embryonic stem cells. We constructed a catalytically inactive version of the Cas9 ...
10-Mar-2014

Base stacking in DNA is related to long-living excited states whose molecular nature is still under debate. To elucidate the molecular background we study well-defined oligonucleotides with natural bases, which allow selective UV excitation of one single base in the strand. IR probing in the picosecond regime enables us to dissect the contribution of different ...
06-Mar-2014
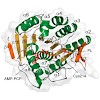
Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP) is the active vitamer of vitamin B6 and acts as an essential cofactor in many aspects of amino acid and sugar metabolism. The virulence and survival of pathogenic bacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis depend on PLP, and deficiencies in humans have also been associated with neurological disorders and inflammation. While PLP can ...
05-Mar-2014

Aggregates formed by amyloidogenic peptides and proteins and reconstituted membrane protein preparations differ significantly in terms of the spectral quality that they display in solid-state NMR experiments. Structural heterogeneity and dynamics can both in principle account for that observation. This perspectives article aims to point out challenges and ...
03-Mar-2014

Understanding and controlling proteolysis is an important goal in therapeutic chemistry. Among the natural products specifically inhibiting proteases microviridins are particularly noteworthy. Microviridins are ribosomally produced and posttranslationally modified peptides that are processed into a unique, cagelike architecture. Here, we report a combined ...
27-Feb-2014

In eukaryotes, Dom34 is involved in the rescue of ribosomes that stall on mRNAs during protein synthesis. Using ribosome profiling, Guydosh and Green reveal that, in addition to rescue of ribosomes stalled on truncated mRNAs, Dom34 also recycles ribosomes that are unexpectedly found in the 3′ untranslated regions of many cellular mRNAs.
26-Feb-2014

Inducible switching between phenotypes is a common strategy of bacteria to adapt to fluctuating environments. Here, we analyze the switching kinetics of a paradigmatic inducible system, the arabinose utilization system in E. coli. Using time-lapse fluorescence microscopy of microcolonies in a microfluidic chamber, which permits sudden up- and down-shifts in the ...
25-Feb-2014

The ATP-dependent degradation of polyubiquitylated proteins by the 26S proteasome is essential for the maintenance of proteome stability and the regulation of a plethora of cellular processes. Degradation of substrates is preceded by the removal of polyubiquitin moieties through the isopeptidase activity of the subunit Rpn11. Here we describe three crystal ...
24-Feb-2014
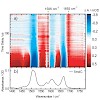
Methylated cytidine plays an important role as an epigenetic signal in gene regulation. Its oxidation products are assumed to be involved in active demethylation processes but also in damaging DNA. Here, we report the photochemical production of the 5-methyl-2′-deoxycytidine radical cation via a two-photon ionization process. The radical cation is detected by ...
20-Feb-2014
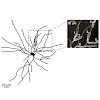
High-frequency bursts of action potentials (APs) are a distinctive form of signaling in various types of mammalian central neurons. In CA1 hippocampal pyramidal neurons in vivo, such complex spike bursts (CSs) are detected during various behaviors and are considered to be particularly important for learning- and memory-related synaptic plasticity. Here, we ...
20-Feb-2014

Skin infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus are a major clinical concern, especially if they are caused by multi-resistant strains. In these cases, a spread into deeper soft tissues or the bloodstream results in life-threatening conditions that are difficult to treat by conventional antibiotics. Previous in vitro experiments with a small β-lactone-based ...
19-Feb-2014

We want to deeply thank you for all your great contributions at this years’ Wildbad Kreuth conference! We enjoyed each one of your lectures and posters. Because of the good overall standard presented by the members of the CIPSM Graduate Forum it was hard to come down to the laureates of our CIPSM AWARDS: The CIPSM AWARD for the best lecture goes to: Dr. Eva Huber ...
18-Feb-2014
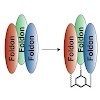
C 3-Symmetric trimesic acid scaffolds, functionalized with bromoacetyl, aminooxyacetyl and azidoacetyl moieties, respectively, were synthesized and compared regarding their utility for the trivalent presentation of peptides using three different chemoselective ligation reactions, i.e. thioether and oxime formation, as well as the “click” reaction. The latter ...
18-Feb-2014

Aneuploidy, a karyotype deviating from multiples of a haploid chromosome set, affects the physiology of eukaryotes. In humans, aneuploidy is linked to pathological defects such as developmental abnormalities, mental retardation or cancer, but the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. There are many different types and origins of aneuploidy, but whether there is a ...
18-Feb-2014

Intracellular membrane trafficking requires correct and specific localization of Rab GTPases. The hypervariable C-terminal domain (HVD) of Rabs is posttranslationally modified by isoprenyl moieties that enable membrane association. A model asserting HVD-directed targeting has been contested in previous studies, but the role of the Rab HVD and the mechanism of Rab ...
17-Feb-2014
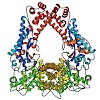
The Gram-negative bacterium Legionella pneumophila is the causative agent of Legionnaires’ disease. During infection of eukaryotic cells, the bacterium releases about 300 different bacterial effector molecules that aid in the establishment of the Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV) among which SidC is one of these secreted proteins. However, apart from membrane ...
16-Feb-2014
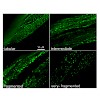
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a hallmark of skeletal muscle degeneration during aging. One mechanism through which mitochondrial dysfunction can be caused is through changes in mitochondrial morphology. To determine the role of mitochondrial morphology changes in age-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction, we studied mitochondrial morphology in body wall muscles of ...
14-Feb-2014

Despite its ubiquity in cancer, link with other pathologies, and role in promoting adaptive evolution, the effects of aneuploidy or imbalanced chromosomal content on cellular physiology have remained incompletely characterized. Significantly, it appears that the detrimental as well as beneficial effects of aneuploidy are due to the altered gene expression ...
14-Feb-2014
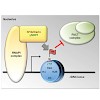
Chemical modifications of histone proteins directly and indirectly affect chromatin structure and thereby contribute to the multilayered control of diverse DNA-based processes. A recent study in Nature enriches this list of enzyme-dependent posttranslational histone marks by H2A glutamine methylation that appears to be dedicated to only one specific cellular ...
13-Feb-2014
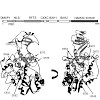
The N-terminal regulatory part of DNA methyltransferase 1 (Dnmt1) contains a replication foci targeting sequence (RFTS) domain, which is involved in the recruitment of Dnmt1 to replication forks. The RFTS domain has been observed in a crystal structure to bind to the catalytic domain of the enzyme and block its catalytic centre. Removal of the RFTS domain led to ...
12-Feb-2014
Robust immune responses are essential for eliminating pathogens but must be metered to avoid prolonged immune activation and potential host damage. Upon recognition of microbial DNA, the cytosolic DNA sensor cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) synthetase (cGAS) produces the second messenger cGAMP to initiate the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) pathway and subsequent ...
12-Feb-2014

The functional identity of centromeres arises from a set of specific nucleoprotein particle subunits of the centromeric chromatin fibre. These include CENP-A and histone H3 nucleosomes and a novel nucleosome-like complex of CENPs -T, -W, -S and -X. Fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy and Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) revealed that human CENP-S ...
11-Feb-2014
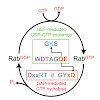
Ras superfamily GTPase activation and inactivation occur by canonical nucleotide exchange and GTP hydrolysis mechanisms. Despite conservation of active-site residues, the Ras-related Rab GTPase activation pathway differs from Ras and between different Rabs. Analysis of DENND1-Rab35, Rabex-Rab5, TRAPP-Rab1 and DrrA-Rab1 suggests Rabs have the potential for ...
10-Feb-2014

A system for naming ribosomal proteins is described that the authors intend to use in the future. They urge others to adopt it. The objective is to eliminate the confusion caused by the assignment of identical names to ribosomal proteins from different species that are unrelated in structure and function. In the system proposed here, homologous ribosomal proteins ...
07-Feb-2014
The noncanonical alcohol dehydrogenase AlkJ is encoded on the alkane-metabolizing alk operon of the mesophilic bacterium Pseudomonas putida GPo1. To gain insight into the enzymology of AlkJ, we have produced the recombinant protein in Escherichia coli and purified it to homogeneity using His6 tag affinity and size exclusion chromatography (SEC). Despite synthesis ...
06-Feb-2014
Multi-potent adult mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from bone marrow have therapeutic potential for bone diseases and regenerative medicine. However, an intrinsic heterogeneity in their phenotype, which in turn results in various differentiation potentials, makes it difficult to predict the response of these cells. The aim of this study is to investigate ...
06-Feb-2014

ISWI is the catalytic subunit of several ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling factors that catalyse the sliding of nucleosomes along DNA and thereby endow chromatin with structural flexibility. Full activity of ISWI requires residues of a basic patch of amino acids in the N-terminal ‘tail’ of histone H4. Previous studies employing oligopeptides and mononucleosomes ...
05-Feb-2014
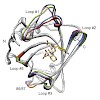
Modern strategies in radio-immuno therapy and in vivo imaging require robust, small, and specific ligand-binding proteins. In this context we have previously developed artificial lipocalins, so-called Anticalins, with high binding activity toward rare-earth metal–chelate complexes using combinatorial protein design. Here we describe further improvement of the ...
05-Feb-2014
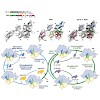
The ribosome and protein synthesis are major targets within the cell for inhibition by antibiotics, such as the tetracyclines. The tetracycline family of antibiotics represent a large and diverse group of compounds, ranging from the naturally produced chlortetracycline, introduced into medical usage in the 1940s, to second and third generation semi-synthetic ...
03-Feb-2014
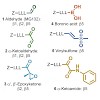
The ubiquitin–proteasome system (UPS) has been successfully targeted by both academia and the pharmaceutical industry for oncological and immunological applications. Typical proteasome inhibitors are based on a peptidic backbone endowed with an electrophilic C-terminus by which they react with the active proteolytic sites. Although the peptide moiety has ...
03-Feb-2014

Impaired olfaction is an early symptom in Parkinson disease (PD), although the exact cause is as yet unknown. Here, we investigated the link between PD-related mutant α-Synuclein (α-SYN) pathology and olfactory deficit, by examining the integration of adult-born neurons in the olfactory bulb (OB) of A30P α-SYN overexpressing mice. To this end, we chose to label ...
01-Feb-2014

Calcium is an important second messenger in eukaryotic cells that regulates many different cellular processes. To elucidate calcium regulation in chloroplasts, we identified the targets of calcium-dependent phosphorylation within the stromal proteome. A 73 kDa protein was identified as one of the most dominant proteins undergoing phosphorylation in a ...
31-Jan-2014
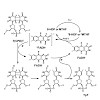
Direct repair of UV-induced DNA lesions represents an elegant method for many organisms to deal with these highly mutagenic and cytotoxic compounds. Although the participating proteins are structurally well investigated, the exact repair mechanism of the photolyase enzymes remains a vivid subject of current research. In this review, we summarize and highlight the ...
31-Jan-2014

Kleine GTPasen fungieren als molekulare Schalter bei der Kontrolle zahlreicher essenzieller zellulärer Prozesse. Während eine fehlerhafte Funktion oder Regulierung von GTPasen in einer Vielzahl von humanen Erkrankungen eine wichtige Rolle spielt, hat es sich als schwierig erwiesen, diese Proteinklasse direkt zu adressieren, da ihre Regulierung und biologische ...
24-Jan-2014
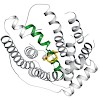
The biosynthesis of terpenes is catalysed by class I and II terpene cyclases. Here we present structural data from a class I hedycaryol synthase in complex with nerolidol, serving as a surrogate for the reaction intermediate nerolidyl diphosphate. This prefolded ligand allows mapping of the active site and hence the identification of a key carbonyl oxygen of ...
23-Jan-2014

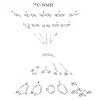
The synthesis of a variety of α-branched trifluoroethyl amines was achieved by reaction of N-aryl hemiaminal ethers with organomagnesium reagents.
23-Jan-2014

An extensive study of error distributions for calculating hydrogen and carbon NMR chemical shifts at Hartree–Fock (HF), density functional theory (DFT), and Møller–Plesset second-order perturbation theory (MP2) levels is presented. Our investigation employs accurate CCSD(T)/cc-pVQZ calculations for providing reference data for 48 hydrogen and 40 carbon nuclei ...
21-Jan-2014
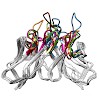
Antibodies, which can recognize a plethora of possible antigens, have been considered as a paradigm of protein engineering performed by nature itself. Lipocalins constitute a distinct family of proteins with functions in ligand binding and transport that occur in many organisms, including man. Like antibodies, lipocalins exhibit a structurally conserved framework ...
20-Jan-2014
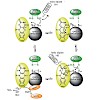
Nature provides a rich source of compounds with diverse chemical structures and biological activities, among them, sulfur-containing metabolites from bacteria and fungi. Some of these compounds bear a disulfide moiety that is indispensable for their bioactivity. Specialized oxidoreductases such as GliT, HlmI, and DepH catalyze the formation of this disulfide ...
20-Jan-2014
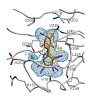
The enzymes of the non-mevalonate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis have been identified as attractive targets with novel modes of action for the development of herbicides for crop protection and agents against infectious diseases. This pathway is present in many pathogenic organisms and plants, but absent in mammals. By using high-throughput screening, we ...
16-Jan-2014
Recent advances in mass spectrometry-based chemical proteomics allow unbiased analysis of drug-target interactions under close to physiological conditions. In this study, we designed and synthesized two small molecule probes targeting fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs) and applied them to evaluate the selectivity profiles of the FGFR inhibitors Dovitinib ...
16-Jan-2014

Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) are responsible for the robust and immediate production of type I IFNs during viral infection. pDCs employ TLR7 and TLR9 to detect RNA and CpG motifs present in microbial genomes. CpG-A was the first synthetic stimulus available that induced large amounts of IFN-α (type I IFN) in pDCs. CpG-B, however, only weakly activates pDCs ...
14-Jan-2014
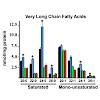
The circadian clock regulates a wide range of physiological and metabolic processes, and its disruption leads to metabolic disorders such as diabetes and obesity. Accumulating evidence reveals that the circadian clock regulates levels of metabolites that, in turn, may regulate the clock. Here we demonstrate that the circadian clock regulates the intracellular ...
12-Jan-2014

At the 3′ ends of protein-coding genes, RNA polymerase (Pol) II is dephosphorylated at tyrosine residues (Tyr1) of its C-terminal domain (CTD). In addition, the associated cleavage-and-polyadenylation factor (CPF) cleaves the transcript and adds a poly(a) tail. Whether these events are coordinated and how they lead to transcription termination remains poorly ...
10-Jan-2014
The ribosome is one of the main antibiotic targets in the bacterial cell. Crystal structures of naturally produced antibiotics and their semi-synthetic derivatives bound to ribosomal particles have provided unparalleled insight into their mechanisms of action, and they are also facilitating the design of more effective antibiotics for targeting ...
09-Jan-2014
The coordination of signal transduction and substrate transport represents a sophisticated way to integrate information on metabolite fluxes into transcriptional regulation. This widely distributed process involves protein-protein interactions between two integral membrane proteins. Here we report new insights into the molecular mechanism of the regulatory ...
07-Jan-2014
Despite their structural similarity, the natural products omuralide and vibralactone have different biological targets. While omuralide blocks the chymotryptic activity of the proteasome with an IC50 value of 47 nM, vibralactone does not have any effect at this protease up to a concentration of 1 mM. Activity-based protein profiling in HeLa cells revealed that ...
07-Jan-2014
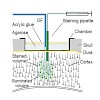
Brain mapping experiments involving electrical microstimulation indicate that the primary motor cortex (M1) directly regulates muscle contraction and thereby controls specific movements. Possibly, M1 contains a small circuit “map” of the body that is formed by discrete local networks that code for specific movements. Alternatively, movements may be controlled by ...
07-Jan-2014
Die photochemischen Eigenschaften des Indigo, eines weit verbreiteten industriellen Produkts, haben von Anfang an das Interesse von Wissenschaftlern geweckt. Die Photostabilität von Indigo war Gegenstand intensiver Forschungen. In neuerer Zeit wurde vorgeschlagen, dass nach Photoanregung ein intramolekularer Protonentransfer auftritt, der gefolgt von einem ...
06-Jan-2014
The mitochondrial genome is transcribed by a single-subunit T7 phage-like RNA polymerase (mtRNAP), structurally unrelated to cellular RNAPs. In higher eukaryotes, mtRNAP requires two transcription factors for efficient initiation—TFAM, a major nucleoid protein, and TFB2M, a transient component of mtRNAP catalytic site. The mechanisms behind assembly of the ...
03-Jan-2014
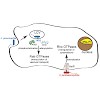
Pathogenic bacteria have developed a variety of mechanisms with which to manipulate the functions of proteins in important cellular pathways of host organisms. Because of their pivotal role in the regulation of cell physiology, members of the family of G-proteins and cytoskeletal proteins are frequent targets for pathogens. They are modified both by noncovalent ...
03-Jan-2014
A 5-formyl-2’-deoxycytidine (fdC) phosphoramidite building block that enables the synthesis of fdC-containing DNA with excellent purity and yield has been developed. In combination with phosphoramidites for 5-methyl-dC, 5-hydroxymethyl-dC, and carboxy-dC, it was possible to prepare a segment of the OCT-4 promoter that contains all four epigenetic bases. Because ...
02-Jan-2014

Peptides have the specificity and size required to target the protein–protein interactions involved in many diseases. Some cyclic peptides have been utilised as scaffolds for peptide drugs because of their stability; however, other cyclic peptide scaffolds remain to be explored. θ-Defensins are cyclic peptides from mammals; they are characterised by a cyclic ...
01-Jan-2014

In eukaryotic cells, the ubiquitin–proteasome-system (UPS) is responsible for the non-lysosomal degradation of proteins and plays a pivotal role in such vital processes as protein homeostasis, antigen processing or cell proliferation. Therefore, it is an attractive drug target with various applications in cancer and immunosuppressive therapies. Being an ...










