Research Area B - Publications 2013
31-Oct-2013
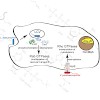
Pathogenic bacteria have developed a variety of mechanisms with which to manipulate the functions of proteins in important cellular pathways of host organisms. Because of their pivotal role in the regulation of cell physiology, members of the family of G-proteins and cytoskeletal proteins are frequent targets for pathogens.
18-Oct-2013
Journal of Biological Chemistry, online article
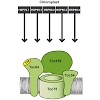
The three tetratricopeptide repeat domain-containing docking proteins Toc64, OM64, and AtTPR7 reside in the chloroplast, mitochondrion, and endoplasmic reticulum of Arabidopsis thaliana, respectively. They are suggested to act during post-translational protein import by association with chaperone-bound preprotein complexes. Here, we performed a detailed ...
09-Oct-2013
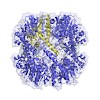
Over 100 protease inhibitors are currently used in the clinics, and most of them use blockage of the active site for their mode of inhibition. Among the protease drug targets are several enzymes for which the correct multimeric assembly is crucial to their activity, such as the proteasome and the HIV protease. Here, we present a novel mechanism of protease ...
01-Oct-2013
PNAS, online article
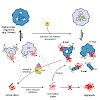
The small heat shock protein αB-crystallin is an oligomeric molecular chaperone that binds aggregation-prone proteins. As a component of the proteostasis system, it is associated with cataract, neurodegenerative diseases, and myopathies. The structural determinants for the regulation of its chaperone function are still largely elusive. Combining different ...
26-Sep-2013

Small G-proteins of the Ras superfamily control the temporal and spatial coordination of intracellular signaling networks by acting as molecular on/off switches. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) regulate the activation of these G-proteins through catalytic replacement of GDP by GTP. During nucleotide exchange, three distinct substrate·enzyme complexes ...
19-Sep-2013

The causative agent of Legionnaires' disease, Legionella pneumophila, uses the Icm/Dot type IV secretion system (T4SS) to form in phagocytes a distinct “Legionella-containing vacuole” (LCV), which intercepts endosomal and secretory vesicle trafficking. Proteomics revealed the presence of the small GTPase Ran and its effector RanBP1 on purified LCVs. Here we ...
13-Sep-2013
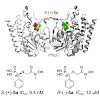
The emergence and spread of multidrug-resistant pathogens are widely believed to endanger human health. New drug targets and lead compounds exempt from cross-resistance with existing drugs are urgently needed. We report on the synthesis and properties of “reverse” thia analogs of fosmidomycin, which inhibit the first committed enzyme of a metabolic pathway that ...
12-Sep-2013
Cell, online article

INO80/SWR1 family chromatin remodelers are complexes composed of >15 subunits and molecular masses exceeding 1 MDa. Their important role in transcription and genome maintenance is exchanging the histone variants H2A and H2A.Z. We report the architecture of S. cerevisiae INO80 using an integrative approach of electron microscopy, crosslinking and mass ...
10-Sep-2013
J. Am. Chem. Soc., online article

The CH3 homodimer at the C-terminal end of the antibody heavy chain is the key noncovalent interaction stabilizing antibody proteins. Here, we use single-molecule force spectroscopy to investigate the dissociation mechanics of CH3 as a proxy for antibody mechanical stability. We find the CH3 homodimer to be a highly stable complex, and its dissociation force of ...
26-Aug-2013
Plants, online article
Calcium plays an important role in the regulation of several chloroplast processes. However, very little is still understood about the calcium fluxes or calcium-binding proteins present in plastids. Indeed, classical EF-hand containing calcium-binding proteins appears to be mostly absent from plastids. In the present study we analyzed the stroma fraction of ...
14-Aug-2013
Plant Molecular Biology, online article
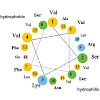
Matrix enzymes are imported into peroxisomes and glyoxysomes, a subclass of peroxisomes involved in lipid mobilization. Two peroxisomal targeting signals (PTS), the C-terminal PTS1 and the N-terminal PTS2, mediate the translocation of proteins into the organelle. PTS2 processing upon import is conserved in higher eukaryotes, and in watermelon the glyoxysomal ...
13-Aug-2013
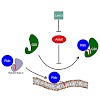
Membrane trafficking is regulated by small Ras-like GDP/GTP binding proteins of the Rab subfamily (Rab GTPases) that cycle between membranes and cytosol depending on their nucleotide state. The GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) solubilizes prenylated Rab GTPases from and shuttles them between membranes in the form of a soluble cytosolic complex. We use attenuated ...
05-Aug-2013
Curr Top Microbiol Immunol., online article

The pathogenic bacterium Legionella pneumophila interacts intimately with signaling molecules during the infection of eukaryotic host cells. Among a diverse set of regulatory molecules, host small GTPases appear to be prominent and significant targets. Small GTPases are molecular switches that regulate cellular signaling via their respective nucleotide-bound ...
09-Jul-2013

Caseinolytic proteases (ClpPs) are large oligomeric protein complexes that contribute to cell homeostasis as well as virulence regulation in bacteria. Although most organisms possess a single ClpP protein, some organisms encode two or more ClpP isoforms. Here, we elucidated the crystal structures of ClpP1 and ClpP2 from pathogenic Listeria monocytogenes and ...
01-Jul-2013
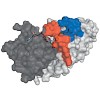
The final step in the biosynthesis of the 22nd genetically encoded amino acid, pyrrolysine, is catalyzed by PylD, a structurally and mechanistically unique dehydrogenase. This catalyzed reaction includes an induced-fit mechanism achieved by major structural rearrangements of the N-terminal helix upon substrate binding. Different steps of the reaction trajectory ...
30-Jun-2013
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
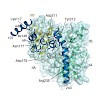
The Hsp70-interacting protein, Hip, cooperates with the chaperone Hsp70 in protein folding and prevention of aggregation. Hsp70 interacts with non-native protein substrates in an ATP-dependent reaction cycle regulated by J-domain proteins and nucleotide exchange factors (NEFs). Hip is thought to delay substrate release by slowing ADP dissociation from Hsp70. Here ...
18-Jun-2013
PNAS, online article

IgM is the first antibody produced during the humoral immune response. Despite its fundamental role in the immune system, IgM is structurally only poorly described. In this work we used X-ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy to determine the atomic structures of the constant IgM Fc domains (Cµ2, Cµ3, and Cµ4) and to address their roles in IgM oligomerization. ...
01-May-2013

Protein synthesis in all cells is carried out by macromolecular machines called ribosomes. Although the structures of prokaryotic, yeast and protist ribosomes have been determined, the more complex molecular architecture of metazoan 80S ribosomes has so far remained elusive. Here we present structures of Drosophila melanogaster and Homo sapiens 80S ribosomes in ...
29-Mar-2013
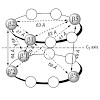
Noncovalent proteasome inhibitors introduce an alternative mechanism of inhibition to that of covalent inhibitors used in cancer therapy. Starting from a noncovalent linear mimic of TMC-95A, a series of dimerized inhibitors using polyaminohexanoic acid spacers has been designed and optimized to target simultaneously two of the six active sites of the eukaryotic ...
29-Mar-2013
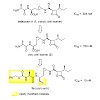
The natural product belactosin A (1) with a trans-cyclopropane structure is a useful prototype compound for developing potent proteasome (core particle, CP) inhibitors. To date, 1 and its analogues are the only CP ligands that bind to both the nonprimed S1 pocket as well as the primed substrate binding channel; however, these molecules harbor a high IC50 value of ...
18-Mar-2013

The heat shock protein (Hsp)90 chaperone machinery regulates the activity of hundreds of client proteins in the eukaryotic cytosol. It undergoes large conformational changes between states that are similar in energy. These transitions are rate-limiting for the ATPase cycle. It has become evident that several of the many Hsp90 co-chaperones affect the ...
11-Feb-2013

The iron–sulfur protein IspH catalyzes a key step in isoprenoid biosynthesis in bacteria and malaria parasites. Crystal structures of IspH complexed with three substrate analogues reveal their mode of binding and suggest new routes to inhibitor design.
10-Feb-2013
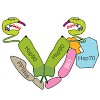
Heat-shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is an ATP-dependent molecular chaperone that associates dynamically with various co-chaperones during its chaperone cycle. Here we analyzed the role of the activating co-chaperone Aha1 in the progression of the yeast Hsp90 chaperone cycle and identified a critical ternary Hsp90 complex containing the co-chaperones Aha1 and Cpr6. Aha1 ...
08-Feb-2013
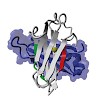
Hsp70s are molecular chaperones involved in the folding and assembly of proteins. They recognize hydrophobic amino acid stretches in their substrate binding groove. However, a detailed understanding of substrate specificity is still missing. Here, we use the endoplasmic reticulum-resident Hsp70 BiP to identify binding sites in a natural client protein. Two sites ...
04-Feb-2013
JCB, online article

Eukaryotic cells critically depend on the correct regulation of intracellular vesicular trafficking to transport biological material. The Rab subfamily of small guanosine triphosphatases controls these processes by acting as a molecular on/off switch. To fulfill their function, active Rab proteins need to localize to intracellular membranes via ...
25-Jan-2013
Plos, online article

DEAF-1 is an important transcriptional regulator that is required for embryonic development and is linked to clinical depression and suicidal behavior in humans. It comprises various structural domains, including a SAND domain that mediates DNA binding and a MYND domain, a cysteine-rich module organized in a Cys4-Cys2-His-Cys (C4-C2HC) tandem zinc binding motif. ...
15-Jan-2013
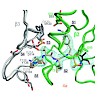
Proteasomes degrade the majority of proteins in mammalian cells by a concerted action of three distinct pairs of active sites. The chymotrypsin-like sites are targets of antimyeloma agents bortezomib and carfilzomib. Inhibitors of the trypsin-like site sensitize multiple myeloma cells to these agents. Here we describe systematic effort to develop inhibitors with ...
09-Jan-2013
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article
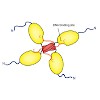
The tumor suppressor protein p53 is often referred to as the guardian of the genome. In the past, controversial findings have been presented for the role of the C-terminal regulatory domain (RD) of p53 as both a negative regulator and a positive regulator of p53 activity. However, the underlying mechanism remained enigmatic. To understand the function of the RD ...
04-Jan-2013
EMBO reports, online article
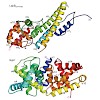
Legionella pneumophila is an intracellularly surviving pathogen that releases about 270 different proteins into the host cell during infection. A set of secreted proteins takes control of the vesicular trafficking regulator Rab1. Legionella LepB inactivates Rab1 by acting as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP). We present the crystal structure of the Rab1b:LepB ...










