Research Area B - Publications 2016
09-Dec-2016
Protoplasma, DOI 10.1007/s00709-016-1057-9
Protoplasma, online article

Here, we describe the development of chloroplasts and the buildup of the thylakoid membranes in growing Arabidopsis leaves. Organelles were analyzed from three distinct positions, namely, at the tip, the upper leaf margin, and the base from leaves 1, 3, 5, and 7 of 14-day-old plants. Clear developmental gradients are described within a given leaf and between ...
09-Dec-2016
Plant Mol Biol, DOI 10.1007/s11103-016-0566-4
Plant Mol Biol, online article
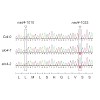
Pentatricopeptide repeat (PPR) proteins constitute a large protein family in flowering plants and are thought to be mostly involved in organellar RNA metabolism. The subgroup of PLS-type PPR proteins were found to be the main specificity factors of cytidine to uridine RNA editing. Identifying the targets of PLS-type PPR proteins can help in elucidating the ...
08-Dec-2016
BBA, Volume 1860, Issue 5, Pages 560-570, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.11.008
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, online article

Background
The CCAAT binding complex (CBC), consisting of a heterotrimeric core structure, is highly conserved in eukaryotes and constitutes an important general transcriptional regulator.
Scope of the review.
In this review we discuss the scientific history and the current state of knowledge of the multiple gene regulatory functions, protein motifs and structure ...
01-Dec-2016
Nature, volume 541, pages 546–549, doi:10.1038/nature20821
Nature, online article

In bacteria, ribosomes stalled on truncated mRNAs that lack a stop codon are rescued by the transfer-messenger RNA (tmRNA), alternative rescue factor A (ArfA) or ArfB systems1. Although tmRNA–ribosome and ArfB–ribosome structures have been determined2,3,4,5,6,7, how ArfA recognizes the presence of truncated mRNAs and recruits the canonical termination release ...
01-Dec-2016
Nature, doi:10.1038/nature20821
Nature, online article
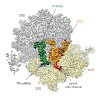
In bacteria, ribosomes stalled on truncated mRNAs lacking a stop codon are rescued by either the transfer-messenger RNA (tmRNA), alternative rescue factor A (ArfA) or ArfB rescue systems1. While tmRNA- and ArfB-ribosome structures have been elucidated2–7, structural insight into how ArfA recognizes the presence of truncated mRNAs and recruits the canonical ...
30-Nov-2016
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY, VOL. 292, NO. 2, pp. 672–684, DOI 10.1074/jbc.M116.760413
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY, online article
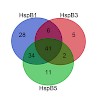
Small heat shock proteins (sHsps) are a ubiquitous family of molecular chaperones that suppress the unspecific aggregation of miscellaneous proteins. Multicellular organisms contain a large number of different sHsps, raising questions as to whether they function redundantly or are specialized in terms of substrates and mechanism. To gain insight into this issue, ...
21-Nov-2016
Nature Methods, doi:10.1038/nmeth.4079
Nature Methods, online article
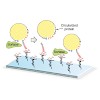
We engineered covalently circularized nanodiscs (cNDs) which, compared with standard nanodiscs, exhibit enhanced stability, defined diameter sizes and tunable shapes. Reconstitution into cNDs enhanced the quality of nuclear magnetic resonance spectra for both VDAC-1, a β-barrel membrane protein, and the G-protein-coupled receptor NTR1, an α-helical membrane ...
27-Oct-2016
Plant Physiology, vol. 172, no. 4, 2471-2490, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.01519
Plant Physiology, online article
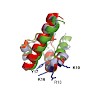
A variety of eukaryotes, in particular plants, do not contain the required number of tRNAs to support the translation of mitochondria-encoded genes and thus need to import tRNAs from the cytosol. This study identified two Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) proteins, Tric1 and Tric2 (for tRNA import component), which on simultaneous inactivation by T-DNA insertion ...
27-Oct-2016
Molecular Cell, Volume 64, Issue 4, p688–703, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.031
Molecular Cell, online article

Covalent DNA-protein crosslinks (DPCs) are toxic DNA lesions that interfere with essential chromatin transactions, such as replication and transcription. Little was known about DPC-specific repair mechanisms until the recent identification of a DPC-processing protease in yeast. The existence of a DPC protease in higher eukaryotes is inferred from data in Xenopus ...
A humanized yeast proteasome identifies unique binding modes of inhibitors for the immunosubunit β5i
27-Oct-2016
The EMBO Journal e201695222 (2016), Volume 35, Issue 23, DOI 10.15252/embj.201695222
The EMBO Journal, online article
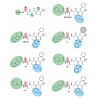
Inhibition of the immunoproteasome subunit β5i alleviates autoimmune diseases in preclinical studies and represents a promising new anti‐inflammatory therapy. However, the lack of structural data on the human immunoproteasome still hampers drug design. Here, we systematically determined the potency of seven α' β' epoxyketone inhibitors with varying N‐caps and ...
26-Oct-2016
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 55, 1 – 7, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201607338
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article

Gram-negative bacteria represent a challenging task for antibacterial drug discovery owing to their impermeable cell membrane and restricted uptake of small molecules. We herein describe the synthesis of natural-product-derived epoxycyclohexenones and explore their antibiotic activity against several pathogenic bacteria. A compound with activity against ...
22-Oct-2016
Molecular Plant, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.10.012
Molecular Plant, online article

Protein import into chloroplasts is an essential process for plant survival. Numerous studies in recent years have revealed many facts about the components involved and mechanistic features, but have also turned up some controversies. Especially the composition and function of the Tic (translocon at the inner envelope of chloroplasts) complex(es) are vividly ...
10-Oct-2016
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 23, 1020–1028, doi:10.1038/nsmb.3305
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
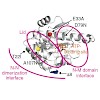
Hsp90 couples ATP hydrolysis to large conformational changes essential for activation of client proteins. The structural transitions involve dimerization of the N-terminal domains and formation of 'closed states' involving the N-terminal and middle domains. Here, we used Hsp90 mutants that modulate ATPase activity and biological function as probes to address the ...
22-Sep-2016
ChemBioChem, Volume 17, Issue 21, Pages 2028–2032, DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201600417
ChemBioChem, online article
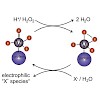
Vanadium-dependent haloperoxidases (VHPOs) are a class of halogenating enzymes found in fungi, lichen, algae, and bacteria. We report the cloning, purification, and characterization of a functional VHPO from the cyanobacterium Acaryochloris marina (AmVHPO), including its structure determination by X-ray crystallography. Compared to other VHPOs, the AmVHPO ...
22-Sep-2016
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., Volume 55, Issue 42, Pages 13330–13334, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201605753
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article

Electrophiles are commonly used for the inhibition of proteases. Notably, inhibitors of the proteasome, a central determinant of cellular survival and a target of several FDA-approved drugs, are mainly characterized by the reactivity of their electrophilic head groups. We aimed to tune the inhibitory strength of peptidic sulfonate esters by varying the leaving ...
20-Sep-2016
Journal of Molecular Biology, Volume 428, Issue 22, Pages 4559–4571, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2016.09.014
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article
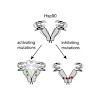
Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is an ATP-dependent molecular chaperone responsible for the activation, maturation, and trafficking of several hundred client proteins in the cell. It is well known that (but not understood how) residues far away from Hsp90's nucleotide binding pocket can regulate its ATPase activity, a phenomenon called allosteric regulation. Here, ...
09-Sep-2016
Journal of Molecular Biology, Volume 428, Issue 20, Pages 4185–4196, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2016.09.002
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article

The molecular chaperone Hsp90 and its cofactor Cdc37 are required for the stability of protein kinases in the cellular environment. Upon pharmacological inhibition of Hsp90, the Hsp90-dependent kinases are degraded quickly by the proteasome. Clear physiological evidence for the formation of heterooligomeric complexes between the chaperone system and its kinase ...
08-Sep-2016
Journal of Cell Science, 129, 3935-3947, doi:10.1242/jcs.190975
Journal of Cell Science, online article

Twin-arginine translocation pathways have been well characterized in bacteria and chloroplasts. However, genes encoding for a TatC protein are found in almost all plant mitochondrial genomes. For the first time it could be demonstrated that this mitochondrial encoded TatC is a functional gene which is translated into a protein in the model plant Arabidopsis ...
19-Aug-2016
The Plant Cell, vol. 28, no. 9, 2238-2260, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00491
The Plant Cell, online article
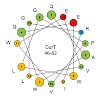
Photosynthesis occurs in thylakoids, a highly specialized membrane system. In the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp PCC 6803 (hereafter Synechocystis 6803), the thylakoids are arranged parallel to the plasma membrane and occasionally converge toward it to form biogenesis centers. The initial steps in PSII assembly are thought to take place in these regions, which ...
18-Aug-2016
Molecular Cell, 63, 1–14, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.07.012
Molecular Cell, online article
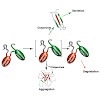
Protein maturation in the endoplasmic reticulum is controlled by multiple chaperones, but how they recognize and determine the fate of their clients remains unclear. We developed an in vivo peptide library covering substrates of the ER Hsp70 system: BiP, Grp170, and three of BiP’s DnaJ-family co-factors (ERdj3, ERdj4, and ERdj5). In vivo binding studies revealed ...
20-Jul-2016
J. Med. Chem., 59 (15), pp 7177–7187, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00705
J. Med. Chem., online article
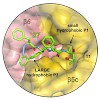
This work reports the development of highly potent and selective inhibitors of the β5c catalytic activity of human constitutive proteasomes. The work describes the design principles, large hydrophobic P3 residue and small hydrophobic P1 residue, that led to the synthesis of a panel of peptide epoxyketones; their evaluation and the selection of the most promising ...
13-Jul-2016
Proteins, Volume 84, Issue 10, Pages 1390–1407, DOI: 10.1002/prot.25084
Proteins, online article

Substrate binding to Hsp70 chaperones is involved in many biological processes, and the identification of potential substrates is important for a comprehensive understanding of these events. We present a multi-scale pipeline for an accurate, yet efficient prediction of peptides binding to the Hsp70 chaperone BiP by combining sequence-based prediction with ...
06-Jul-2016
Nature Communications, 7, Article number: 12026, doi:10.1038/ncomms12026
Nature Communications, online article
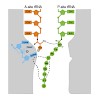
Nascent polypeptides can induce ribosome stalling, regulating downstream genes. Stalling of ErmBL peptide translation in the presence of the macrolide antibiotic erythromycin leads to resistance in Streptococcus sanguis. To reveal this stalling mechanism we obtained 3.6-Å-resolution cryo-EM structures of ErmBL-stalled ribosomes with erythromycin. The nascent ...
01-Jul-2016
Science, Vol. 353, Issue 6294, DOI: 10.1126/science.aac4354
Science, online article
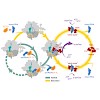
Proteins are synthesized on ribosomes as linear chains of amino acids and must fold into unique three-dimensional structures to fulfill their biological functions. Protein folding is intrinsically error-prone, and how it is accomplished efficiently represents a problem of great biological and medical importance. During folding, the nascent polypeptide must ...
23-Jun-2016
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY, VOL. 291, NO. 34, pp. 17848–17860, DOI 10.1074/jbc.M115.712398
JBC, online article
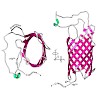
Chloroplasts and mitochondria are unique endosymbiotic cellular organelles surrounded by two membranes. Essential metabolic networking between these compartments and their hosting cells requires the exchange of a large number of biochemical pathway intermediates in a directed and coordinated fashion across their inner and outer envelope membranes. Here we ...
25-May-2016
Nucleic Acids Research,1, doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw470
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
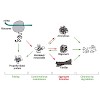
Under stress conditions, such as nutrient starvation, deacylated tRNAs bound within the ribosomal A-site are recognized by the stringent factor RelA, which converts ATP and GTP/GDP to (p)ppGpp. The signaling molecules (p)ppGpp globally rewire the cellular transcriptional program and general metabolism, leading to stress adaptation. Despite the additional ...
30-Apr-2016
Molecular Plant, Volume 9, Issue 6, p798–812, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.04.014
Molecular Plant, online article
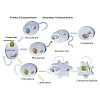
Protein import into chloroplasts has been a focus of research for several decades. The first publications dealing with this fascinating topic appeared in the 1970s. From the initial realization that many plastid proteins are being encoded for in the nucleus and require transport into their target organelle to the identification of import components in the ...
21-Apr-2016
Microbial Cell, Vol. 3, No. 6, pp. 236 - 247; DOI: 10.15698/mic2016.06.505
Microbial Cell, online article

DNA-Microarrays are powerful tools to obtain expression data on the genome-wide scale. We performed microarray experiments to elucidate the transcriptional networks, which are up- or down-regulated in response to the expression of toxic polyglutamine proteins in yeast. Such experiments initially generate hit lists containing differentially expressed genes. To ...
15-Apr-2016
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6370–6372, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201602519
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., online article

One life, two strategies: Crucial structural differences between the human and the Plasmodium falciparum proteasomes were recently identified. A combination of cryo-EM and functional characterization enabled the design of a selective antimalarial proteasome inhibitor that shows low toxicity in the host. When used with artemisinin, this ligand offers a new ...
29-Mar-2016
J. Exp. Bot., doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw101

Calmodulins (CaMs) are important mediators of Ca2+ signals that are found ubiquitously in all eukaryotic organisms. Plants contain a unique family of calmodulin-like proteins (CMLs) that exhibit greater sequence variance compared to canonical CaMs. The Arabidopsis thaliana proteins AtCML4 and AtCML5 are members of CML subfamily VII and possess a CaM domain ...
11-Mar-2016
Nature Communications, 7, Article number: 10900, doi:10.1038/ncomms10900
Nature Communications, online article

Biogenesis of the 20S proteasome is tightly regulated. The N-terminal propeptides protecting the active-site threonines are autocatalytically released only on completion of assembly. However, the trigger for the self-activation and the reason for the strict conservation of threonine as the active site nucleophile remain enigmatic. Here we use mutagenesis, X-ray ...
11-Mar-2016
Molecular Plant, Volume 9, Issue 6, p885–899, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2016.03.002
Molecular Plant, online article

ATP synthases in chloroplasts (cpATPase) and mitochondria (mtATPase) are responsible for ATP production during photosynthesis and oxidative phosphorylation, respectively. Both enzymes consist of two multisubunit complexes, the membrane-bound coupling factor O and the soluble coupling factor 1. During cpATPase biosynthesis, several accessory factors facilitate ...
29-Feb-2016
Nature, 531, 191–195, doi:10.1038/nature16973
Nature, online article
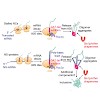
Translation of messenger RNAs lacking a stop codon results in the addition of a carboxy-terminal poly-lysine tract to the nascent polypeptide, causing ribosome stalling. Non-stop proteins and other stalled nascent chains are recognized by the ribosome quality control (RQC) machinery and targeted for proteasomal degradation. Failure of this process leads to ...
07-Feb-2016
Current Opinion in Structural Biology, Volume 37, Pages 123–133, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2016.01.008
Current Opinion in Structural Biology, online article

As the nascent polypeptide chain is being synthesized, it passes through a tunnel within the large ribosomal subunit. Interaction between the nascent polypeptide chain and the ribosomal tunnel can modulate the translation rate and induce translational stalling to regulate gene expression. In this article, we highlight recent structural insights into how the ...
02-Feb-2016
PNAS, vol. 113, no. 5, 1232–1237, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1518827113
PNAS, online article
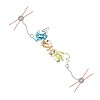
Folding of small proteins often occurs in a two-state manner and is well understood both experimentally and theoretically. However, many proteins are much larger and often populate misfolded states, complicating their folding process significantly. Here we study the complete folding and assembly process of the 1,418 amino acid, dimeric chaperone Hsp90 using ...
29-Jan-2016
Journal of Molecular Biology, Volume 428, Issue 6, Pages 1315–1332, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2016.01.015
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article

The aggregation of mostly antibody light chain variable (VL) domains into amyloid fibrils in various tissues is the main cause of death in systemic amyloid light chain amyloidosis. Point mutations within the domain are important to shift the VL into the fibrillar pathway, but why and how only some site-specific mutations achieve this still remains elusive. We ...
25-Jan-2016
ACS Chem. Biol., 2016, 11 (4), pp 1082–1089, DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00905
ACS Chem. Biol., online article
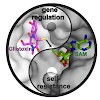
The epipolythiodioxopiperazine (ETP) gliotoxin mediates toxicity via its reactive thiol groups and thereby contributes to virulence of the human pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Self-intoxication of the mold is prevented either by reversible oxidation of reduced gliotoxin or by irreversible conversion to bis(methylthio)gliotoxin. The latter is produced by ...
04-Jan-2016
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA), Volume 1860, Issue 1, Part B, Pages 149–166, doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.06.008

Background
The two α-crystallins (αA- and αB-crystallin) are major components of our eye lenses. Their key function there is to preserve lens transparency which is a challenging task as the protein turnover in the lens is low necessitating the stability and longevity of the constituent proteins. α-Crystallins are members of the small heat shock protein family. ...
02-Jan-2016
That is pretty cool: „The vast majority of the proteasome core structures added to the wwPDB archive in 2015 were from CIPSM investigator Michael Groll’s group.“










