Research Area B - Publications 2018
08-Nov-2018
J Mol Biol (2018) 430, 4925–4940, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2018.10.024
JMB, online article

The antibody light chain (LC) consists of two domains and is essential for antigen binding in mature immunoglobulins. The two domains are connected by a highly conserved linker that comprises the structurally important Arg108 residue. In antibody light chain (AL) amyloidosis, a severe protein amyloid disease, the LC and its N-terminal variable domain (VL) convert ...
26-Oct-2018
PNAS, vol. 115, no. 46, 11688–11693, www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1807618115
PNAS, online article

The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is a prominent nuclear receptor linked to a variety of diseases and an important drug target. Binding of hormone to its ligand binding domain (GR-LBD) is the key activation step to induce signaling. This process is tightly regulated by the molecular chaperones Hsp70 and Hsp90 in vivo. Despite its importance, little is known about ...
18-Sep-2018
J. Biol. Chem. (2018) 293(44) 17107–17118, DOI 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005475
J. Biol. Chem., online article

Despite their importance for antibody architecture and design, the principles governing antibody domain stability are still not understood in sufficient detail. Here, to address this question, we chose a domain from the invariant part of IgG, the CH2 domain. We found that compared with other Ig domains, the isolated CH2 domain is a surprisingly unstable monomer, ...
04-May-2018
Nature Communications, volume 9, Article number: 1806 (2018), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04139-2
Nature Communications, online article

Pore-forming toxins (PFT) are virulence factors that transform from soluble to membrane-bound states. The Yersinia YaxAB system represents a family of binary α-PFTs with orthologues in human, insect, and plant pathogens, with unknown structures. YaxAB was shown to be cytotoxic and likely involved in pathogenesis, though the molecular basis for its two-component ...
16-Apr-2018
Nature Communications, volume 9, Article number: 1472, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-03946-x
Nature Communications, online article
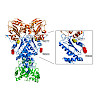
Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is a dimeric molecular chaperone that undergoes large conformational changes during its functional cycle. It has been established that conformational switch points exist in the N-terminal (Hsp90-N) and C-terminal (Hsp90-C) domains of Hsp90, however information for switch points in the large middle-domain (Hsp90-M) is scarce. Here we ...
16-Apr-2018
Nature Communications, volume 9, Article number: 1472 (2018), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03946-x
Nature Communications, online article

Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is a dimeric molecular chaperone that undergoes large conformational changes during its functional cycle. It has been established that conformational switch points exist in the N-terminal (Hsp90-N) and C-terminal (Hsp90-C) domains of Hsp90, however information for switch points in the large middle-domain (Hsp90-M) is scarce. Here we ...
13-Apr-2018
Science, 360, 215–219, DOI: 10.1126/science.aar7899
Science, online article
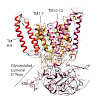
Protein synthesis, transport and N-glycosylation are coupled at the mammalian endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by complex formation between the ribosome, the Sec61 protein-conducting channel and the oligosaccharyltransferase (OST). Here, we used different cryo-electron microscopy approaches to determine structures of native and solubilized ribosome-Sec61-OST complexes. ...
13-Apr-2018
Scientific Reports, volume 8, Article number: 5975 (2018), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-24199-0
Scientific Reports, online aticle

By N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU) mutagenesis, we generated the mutant mouse line TUB6 that is characterised by severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) and systemic sterile autoinflammation in homozygotes, and a selective T cell defect in heterozygotes. The causative missense point mutation results in the single amino acid exchange G170W in multicatalytic ...
21-Mar-2018
Nature Communications, volume 9, Article number: 1168 (2018), DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-03442-2
Nature Communications, online article
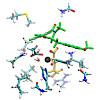
The recently discovered FeII/α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase AsqJ from Aspergillus nidulans stereoselectively catalyzes a multistep synthesis of quinolone alkaloids, natural products with significant biomedical applications. To probe molecular mechanisms of this elusive catalytic process, we combine here multi-scale quantum and classical molecular ...
27-Feb-2018
Essays In Biochemistry, 62(1) 65-75; DOI: 10.1042/EBC20170093
Essays In Biochemistry, online article

Import of preproteins into chloroplasts is an essential process, requiring two major multisubunit protein complexes that are embedded in the outer and inner chloroplast envelope membrane. Both the translocon of the outer chloroplast membrane (Toc), as well as the translocon of the inner chloroplast membrane (Tic) have been studied intensively with respect to ...
24-Feb-2018
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19(2), 641; doi:10.3390/ijms19020641
Int. J. Mol. Sci., online article

During the biogenesis of the mitochondrial inner membrane, most nuclear-encoded inner membrane proteins are laterally released into the membrane by the TIM23 and the TIM22 machinery during their import into mitochondria. A subset of nuclear-encoded mitochondrial inner membrane proteins and all the mitochondrial-encoded inner membrane proteins use the Oxa ...
24-Feb-2018
JMB, Volume 430, Issue 5, Pages 628-640, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2018.01.004
JMB, online article
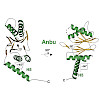
The 20S proteasome is a key player in eukaryotic and archaeal protein degradation, but its progenitor in eubacteria is unknown. Recently, the ancestral β-subunit protein (Anbu) was predicted to be the evolutionary precursor of the proteasome. We crystallized Anbu from Hyphomicrobium sp. strain MC1 in four different space groups and solved the structures by ...
31-Jan-2018
Mitochondrion, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2018.01.005
Mitochondrion, online ablage
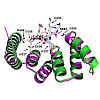
Mitochondrial localized proteins are mostly synthesized in the cytosol and translocated across the outer mitochondrial membrane via the translocase of the outer membrane (TOM) complex. Although the channel protein is conserved among eukaryotes, the receptor proteins are more divergent and show features specific to the plant lineage. OM64, which is a paralogue of ...
03-Jan-2018
Nature Communications, volume 9, Article number: 44 (2018), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02110-1
Nature Communications, online article

Salmonella infections require the delivery of bacterial effectors into the host cell that alter the regulation of host defense mechanisms. The secreted cysteine protease GtgE from S. Typhimurium manipulates vesicular trafficking by modifying the Rab32 subfamily via cleaving the regulatory switch I region. Here we present a comprehensive biochemical, structural, ...
01-Jan-1970
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, volume 25, 90–100 (2018), doi:10.1038/s41594-017-0012-6
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article

BiP is the endoplasmic member of the Hsp70 family. BiP is regulated by several co-chaperones including the nucleotide-exchange factor (NEF) Bap (Sil1 in yeast). Bap is a two-domain protein. The interaction of the Bap C-terminal domain with the BiP ATPase domain is sufficient for its weak NEF activity. However, stimulation of the BiP ATPase activity requires ...










