Research Area C - Publications 2017
21-Dec-2017
J. Cell Biol., Vol. 217, No. 2, 745–762, https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201709092
J. Cell Biol., online article
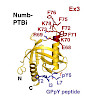
Numb functions as an oncosuppressor by inhibiting Notch signaling and stabilizing p53. This latter effect depends on the interaction of Numb with Mdm2, the E3 ligase that ubiquitinates p53 and commits it to degradation. In breast cancer (BC), loss of Numb results in a reduction of p53-mediated responses including sensitivity to genotoxic drugs and maintenance of ...
27-Nov-2017
Scientific Reports, volume 7, Article number: 16363 (2017), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16385-3
Scientific Reports, online article
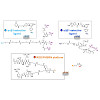
Engineering the interface between biomaterials and tissues is important to increase implant lifetime and avoid failures and revision surgeries. Permanent devices should enhance attachment and differentiation of stem cells, responsible for injured tissue repair, and simultaneously discourage bacterial colonization; this represents a major challenge. To take first ...
17-Nov-2017
ChemPhysChem, 19, 34 – 39, https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201701238
ChemPhysChem, online article
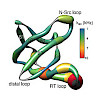
Conformational exchange in proteins is a major determinant in protein functionality. In particular, the μs–ms timescale is associated with enzymatic activity and interactions between biological molecules. We show here that a comprehensive data set of R1ρ relaxation dispersion profiles employing multiple effective fields and tilt angles can be easily obtained in ...
13-Oct-2017
Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 45, Issue 21, Pages 12536–12550, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx886
Nucleic Acids Research, online article
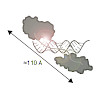
RNA interference defends against RNA viruses and retro-elements within an organism's genome. It is triggered by duplex siRNAs, of which one strand is selected to confer sequence-specificity to the RNA induced silencing complex (RISC). In Drosophila, Dicer-2 (Dcr-2) and the double-stranded RNA binding domain (dsRBD) protein R2D2 form the RISC loading complex (RLC) ...
12-Oct-2017
Cell, 171, 1–15, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.039
Cell, online article
Detection of cytosolic DNA constitutes a central event in the context of numerous infectious and sterile inflammatory conditions. Recent studies have uncovered a bipartite mode of cytosolic DNA recognition, in which the cGAS-STING axis triggers antiviral immunity, whereas AIM2 triggers inflammasome activation. Here, we show that AIM2 is dispensable for ...
13-Sep-2017
Nature, 549, 394–398, doi:10.1038/nature23890
Nature, online article

Cytosolic DNA arising from intracellular pathogens triggers a powerful innate immune response. It is sensed by cyclic GMP–AMP synthase (cGAS), which elicits the production of type I interferons by generating the second messenger 2′3′-cyclic-GMP–AMP (cGAMP). Endogenous nuclear or mitochondrial DNA can also be sensed by cGAS under certain conditions, resulting in ...
07-Sep-2017
RNA 2017, 23: 1780-1787, doi: 10.1261/rna.062901.117
RNA, online article

The nuclear exosome and the associated RNA helicase Mtr4 participate in the processing of several ribonucleoprotein particles (RNP), including the maturation of the large ribosomal subunit (60S). S. cerevisiae Mtr4 interacts directly with Nop53, a ribosomal biogenesis factor present in late pre-60S particles containing precursors of the 5.8S rRNA. The Mtr4–Nop53 ...
04-Sep-2017
Cancers 2017, 9(9), 116; https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9090116
Cancers, online article
Integrins are key regulators of communication between cells and with their microenvironment. Eight members of the integrin superfamily recognize the tripeptide motif Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) within extracelluar matrix (ECM) proteins. These integrins constitute an important subfamily and play a major role in cancer progression and metastasis via their tumor biological ...
31-Aug-2017
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, Volume 26, Issue 10, Pages 2766-2773, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2017.08.031
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, online article
The renaissance of peptides in pharmaceutical industry results from their importance in many biological functions. However, low metabolic stability and the lack of oral availability of most peptides is a certain limitation. Whereas metabolic instability may be often overcome by development of small cyclic peptides containing d-amino acids, the very low oral ...
29-Aug-2017
Anal. Chem., 2017, 89 (18), pp 10054–10062, DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b02743
Anal. Chem., online article

The formation of new types of sensitive conductive surfaces for the detection and transduction of cell–extracellular matrix recognition events in a real time, label-free manner is of great interest in the field of biomedical research. To study molecularly defined cell functions, biologically inspired materials that mimic the nanoscale order of extracellular ...
28-Aug-2017
J. Biol. Chem., (2017) 292(41), 17073–17083, DOI 10.1074/jbc.M117.797829
J. Biol. Chem., online article

The eukaryotic Hsp90 chaperone machinery comprises many co-chaperones and regulates the conformation of hundreds of cytosolic client proteins. Therefore, it is not surprising that the Hsp90 machinery has become an attractive therapeutic target for diseases such as cancer. The compounds used so far to target this machinery affect the entire Hsp90 system. However, ...
16-Aug-2017
Nature Communications, volume 8, Article number: 266, doi:10.1038/s41467-017-00366-1
Nature Communications, online article
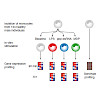
The immune system plays a major role in human health and disease, and understanding genetic causes of interindividual variability of immune responses is vital. Here, we isolate monocytes from 134 genotyped individuals, stimulate these cells with three defined microbe-associated molecular patterns (LPS, MDP, and 5′-ppp-dsRNA), and profile the transcriptomes at ...
12-Aug-2017
Protein Expression and Purification, Volume 140, Pages 74-80, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2017.08.007
Protein Expression and Purification, online article

Telethonin anchors the N-terminal region of titin in the Z-disk of the sarcomere by binding to two immunoglobulin-like (Ig) domains (Z1 and Z2) of titin (Z1Z2). Thereby telethonin plays an important role in myofibril assembly and in muscle development and functional regulation. The expression and purification of recombinant telethonin is very challenging. In ...
10-Aug-2017
Chemistry - A European Journal, Volume23, Issue57, Pages 14267-14277, https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201702423
Chemistry, online article
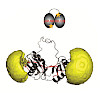
Fluorescence‐based techniques are widely used to study biomolecular conformations, intra‐ and intermolecular interactions, and conformational dynamics of macromolecules. Especially for fluorescence‐based single‐molecule experiments, the choice of the fluorophore and labeling position are highly important. In this work, we studied the biophysical and structural ...
26-Jul-2017
PLoS ONE, 12(7): e0181799, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181799
PLoS ONE, online article

Little structural information is available so far on amyloid fibrils consisting of immunoglobulin light chains. It is not understood which features of the primary sequence of the protein result in fibril formation. We report here MAS solid-state NMR studies to identify the structured core of κ-type variable domain light chain fibrils. The core contains residues ...
17-Jul-2017
Biochemistry, 2017, 56 (32), pp 4201–4209, DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00407
Biochemistry, online article
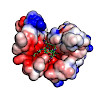
Systematic N-methylated derivatives of the melanocortin receptor ligand, SHU9119, lead to multiple binding and functional selectivity toward melanocortin receptors. However, the relationship between N-methylation-induced conformational changes in the peptide backbone and side chains and melanocortin receptor selectivity is still unknown. We conducted ...
14-Jul-2017
Scientific Reports, 7, Article number: 5393, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-05821-z
Scientific Reports, online article

NMR spectroscopy is a powerful technique to study ribonucleic acids (RNAs) which are key players in a plethora of cellular processes. Although the NMR toolbox for structural studies of RNAs expanded during the last decades, they often remain challenging. Here, we show that solvent paramagnetic relaxation enhancements (sPRE) induced by the soluble, paramagnetic ...
05-Jul-2017
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, DOI: 10.1002/anie.201702904
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, online article

Multi-domain proteins play critical roles in fine-tuning essential processes in cellular signaling and gene regulation. Typically, multiple globular domains that are connected by flexible linkers undergo dynamic rearrangements upon binding to protein, DNA or RNA ligands. RNA binding proteins (RBPs) represent an important class of multi-domain proteins, which ...
03-Jul-2017
Microbial Cell, Vol. 4, No. 7, pp. 229 - 232; DOI: 10.15698/mic2017.07.581
Microbial Cell, online article

Vector-borne trypanosomatid parasite infections in tropical and sub-tropical countries constitute a major threat to humans and livestock. Trypanosoma brucei parasites are transmitted by tsetse fly and lead to African sleeping sickness in humans and Nagana in cattle. In Latin American countries, Trypanosoma cruzi infections spread by triatomine kissing bugs lead ...
16-Jun-2017
Scientific Reports, volume 7, Article number: 3711 (2017), https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03701-0
Scientific Reports, online article
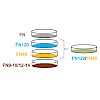
The precise mechanisms through which insoluble, cell-adhesive ligands induce and regulate directional cell migration remain obscure. We recently demonstrated that elevated surface density of physically adsorbed plasma fibronectin (FN) promotes high directional persistence in fibroblast migration. While cell-FN association through integrins α5β1 and αvβ3 was ...
23-May-2017
J. Phys. Chem. B, 2017, 121 (25), pp 6117–6130, DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b03333
J. Phys. Chem. B., online article
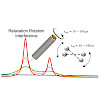
This paper deals with the theoretical foundation of proton magic angle spinning rotating-frame relaxation (R1ρ) and establishes the range of validity and accuracy of the presented approach to describe low-amplitude microsecond time scale motion in the solid state. Beside heteronuclear dipolar and chemical shift anisotropy interactions, a major source of ...
21-Apr-2017
Scientific Reports, 7, Article number: 1051, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-01031-9
Scientific Reports, online article
The transmembrane DNA-binding protein CadC of E. coli, a representative of the ToxR-like receptor family, combines input and effector domains for signal sensing and transcriptional activation, respectively, in a single protein, thus representing one of the simplest signalling systems. At acidic pH in a lysine-rich environment, CadC activates the transcription of ...
14-Apr-2017
J. Biol. Chem. (2017) 292(22) 9000–9009, doi: 10.1074/jbc.R117.788398 jbc.R117.788398
J. Biol. Chem., online article

RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) are cytosolic innate immune sensors that detect pathogenic RNA and induce a systemic antiviral response. During the last decade many studies focused on their molecular characterization and the identification of RNA agonists. Thereby it became more and more clear that RLR activation needs to be carefully regulated, since constitutive ...
14-Apr-2017
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, Volume 87, Pages 86-95, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssnmr.2017.04.002
Solid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, online article
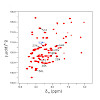
Solid-state NMR spectroscopy can provide site-resolved information about protein dynamics over many time scales. Here we combine protein deuteration, fast magic-angle spinning (~45–60 kHz) and proton detection to study dynamics of ubiquitin in microcrystals, and in particular a mutant in a region that undergoes microsecond motions in a β-turn region in the ...
09-Apr-2017
Journal of Biomolecular NMR, Volume 68, Issue 1, pp 7–17, DOI 10.1007/s10858-017-0110-0
Journal of Biomolecular NMR, online article
We demonstrate measurement of non-equilibrium backbone amide hydrogen–deuterium exchange rates (HDX) for solid proteins. The target of this study are the slowly exchanging residues in solid samples, which are associated with stable secondary-structural elements of proteins. These hydrogen exchange processes escape methods measuring equilibrium exchange rates of ...
31-Mar-2017
Science, Vol. 355, Issue 6332, pp. 1416-1420, DOI: 10.1126/science.aal1807
Science, online article

The parasitic protists of the Trypanosoma genus infect humans and domestic mammals, causing severe mortality and huge economic losses. The most threatening trypanosomiasis is Chagas disease, affecting up to 12 million people in the Americas. We report a way to selectively kill Trypanosoma by blocking glycosomal/peroxisomal import that depends on the PEX14-PEX5 ...
16-Mar-2017
Methods, Volumes 118–119, Pages 119-136, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2017.03.015
Methods, online article
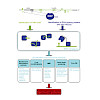
Recent advances in RNA sequencing technologies have greatly expanded our knowledge of the RNA landscape in cells, often with spatiotemporal resolution. These techniques identified many new (often non-coding) RNA molecules. Large-scale studies have also discovered novel RNA binding proteins (RBPs), which exhibit single or multiple RNA binding domains (RBDs) for ...
10-Mar-2017
Nature Communications, 8, Article number: 14635 (2017), doi:10.1038/ncomms14635
Nature Communications, online article
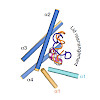
The transport of peroxisomal membrane proteins (PMPs) requires the soluble PEX19 protein as chaperone and import receptor. Recognition of cargo PMPs by the C-terminal domain (CTD) of PEX19 is required for peroxisome biogenesis in vivo. Farnesylation at a C-terminal CaaX motif in PEX19 enhances the PMP interaction, but the underlying molecular mechanisms are ...
23-Feb-2017
BioNanoMat 2017; 18(1-2): 20160014, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/bnm-2016-0014
BioNanoMat 2017, online aticle
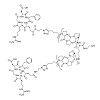
In this study we investigate the impact of ligand presentation by various molecular spacers on integrin-based focal adhesion formation. Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) arranged in hexagonal patterns were biofunctionalized with the same ligand head group, cyclic Arg-Gly-Asp [c(-RGDfX-)], but with different molecular spacers, each of which couples the head group to the ...
30-Jan-2017
GLIA, DOI: 10.1002/glia.23115
GLIA, online article
Glia play crucial roles in the development and homeostasis of the nervous system. While the GLIA in the Drosophila embryo have been well characterized, their study in the adult nervous system has been limited. Here, we present a detailed description of the glia in the adult nervous system, based on the analysis of some 500 glial drivers we identified within a ...
27-Jan-2017
Scientific Reports, volume 7, Article number: 41515, doi:10.1038/srep41515
Scientific Reports, online article

Antibody light chain amyloidosis is a rare disease caused by fibril formation of secreted immunoglobulin light chains (LCs). The huge variety of antibody sequences puts a serious challenge to drug discovery. The green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is known to interfere with fibril formation in general. Here we present solution- and solid-state ...
26-Jan-2017
J. Am. Chem. Soc., Just Accepted Manuscript, DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6b09619
J. Am. Chem. Soc., online article

Fibrillar aggregates of Aβ and Tau in the brain are the major hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. Most Tau fibers have a twisted appearance but the twist can be variable and even absent. This ambiguity, which has also been associated with different phenotypes of tauopathies, has led to controversial assumptions about fibril constitution, and it is unclear to-date ...
20-Jan-2017
Biology Open, Online ISSN 2046-6390, doi: 10.1242/bio.020669
Biology Open, online article
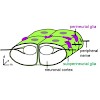
During development, many epithelia are formed by a mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET). Here, we examine the major stages and underlying mechanisms of MET during blood-brain barrier formation in Drosophila. We show that contact with the basal lamina is essential for the growth of the barrier-forming subperineurial glia (SPG). Septate junctions (SJs), which ...
16-Jan-2017
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 24, 152–161, doi:10.1038/nsmb.3351
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
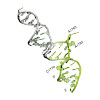
mRNA localization is an essential mechanism of gene regulation and is required for processes such as stem-cell division, embryogenesis and neuronal plasticity. It is not known which features in the cis-acting mRNA localization elements (LEs) are specifically recognized by motor-containing transport complexes. To the best of our knowledge, no high-resolution ...
11-Jan-2017
Scientific Reports, 7, Article number: 39805, doi:10.1038/srep39805
Scientific Reports, online article
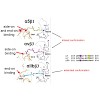
Integrins, a diverse class of heterodimeric cell surface receptors, are key regulators of cell structure and behaviour, affecting cell morphology, proliferation, survival and differentiation. Consequently, mutations in specific integrins, or their deregulated expression, are associated with a variety of diseases. In the last decades, many integrin-specific ...
J Mol Biol, Volume 430, Issue 2, Pages 133-141, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2017.11.013
J Mol Biol., online article
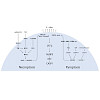
NLRP3 is the most studied inflammasome sensor due to its crucial involvement in sterile and infection-triggered inflammation. Although its molecular mode of activation remains to be defined, it is well established that low intracellular potassium concentrations result in its activation. This functionality allows the classical NLRP3 pathway to serve as a highly ...










