Research Area C - Publications 2011
22-Dec-2011
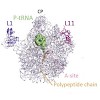
The peptidyltransferase center of the large ribosomal subunit is responsible for catalyzing peptide bonds. This active site is the target of a variety of diverse antibiotics, many of which are used clinically. The past decade has seen a plethora of structures of antibiotics in complex with the large ribosomal subunit, providing unprecedented insight into the ...
19-Dec-2011
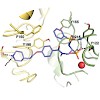
Intervention in integrin-mediated cell adhesion and integrin signaling pathways is an ongoing area of research in medicinal chemistry and drug development. One key element in integrin–ligand interaction is the coordination of the bivalent cation at the metal ion-dependent adhesion site (MIDAS) by a carboxylic acid function, a consistent feature of all integrin ...
15-Dec-2011

Labeling of RGD peptides with near-infrared fluorophores yields optical probes for noninvasive imaging of tumors overexpressing alpha-v-beta3 integrins. An important prerequisite for optimum detection sensitivity in vivo is strongly absorbing and highly emissive probes with a known fluorescence lifetime. The RGD-Cy5.5 optical probe was derived by coupling Cy5.5 ...
04-Dec-2011

Biological solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy developed rapidly in the past two decades and emerged as an important tool for structural biology. Resonance assignment is an essential prerequisite for structure determination and the characterization of motional properties of a molecule. Experiments, which rely on carbon or nitrogen detection, ...
20-Nov-2011
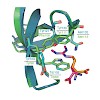
Arginine dimethylation plays critical roles in the assembly of ribonucleoprotein complexes in pre-mRNA splicing and piRNA pathways. We report solution structures of SMN and SPF30 Tudor domains bound to symmetric and asymmetric dimethylated arginine (DMA) that is inherent in the RNP complexes. An aromatic cage in the Tudor domain mediates dimethylarginine ...
18-Oct-2011
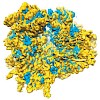
The ribosome is a highly dynamic machine responsible for protein synthesis within the cell. Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and X-ray crystallography structures of ribosomal particles, alone and in complex with diverse ligands (protein factors, RNAs and small molecules), have revealed the dynamic nature of the ribosome and provided much needed insight into ...
07-Oct-2011

RIG-I detects cytosolic viral dsRNA with 5′ triphosphates (5′-ppp-dsRNA), thereby initiating an antiviral innate immune response. Here we report the crystal structure of superfamily 2 (SF2) ATPase domain of RIG-I in complex with a nucleotide analogue. RIG-I SF2 comprises two RecA-like domains 1A and 2A and a helical insertion domain 2B, which together form a ...
26-Sep-2011
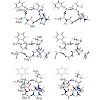
The drug Cilengitide, c(RGDf(NMe)V), is a cyclic RGD pentapeptide (R=arginine, D=aspartic acid, G=glycine) currently in clinical phase III for the treatment of brain tumors and in phase II for other cancer types.[1] The antitumoral properties of this peptide are based on its antagonistic activity for pro-angiogenic integrins, such as alpha-v-beta3, alpha-v-beta5, ...
26-Sep-2011
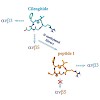
The drug Cilengitide, c(RGDf(NMe)V), is a cyclic RGD pentapeptide (R=arginine, D=aspartic acid, G=glycine) currently in clinical phase III for the treatment of brain tumors and in phase II for other cancer types.The antitumoral properties of this peptide are based on its antagonistic activity for pro-angiogenic integrins, such as alpha-v-beta-3, alpha-v-beta-5, ...
25-Sep-2011

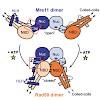
Transcription of the mitochondrial genome is performed by a single-subunit RNA polymerase (mtRNAP) that is distantly related to the RNAP of bacteriophage T7, the pol I family of DNA polymerases, and single-subunit RNAPs from chloroplasts1, 2, 3, 4. Whereas T7 RNAP can initiate transcription by itself, mtRNAP requires the factors TFAM and TFB2M for binding and ...
22-Sep-2011

Cell growth is regulated during RNA polymerase (Pol) I transcription initiation by the conserved factor Rrn3/TIF- IA in yeast/humans. Here we provide a structure–function analysis of Rrn3 based on a combination of structural biology with in vivo and in vitro functional assays. The Rrn3 crystal structure reveals a unique HEAT repeat fold and a surface serine ...
21-Sep-2011
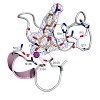
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) threaten genome stability in all kingdoms of life and are linked to cancerogenic chromosome aberrations in humans. The Mre11:Rad50 (MR) complex is an evolutionarily conserved complex of two Rad50 ATPases and a dimer of the Mre11 nuclease that senses and processes DSBs and tethers DNA for repair. ATP binding and hydrolysis by Rad50 ...
14-Sep-2011
The spread of antibiotic resistant bacteria is one of the most pressing problems in human health today. In the case of the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which causes lethal airway infections in cystic fibrosis and immunocompromised patients, the formation of biofilms plays an important role in antibiotic resistance and disease progression. ...
12-Sep-2011
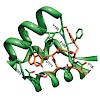
The chemokine receptor CXCR4 is a critical regulator of inflammation and immune surveillance, and it is specifically implicated in cancer metastasis and HIV-1 infection. On the basis of the observation that several of the known antagonists remarkably share a C2 symmetry element, we constructed symmetric dimers with excellent antagonistic activity using a ...
05-Sep-2011
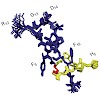
Peptides combine a high specificity for their target receptor with a low toxicity and are therefore a promising source for drug leads.However, their use has been limited because of undesirable physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties. To overcome these obstacles protein scaffolds, such as ultrastable ribosomally assembled peptides, can be used together with ...
04-Sep-2011
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, online article
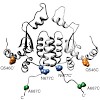
In eukaryotes, the essential dimeric molecular chaperone Hsp90 is required for the activation and maturation of specific substrates such as steroid hormone receptors, tyrosine kinases and transcription factors. Hsp90 is involved in the establishment of cancer and has become an attractive target for drug design. Here we present a structural characterization of the ...
03-Aug-2011

The function of nuclear actin is poorly understood. It is known to be a discrete component of several chromatin-modifying complexes. Nevertheless, filamentous forms of actin are important for various nuclear processes as well. Nuclear actin is often associated with nuclear actin-related protein Arp4 and other actin-related proteins like Arp8 in the INO80 ...
02-Aug-2011
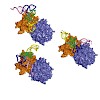
Structural studies of multi-protein complexes, whether by X-ray diffraction, scattering, NMR spectroscopy or electron microscopy, require stringent quality control of the component samples. The inability to produce ‘keystone’ subunits in a soluble and correctly folded form is a serious impediment to the reconstitution of the complexes. Co-expression of the ...
28-Jul-2011
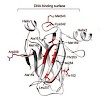
Telethonin (also known as titin-cap or t-cap) is a 19-kDa Z-disk protein with a unique beta-sheet structure, hypothesized to assemble in a palindromic way with the N-terminal portion of titin and to constitute a signalosome participating in the process of cardiomechanosensing. In addition, a variety of telethonin mutations are associated with the development of ...
21-Jul-2011
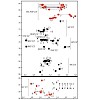
Initiation of X-chromosome inactivation in female mammals depends on the non-coding RNA Xist. We have solved the NMR structure of a 14-nucleotide hairpin with a novel AUCG tetraloop fold from a Xist A-repeat that is essential for silencing. The 1H, 13C, 15N and 31P chemical shift assignments are reported.
21-Jul-2011
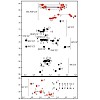
Initiation of X-chromosome inactivation in female mammals depends on the non-coding RNA Xist. We have solved the NMR structure of a 14-nucleotide hairpin with a novel AUCG tetraloop fold from a Xist A-repeat that is essential for silencing. The 1H, 13C, 15N and 31P chemical shift assignments are reported.
20-Jul-2011
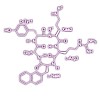
Nowadays, personalized medicine is considered to be of utmost importance to target the different causes of identical phenotypes. For example, cancer of the same type can significantly differ in its biochemical phenotypes and thus its molecular profile between patients. The disease-specific characterization of malignant cells at the molecular level is a ...
15-Jul-2011

The generation of metameric body plans is a key process in development. In Drosophila segmentation, periodicity is established rapidly through the complex transcriptional regulation of the pair-rule genes. The ‘primary’ pair-rule genes generate their 7-stripe expression through stripe-specific cis-regulatory elements controlled by the preceding non-periodic ...
13-Jul-2011

Many cellular functions involve multi-domain proteins, which are composed of structurally independent modules connected by flexible linkers. Although it is often well understood how a given domain recognizes a cognate oligonucleotide or peptide motif, the dynamic interaction of multiple domains in the recognition of these ligands remains to be characterized. Here ...
06-Jul-2011
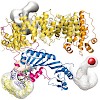
Swi2/Snf2-typeATPases regulate genome-associated processes such as transcription, replication and repair by catalysing the disruption, assembly or remodelling of nucleosomes or other protein–DNA complexes1,2. It has been suggested that ATP-driven motor activity along DNA disrupts target protein–DNA interactions in the remodelling reaction3–5. However, the complex ...
27-May-2011
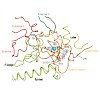
During gene transcription, the RNA polymerase (Pol) active center can catalyze RNA cleavage. This intrinsic cleavage activity is strong for Pol I and Pol III but very weak for Pol II. The reason for this difference is unclear because the active centers of the polymerases are virtually identical. Here we show that Pol II gains strong cleavage activity when the ...
27-May-2011
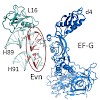
The ribosome is a major target in the bacterial cell for antibiotics. Here, we dissect the effects that the thiopeptide antibiotics thiostrepton (ThS) and micrococcin (MiC) as well as the orthosomycin antibiotic evernimicin (Evn) have on translational GTPases. We demonstrate that, like ThS, MiC is a translocation inhibitor, and that the activation by MiC of the ...
12-May-2011
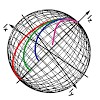
We present a novel concept for rf pulses and optimal control designed cross-polarization experiments for quadrupolar nuclei. The methods are demonstrated for 2H CP-MAS and 2H multiple-pulse NMR of perdeuterated proteins, for which sensitivity enhancements up to an order of magnitude are presented relative to commonly used approaches. The so-called RESPIRATION rf ...
04-May-2011
The barrel-shaped serine protease ClpP degrades misfolded, damaged, and regulatory proteins. Substrate proteins enter the ClpP barrel through the two axial pores, but it is unclear how the peptide products exit the barrel. Here we report the structure of ClpP from Staphylococcus aureus, which reveals a previously unobserved compressed state of the barrel. A ...
02-May-2011

Structural characterization of insoluble proteins often relies on solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Perdeuteration and partial back-substitution of exchangeable protons, as proposed for crystalline model proteins, is now shown to lead to beneficial proton spectra for heterogeneous systems, such as fibrils formed by the Alzheimer's disease β-amyloid peptide Aβ40, the ...
24-Apr-2011

The interleukin-4-inducing principle from Schistosoma mansoni eggs (IPSE/alpha-1) is a major immunogenic component of schistosomes. It potently triggers the release of interleukin-4 from basophilic granulocytes in an IgE-dependent manner, suggesting a key function in the modulation of the host’s immune response to Schistosoma mansoni infection. Here we present ...
22-Apr-2011
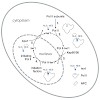
RNA polymerase (Pol) II transcribes protein-coding genes in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and consists of 12 polypeptide subunits. It is unknown how Pol II is imported into the nucleus. Here we show that Pol II nuclear import requires the protein Iwr1 and provide evidence for cyclic Iwr1 function. Iwr1 binds Pol II in the active center cleft between the two ...
17-Apr-2011
Recent progress in peptide synthesis simplified the synthesis of multiple N-methylation of peptides. To evaluate how multiple N-methylation affects the bioavailability of peptides, a poly alanine cyclic hexapeptide library (n = 54), varying in the number of N-methyl (N-Me) groups (1−5 groups) and their position, was synthesized. The peptides were evaluated for ...
17-Apr-2011

The ubiquitous SecY–Sec61 1 complex translocates nascent secretory proteins across cellular membranes and integrates membrane proteins into lipid bilayers. Several structures of mostly detergent-solubilized Sec complexes have been reported. Here we present a single-particle cryo-EM structure of the SecYEG complex in a membrane environment, bound to a translating ...
15-Apr-2011

Mediator is a multiprotein co-activator of RNA poly- merase (Pol) II transcription. Mediator contains a conserved core that comprises the ‘head’ and ‘middle’ modules. We present here a structure– function analysis of the essential Med11/22 hetero- dimer, a part of the head module. Med11/22 forms a conserved four-helix bundle domain with C-terminal extensions, ...
15-Apr-2011

Nuclear actin and actin-related proteins (Arps) are integral components of various chromatin-remodelling complexes. Actin in such nuclear assemblies does not form filaments but associates in defined complexes, for instance with Arp4 and Arp8 in the INO80 remodeller. To understand the relationship between nuclear actin and its associated Arps and to test the ...
04-Apr-2011
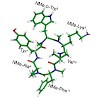
A focused multiply N-methylated library of a cyclic hexapeptidic somatostatin analogue: MK678 cyclo(−MeAYwKVF−) was generated, which resulted in the unexpected observation of an efficacious tetra-N-methylated analogue, cyclo(−MeAYMewMeKVMeF−) with a potent inhibitory action on sensory neuropeptide release in vitro and on acute neurogenic inflammatory response in ...
01-Apr-2011

The MR (Mre11 nuclease and Rad50 ABC ATPase) complex is an evolutionarily conserved sensor for DNA double-strand breaks, highly genotoxic lesions linked to cancer development.MRcan recognize and process DNA ends even if they are blocked and misfolded. To reveal its mechanism, we determined the crystal structure of the catalytic head of Thermotoga maritima MR and ...
01-Apr-2011
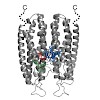
In eukaryotes, hundreds of mRNAs are localized by specialized transport complexes. For localization, transcripts are recognized by RNA-binding proteins and incorporated into motor-containing messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mRNPs). To date, the molecular assembly of such mRNPs is not well understood and most details on cargo specificity remain unresolved. ...
25-Mar-2011
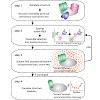
Understanding the function of biomolecular complexes requires their structural analysis at atomic resolution. To solve high-resolution structures by ab initio calculations typically data from NMR spectroscopy or X-ray crystallography are employed. In the latter approach, intrinsic flexibility and dynamics may prevent crystallization or introduce artificial ...
24-Mar-2011

Magic-angle spinning (MAS) solid-state NMR becomes an increasingly important tool for the determination of structures of membrane proteins and amyloid fibrils. Extensive deuteration of the protein allows multidimensional experiments with exceptionally high sensitivity and resolution to be obtained. Here we present an experimental strategy to measure highly ...
18-Mar-2011

Take a look at the new Cell movie clip of CIPSM's Karl-Peter Hopfner and group called "Sensing DMA Damage". Click here to watch "Sensing DMA Damage" on YouTube
15-Mar-2011
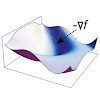
Structural analysis of multi-domain protein complexes is a key challenge in current biology and a prerequisite for understanding the molecular basis of essential cellular processes. The use of solution techniques is important for characterizing the quaternary arrangements and dynamics of domains and subunits of these complexes. In this respect solution NMR is the ...
09-Mar-2011
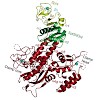
Related RNA polymerases (RNAPs) carry out cellular gene transcription in all three kingdoms of life. The universal conservation of the transcription machinery extends to a single RNAP-associated factor, Spt5 (or NusG in bacteria), which renders RNAP processive and may have arisen early to permit evolution of long genes. Spt5 associates with Spt4 to form the ...
06-Mar-2011
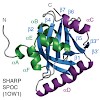
Eukaryotic transcription is regulated by interactions between gene-specific activators and the coactivator complex Mediator. Here we report the NMR structure of the Mediator subunit Med25 (also called Arc92) activator interaction domain (ACID) and analyze the structural and functional interaction of ACID with the archetypical acidic transcription activator VP16. ...
23-Feb-2011

During gene transcription, RNA polymerase (Pol) II moves forwards along DNA and synthesizes messenger RNA. However, at certain DNA sequences, Pol II moves backwards, and such backtracking can arrest transcription. Arrested Pol II is reactivated by transcription factor IIS (TFIIS), which inducesRNAcleavage that is required for cell viability1. Pol II arrest and ...
11-Feb-2011
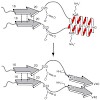
The structures of oligomeric intermediate states in the aggregation process of Alzheimer’s disease b-amyloid peptides have been the subject of debate for many years. Bacterial inclusion bodies contain large amounts of small heat shock proteins (sHSPs), which are highly homologous to those found in the plaques of the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients. sHSPs ...
10-Feb-2011
Current Opinion in Structural Biology, online article

As the nascent polypeptide chain is being synthesized, it passes through a tunnel within the large ribosomal subunit and emerges at the solvent side where protein folding occurs. Despite the universality and conservation of dimensions of the ribosomal tunnel, a functional role for the ribosomal tunnel is only beginning to emerge: Rather than a passive conduit for ...
04-Feb-2011
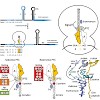
In this issue of Molecular Cell, Ramu et al. demonstrate that nascent peptides located within the ribosomal tunnel can talk back to the peptidyl transferase center to induce translational stalling by restricting the species of aminoacyl-tRNAs that can bind there.
18-Jan-2011
PLOS Biology, online article

As nascent polypeptide chains are synthesized, they pass through a tunnel in the large ribosomal subunit. Interaction between specific nascent chains and the ribosomal tunnel is used to induce translational stalling for the regulation of gene expression. One well-characterized example is the Escherichia coli SecM (secretion monitor) gene product, which induces ...
17-Jan-2011
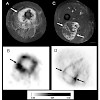
PET imaging of integrin alpha-v-beta-3 expression has been studied intensely by the academia and recently also by the industry. Imaging of integrin alpha-v-beta-3 expression is of great potential value, as the integrin alpha-v-beta-3 is a key player in tumor metastasis and angiogenesis. Therefore PET imaging of this target might be a suitable in-vivo biomarker of ...
04-Jan-2011

To obtain rates of mRNA synthesis and decay in yeast, we established dynamic transcriptome analysis (DTA). DTA combines non-perturbing metabolic RNA labeling with dynamic kinetic modeling. DTA reveals that most mRNA synthesis rates are around several transcripts per cell and cell cycle, and most mRNA half-lives range around a median of 11 min. DTA can monitor the ...
03-Jan-2011

The formation of spider dragline silk is controlled by the relatively small C- and N-terminal domains of the spidroins. The formidable and unrivaled mechanical tensile strength of spider silk fibers is a result of the carefully matched assembly of polyalanine (polyA) or poly(glycinealanine) (polyGA) repeat sequences separated by GGX or GPGXX repeats, which are ...
03-Jan-2011
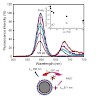
Here we report the synthesis of monofunctional PEGylated amide ligands that were used to prepare bioactivable quantum dots of a 20 nm diameter with a controlled mean number of the covalently grafted ligands. They are stable in aqueous medium of high salinity including a large pH domain
04-Dec-2010

Protein synthesis occurs in macromolecular particles called ribosomes. All ribosomes are composed of RNA and proteins. While the protein composition of bacterial and eukaryotic ribosomes has been well-characterized, a systematic analysis of archaeal ribosomes has been lacking. Here we report the first comprehensive two-dimensional PAGE and mass spectrometry ...
30-Nov--0001











