Research Area F - Publications 2014
16-Dec-2014
J. Org. Chem., 2014, DOI: 10.1021/jo502618g, 80 (4), pp 2042–2055 published on 16.12.2014
J. Org. Chem., online article
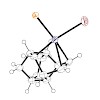
A synthetic strategy toward the intriguing hydrocarbon nanorod polytwistane is outlined. Our approach aims toward the polymerization of acetylene starting from precursors that would provide a helical bias for the formation of polytwistane. Both transition-metal-catalyzed and radical polymerizations were investigated. Two potential initiator molecules were ...
16-Dec-2014
Nature Communications, 5, 5683, doi:10.1038/ncomms6683
Nature Communications, online article

Therapeutic strategies for spinal cord injury (SCI) commonly focus on regenerating disconnected axons. An alternative approach would be to maintain continuity of damaged axons, especially after contusion. The viability of such neuropreservative strategies depends on the degree to which initially injured axons can recover. Here we use morphological and molecular ...
04-Dec-2014
Cell Death and Disease, 5, e1558; doi:10.1038/cddis.2014.512
Cell Death and Disease, online article
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) defines a group of inherited degenerative retinal diseases causing progressive loss of photoreceptors. To this day, RP is still untreatable and rational treatment development will require a thorough understanding of the underlying cell death mechanisms. Methylation of the DNA base cytosine by DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) is an ...
18-Nov-2014
Methods in Enzymology, online article

Visualizing neuronal mitochondria in a living, intact mammalian organism is a challenge that can be overcome in zebrafish larvae, which are highly accessible for optical imaging and genetic manipulation. Here, we detail an approach to visualize neuronal mitochondria in sensory Rohon–Beard axons, which allows quantitatively measuring mitochondrial shape, dynamics, ...
01-Nov-2014
Genetics ,vol. 198, no. 3, 995-1000, doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.170241
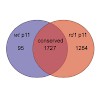
In Caenorhabditis elegans, germline apoptosis is promoted by egl-1 and ced-13 in response to meiotic checkpoint activation. We report that the requirement for these two factors depends on which checkpoints are active. We also identify a regulatory region of egl-1 required to inhibit germline apoptosis in response to DNA damage incurred during meiotic recombination.
26-Oct-2014
Nature Neuroscience, online article
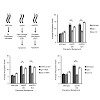
Vertebrate vision relies on two types of photoreceptors, rods and cones, which signal increments in light intensity with graded hyperpolarizations. Rods operate in the lower range of light intensities while cones operate at brighter intensities. The receptive fields of both photoreceptors exhibit antagonistic center-surround organization. Here we show that at ...
12-Sep-2014
Nature Communications, online article
Microtubule dynamics in neurons play critical roles in physiology, injury and disease and determine microtubule orientation, the cell biological correlate of neurite polarization. Several microtubule binding proteins, including end-binding protein 3 (EB3), specifically bind to the growing plus tip of microtubules. In the past, fluorescently tagged end-binding ...
28-Aug-2014
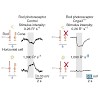
A short total synthesis of the published structure of racemic trichodermatide A is reported. Our synthesis involves a Knoevenagel condensation/Michael addition sequence, followed by the formation of tricyclic hexahydroxanthene-dione and a diastereoselective bis-hydroxylation. The final product, the structure of which was confirmed by X-ray crystallography, has ...
21-Aug-2014
Nature Communications, online article
Endolysosomal organelles play a key role in trafficking, breakdown and receptor-mediated recycling of different macromolecules such as low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol, epithelial growth factor (EGF) or transferrin. Here we examine the role of two-pore channel (TPC) 2, an endolysosomal cation channel, in these processes. Embryonic mouse fibroblasts ...
15-Aug-2014
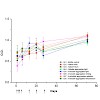
The potential contribution of protein aggregates to the unwanted immunogenicity of protein pharmaceuticals is a major concern. In the present study a murine monoclonal antibody was utilized to study the immunogenicity of different types of aggregates in mice. Samples containing defined types of aggregates were prepared by processes such as stirring, agitation, ...
15-Aug-2014
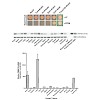
Mucolipidosis type IV (MLIV) is caused by loss of function mutations in the TRPML1 ion channel. We previously reported that tissue zinc levels in MLIV were abnormally elevated; however, the mechanism behind this pathologic accumulation remains unknown. Here, we identify transmembrane (TMEM)-163 protein, a putative zinc transporter, as a novel interacting partner ...
14-Aug-2014
Nature Communications, online article
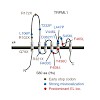
Mucolipidosis type IV (MLIV) is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder often characterized by severe neurodevelopmental abnormalities and neuro-retinal degeneration. Mutations in the TRPML1 gene are causative for MLIV. We used lead optimization strategies to identify—and MLIV patient fibroblasts to test—small-molecule activators for their potential to ...
24-Jun-2014
Human Molecular Genetics, online article
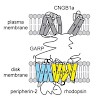
Outer segments (OS) of rod photoreceptors are cellular compartments specialized in the conversion of light into electrical signals. This process relies on the light-triggered change in the intracellular levels of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), which in turn controls the activity of cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channels in the rod OS plasma membrane. The ...
28-May-2014
Nature Communications, 2014, doi:10.1038/ncomms4915, 5, 3915 published on 28.05.2014
Nature Communications, online article

Although the role of noxious α-synuclein (α-SYN) in the degeneration of midbrain dopaminergic neurons and associated motor deficits of Parkinson’s disease is recognized, its impact on non-motor brain circuits and related symptoms remains elusive. Through combining in vivo two-photon imaging with time-coded labelling of neurons in the olfactory bulb of A30P α-SYN ...
18-May-2014
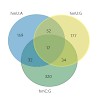
Ten eleven translocation (Tet) enzymes oxidize the epigenetically important DNA base 5-methylcytosine (mC) stepwise to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (hmC), 5-formylcytosine and 5-carboxycytosine. It is currently unknown whether Tet-induced oxidation is limited to cytosine-derived nucleobases or whether other nucleobases are oxidized as well. We synthesized isotopologs ...
07-May-2014
Cell Neuron, online article
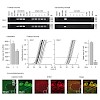
In central mammalian neurons, activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor type1 (mGluR1) evokes a complex synaptic response consisting of IP3 receptor-dependent Ca2+ release from internal Ca2+ stores and a slow depolarizing potential involving TRPC3 channels. It is largely unclear how mGluR1 is linked to its downstream effectors. Here, we explored the role of ...
01-May-2014
G3, vol. 4 no. 5, 795-804 , doi:10.1534/g3.114.010546
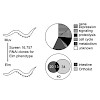
The development and homeostasis of multicellular animals requires precise coordination of cell division and differentiation. We performed a genome-wide RNA interference screen in Caenorhabditis elegans to reveal the components of a regulatory network that promotes developmentally programmed cell-cycle quiescence. The 107 identified genes are predicted to ...
23-Apr-2014
The Journal of Neuroscience, online article
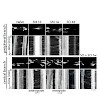
Despite the inability of CNS axons to regenerate, an increased regenerative capacity can be elicited following conditioning lesion to the peripheral branch of dorsal root ganglia neurons (DRGs). By in vivo radiolabeling of rat DRGs, coupled to mass spectrometry and kinesin immunoprecipitation of spinal cord extracts, we determined that the anterograde transport ...
20-Apr-2014
Nature Medicine, online article
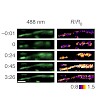
Mitochondrial redox signals have a central role in neuronal physiology and disease. Here we describe a new optical approach to measure fast redox signals with single-organelle resolution in living mice that express genetically encoded redox biosensors in their neuronal mitochondria. Moreover, we demonstrate how parallel measurements with several biosensors can ...
13-Apr-2014
Nature Methods, online article
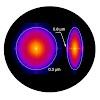
Using a descanned, laser-induced guide star and direct wavefront sensing, we demonstrate adaptive correction of complex optical aberrations at high numerical aperture (NA) and a 14-ms update rate. This correction permits us to compensate for the rapid spatial variation in aberration often encountered in biological specimens and to recover diffraction-limited ...
19-Mar-2014
Cell Neuron, online article
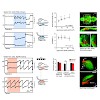
Animals respond to whole-field visual motion with compensatory eye and body movements in order to stabilize both their gaze and position with respect to their surroundings. In zebrafish, rotational stimuli need to be distinguished from translational stimuli to drive the optokinetic and the optomotor responses, respectively. Here, we systematically characterize ...
18-Mar-2014
Biophysical Journal, online article

Many transmembrane helices contain serine and/or threonine residues whose side chains form intrahelical H-bonds with upstream carbonyl oxygens. Here, we investigated the impact of threonine side-chain/main-chain backbonding on the backbone dynamics of the amyloid precursor protein transmembrane helix. This helix consists of a N-terminal dimerization region and a ...
20-Feb-2014
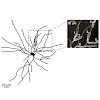
High-frequency bursts of action potentials (APs) are a distinctive form of signaling in various types of mammalian central neurons. In CA1 hippocampal pyramidal neurons in vivo, such complex spike bursts (CSs) are detected during various behaviors and are considered to be particularly important for learning- and memory-related synaptic plasticity. Here, we ...
16-Feb-2014
AGING, Vol 6, No 2 , pp 118-130
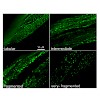
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a hallmark of skeletal muscle degeneration during aging. One mechanism through which mitochondrial dysfunction can be caused is through changes in mitochondrial morphology. To determine the role of mitochondrial morphology changes in age-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction, we studied mitochondrial morphology in body wall muscles of ...
03-Feb-2014
Scientific Reports, online article

Impaired olfaction is an early symptom in Parkinson disease (PD), although the exact cause is as yet unknown. Here, we investigated the link between PD-related mutant α-Synuclein (α-SYN) pathology and olfactory deficit, by examining the integration of adult-born neurons in the olfactory bulb (OB) of A30P α-SYN overexpressing mice. To this end, we chose to label ...
07-Jan-2014
PNAS, online article
Brain mapping experiments involving electrical microstimulation indicate that the primary motor cortex (M1) directly regulates muscle contraction and thereby controls specific movements. Possibly, M1 contains a small circuit “map” of the body that is formed by discrete local networks that code for specific movements. Alternatively, movements may be controlled by ...










