- Home ·
- Publications ·
- Research Area F ·
- 2009 ·
Research Area F - Publications 2009
15-Dec-2009
Blanca Isabel Pérez-Revuelta, Akio Fukumori, Sven Lammich, Aya Yamasaki, Christian Haass, Harald Steiner
Journal of Neurochemisty, 2009, 112, 4, 940 - 50 published on 15.12.2009
Journal of Neurochmisry, online article
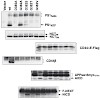
γ-Secretase is a pivotal intramembrane-cleaving protease complex and important drug target for Alzheimer's disease. The protease not only releases small peptides, such as the amyloid-β peptide, which drives Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis, but also intracellular domains, which can have critical functions in nuclear signaling. Unlike typical aspartyl proteases, ...
01-Nov-2009
Nature Neuroscience, online article

The adult mouse subependymal zone (SEZ) harbors neural stem cells that are thought to exclusively generate GABAergic interneurons of the olfactory bulb. We examined the adult generation of glutamatergic juxtaglomerular neurons, which had dendritic arborizations that projected into adjacent glomeruli, identifying them as short-axon cells. Fate mapping revealed ...
13-Sep-2009
Nature Neuroscience, online article
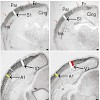
An important feature of the cerebral cortex is its layered organization, which is modulated in an area-specific manner. We found that the transcription factor AP2gamma regulates laminar fate in a region-specific manner. Deletion of AP2gamma (also known as Tcfap2c) during development resulted in a specific reduction of upper layer neurons in the occipital cortex, ...
01-Sep-2009
Neuroscience, online article

Elimination of redundant synapses and strengthening of the surviving ones are crucial steps in the development of the nervous system. Both processes can be readily followed at the climbing fiber to Purkinje cell synapse in the cerebellum. Shortly after birth, around five equally strong climbing fiber synapses are established. Subsequently, one of these five ...
28-Aug-2009
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, online article
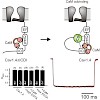
Cav1.4 channels are unique among the high voltage-activated (HVA) Ca2+ channel family because they completely lack Ca2+-dependent inactivation (CDI) and display very slow voltage-dependent inactivation (VDI). Both properties are of crucial importance in ribbon synapses of retinal photoreceptors and bipolar cells where sustained Ca2+ influx through Cav1.4 channels ...
09-Jul-2009
Martin Biel, Christian Wahl-Schott, Stylianos Michalakis, Xiangang Zong
Physiological Reviews, 2009, doi:10.1152/physrev.00029.2008, published on 09.07.2009
Physiological Reviews, online article
Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels comprise a small subfamily of proteins within the superfamily of pore-loop cation channels. In mammals, the HCN channel family comprises four members (HCN1-4) that are expressed in heart and nervous system. The current produced by HCN channels has been known as Ih (or If or Iq). Ih has also been ...
09-Jul-2009
Nathalie L. Rochefort, Olga Garaschuk, Ruxandra-Iulia Milos, Madoka Narushima, Nima Marandi, Bruno Pichler, Yury Kovalchuk, Arthur Konnerth
PNAS, 2009, 106(35), 15049–15054 published on 09.07.2009
PNAS, online article

Eye-opening represents a turning point in the function of the visual cortex. Before eye-opening, the visual cortex is largely devoid of sensory inputs and neuronal activities are generated intrinsically. After eye-opening, the cortex starts to integrate visual information. Here we used in vivo two-photon calcium imaging to explore the developmental changes of the ...
01-Jul-2009

Cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channels are ion channels which are activated by the binding of cGMP or cAMP. The channels are important cellular switches which transduce changes in intracellular concentrations of cyclic nucleotides into changes of the membrane potential and the Ca2+ concentration. CNG channels play a central role in the signal transduction ...
26-Jun-2009
European Journal of Physiology, online article
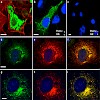
Second messenger-induced Ca2+-release from intracellular stores plays a key role in a multitude of physiological processes. In addition to 1,4,5-inositol trisphosphate (IP3), Ca2+, and cyclic ADP ribose (cADPR) that trigger Ca2+-release from the endoplasmatic reticulum (ER), nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) has been identified as a cellular ...
09-Jun-2009
J Neurochem, online article

Neuronal and glial deposition of misfolded, proteolytically processed, polyubiquitinated and abnormally phosphorylated C-terminal fragments (CTFs) of the TAR DNA binding protein-43 (TDP-43) is a pathological hallmark of frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin positive inclusions (FTLD-U) and certain cases of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. We demonstrate ...
16-Apr-2009
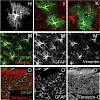
Astrocytes play many pivotal roles in the adult brain, including their reaction to injury. A hallmark of astrocytes is the contact of their endfeet with the basement membrane surrounding blood vessels, but still relatively little is known about the signaling mediated at the contact site. Here, we examine the role of ß1-integrin at this interface by its ...
14-Apr-2009
http://www.jci.org, online article
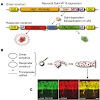
Our aging society is confronted with a dramatic increase of patients suffering from tauopathies, which include Alzheimer disease and certain frontotemporal dementias. These disorders are characterized by typical neuropathological lesions including hyperphosphorylation and subsequent aggregation of TAU protein and neuronal cell death. Currently, no mechanism-based ...
03-Apr-2009
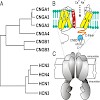
Cyclic nucleotide-regulated cation channels are ion channels whose activation is regulated by the direct binding of cAMP or cGMP to the channel protein. Two structurally related families of channels regulated by cyclic nucleotides have been identified, the cyclic nucleotide-gated channels and the hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. ...
27-Feb-2009
Intramembrane proteolysis is now widely recognized as an important physiological pathway required for reverse signaling and membrane protein degradation. Aspartyl intramembrane cleaving proteases of the GXGD-type play an important regulatory role in health and disease. Besides -secretase/presenilin, signal peptide peptidase (SPP) and SPP-like (SPPL) peptidases ...
01-Feb-2009
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, online article
Hyperpolarization-activated and cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels belong to the superfamily of voltage-gated pore loop channels. HCN channels are unique among vertebrate voltage-gated ion channels, in that they have a reverse voltage-dependence that leads to activation upon hyperpolarization. In addition, voltage-dependent opening of these channels is ...
01-Feb-2009
The Journal of Neuroscience, online article
Adult neuronal precursors retain the remarkable capacity to migrate long distances from the posterior (subventricular zone) to the most anterior [olfactory bulb (OB)] parts of the brain. The knowledge about the mechanisms that keep neuronal precursors in the migratory stream and organize this long-distance migration is incomplete. Here we show that blood vessels ...
21-Jan-2009

γ-Secretase is a unique intramembrane-cleaving protease complex, which cleaves the Alzheimer′s disease-associated b-amyloid precursor protein (APP) and a number of other type I membrane proteins. Human γ-secretase consists of the catalytic subunit presenilin (PS) (PS1 or PS2), the substrate receptor nicastrin, APH-1 (APH-1a or APH-1b), and PEN-2. To facilitate ...
01-Jan-2009
Naoyuki Tanimoto, Regine L. Muehlfriedel, M. Dominik Fischer, Edda Fahl, Peter Humphries, Martin Biel, Mathias W. Seeliger
Front Biosci., 2009, 1 Issue 14, 2730-7 published on 01.01.2009
Frontiers in Bioscience, online article

Electroretinography (ERG) is an established diagnostic technique in clinical ophthalmology and provides objective information about retinal function. This technique is also applied in basic research, where animal models of hereditary retinopathies have significantly contributed to our understanding of the composition of ERG responses in general and how retinal ...
19-Mar-2008

Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels comprise a small subfamily of proteins within the superfamily of pore-loop cation channels. In mammals, the HCN channel family comprises four members (HCN1-4) that are expressed in heart and nervous system. The current produced by HCN channels has been known as Ih (or If or Iq). Ih has also been ...










