Research Area B - Publications 2014
16-Dec-2014
PNAS, online article
The heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is a dimeric molecular chaperone essential in numerous cellular processes. Its three domains (N, M, and C) are connected via linkers that allow the rearrangement of domains during Hsp90’s chaperone cycle. A unique linker, called charged linker (CL), connects the N- and M-domain of Hsp90. We used an integrated approach, combining ...
12-Dec-2014
EMBO reports, online article

In eukaryotes, the molecular chaperones Hsp90 and Hsp70 are connected via the co-chaperone Sti1/Hop, which allows transfer of clients. Here, we show that the basic functions of yeast Sti1 and human Hop are conserved. These include the simultaneous binding of Hsp90 and Hsp70, the inhibition of the ATPase activity of Hsp90, and the ability to support client ...
08-Dec-2014
ACS Chem. Biol,.online article
In the cell, proteins are frequently modified covalently at specific amino acids with post-translational modifications, leading to a diversification of protein functions and activities. Since the introduction of high-resolution mass spectrometry, new post-translational modifications are constantly being discovered. One particular modification is the adenylylation ...
19-Nov-2014
Nature Communications, online article
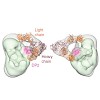
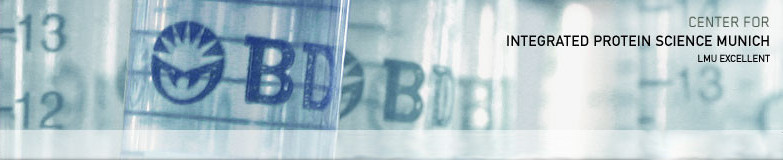
In eukarya, chaperones Hsp70 and Hsp90 act coordinately in the folding and maturation of a range of key proteins with the help of several co-chaperones, especially Hop. Although biochemical data define the Hop-mediated Hsp70–Hsp90 substrate transfer mechanism, the intrinsic flexibility of these proteins and the dynamic nature of their complexes have limited ...
08-Oct-2014
Molecular Cell, 2014, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.09.014, 56, 1–7, published on 08.10.2014
Molecular Cell, online article

During protein synthesis, nascent polypeptide chains within the ribosomal tunnel can act in cis to induce ribosome stalling and regulate expression of downstream genes. The Staphylococcus aureus ErmCL leader peptide induces stalling in the presence of clinically important macrolide antibiotics, such as erythromycin, leading to the induction of the downstream ...
06-Oct-2014
Neurobiology of Disease, online article

Alpha-synuclein (αlphaS) misfolding is associated with Parkinson's disease (PD) but little is known about the mechanisms underlying αS toxicity. Increasing evidence suggests that defects in membrane transport play an important role in neuronal dysfunction. Here we demonstrate that the GTPase Rab8a interacts with αS in rodent brain. NMR spectroscopy reveals that ...
22-Sep-2014
Chemistry - A European Journal, 2014, DOI: 10.1002/chem.201403839, Volume 20, Issue 44, pages 14201–14206, published on 22.09.2014
Chemistry - A European Journal, online article
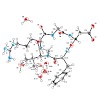
The X-ray crystal and NMR spectroscopic structures of the peptide drug candidate Cilengitide (cyclo(RGDf(NMe)Val)) in various solvents are obtained and compared in addition to the integrin receptor bound conformation. The NMR-based solution structures exhibit conformations closely resembling the X-ray structure of Cilengitide bound to the head group of integrin ...
22-Sep-2014
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, online article
The concept of proteasome inhibition ranks among the latest achievements in the treatment of blood cancer and represents a promising strategy for modulating autoimmune diseases. In this study, we describe peptidic sulfonyl fluoride inhibitors that selectively block the catalytic β5 subunit of the immunoproteasome by inducing only marginal cytotoxic effects. ...
22-Sep-2014
Angewandte Chemie International Edition, online article
The molecular chaperone Hsp90 undergoes an ATP-driven cycle of conformational changes in which large structural rearrangements precede ATP hydrolysis. Well-established small-molecule inhibitors of Hsp90 compete with ATP-binding. We wondered whether compounds exist that can accelerate the conformational cycle. In a FRET-based screen reporting on conformational ...
09-Sep-2014
Journal of Molecular Biology, online article
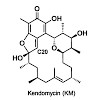
Natural products are a valuable source for novel lead structures in drug discovery, but for the majority of isolated bioactive compounds, the cellular targets are unknown. The structurally unique ansa-polyketide kendomycin (KM) was reported to exert its potent cytotoxic effects via impairment of the ubiquitin proteasome system, but the exact mode of action ...
05-Aug-2014
The Journal of Biological Chemistry, online article
Variable (V) domains of antibodies are essential for antigen recognition by our adaptive immune system. However, some variants of the light chain V domains (VL) form pathogenic amyloid fibrils in patients. It is so far unclear which residues play a key role in governing these processes. Here, we show that the conserved residue 2 of VL domains is crucial for ...
01-Aug-2014
ChemMedChem, online article
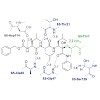
The major challenge for proteasome inhibitor design lies in achieving high selectivity for, and activity against, the target, which requires specific interactions with the active site. Novel ligands aim to overcome off-target-related side effects such as peripheral neuropathy, which is frequently observed in cancer patients treated with the FDA-approved ...
28-Jul-2014
Angewandte Chemie, online article
The dehydrogenase PylD catalyzes the ultimate step of the pyrrolysine pathway by converting the isopeptide L-lysine-Nε-3R-methyl-D-ornithine to the 22nd proteinogenic amino acid. In this study, we demonstrate how PylD can be harnessed to oxidize various isopeptides to novel amino acids by combining chemical synthesis with enzyme kinetics and X-ray ...
14-Jul-2014
Infection and Immunity, online article

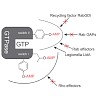
Legionella spp. cause the severe pneumonia Legionnaires' disease. The environmental bacteria replicate intracellularly in free-living amoebae and human alveolar macrophages within a distinct, endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-derived compartment termed the Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV). LCV formation requires the bacterial Icm/Dot type IV secretion system (T4SS) ...
09-Jul-2014
J. Med. Chem., online article

Mammalian genomes encode seven catalytic proteasome subunits, namely, β1c, β2c, β5c (assembled into constitutive 20S proteasome core particles), β1i, β2i, β5i (incorporated into immunoproteasomes), and the thymoproteasome-specific subunit β5t. Extensive research in the past decades has yielded numerous potent proteasome inhibitors including compounds currently ...
08-Jul-2014
Structure, online article
Repeat proteins consisting of helical segments seem to fold by a matrix-assisted mechanism in which folded segments induce structure in intrinsically disordered parts of the protein, as shown by Watson and colleagues in this issue of Structure for an Armadillo repeat protein and previously by the Balbach group for an Ankyrin repeat protein.
01-Jul-2014
PNAS, online article
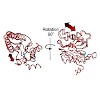
Two clusters of configurations of the main proteolytic subunit β5 were identified by principal component analysis of crystal structures of the yeast proteasome core particle (yCP). The apo-cluster encompasses unliganded species and complexes with nonpeptidic ligands, and the pep-cluster comprises complexes with peptidic ligands. The murine constitutive CP ...
19-Jun-2014
Chemistry & Biology, online article

Hydroamination reactions involving the addition of an amine to an inactivated alkene are entropically prohibited and require strong chemical catalysts. While this synthetic process is efficient at generating substituted amines, there is no equivalent in small molecule-mediated enzyme inhibition. We report an unusual mechanism of proteasome inhibition that ...
13-Jun-2014
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, online article

Antibodies are uniquely suited to serve essential roles in the human immune defense as they combine several specific functions in one hetero-oligomeric protein. Their constant regions activate effector functions and their variable domains provide a stable framework that allows incorporation of highly diverse loop sequences. The combination of non-germline DNA ...
06-Jun-2014
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, DOI: 10.1021/ja501496d, 136 (26), pp 9338–9345 published on 06.06.2014
J. Am. Chem. Soc., online article
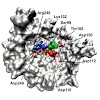
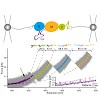
Modulation of the function of small GTPases that regulate vesicular trafficking is a strategy employed by several human pathogens. Legionella pneumophila infects lung macrophages and injects a plethora of different proteins into its host cell. Among these is DrrA/SidM, which catalyzes stable adenylylation of Rab1b, a regulator of endoplasmatic reticulum to Golgi ...
The structural analysis of shark IgNAR antibodies reveals evolutionary principles of immunoglobulins
03-Jun-2014
PNAS, online article
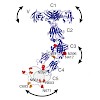
Sharks and other cartilaginous fish are the phylogenetically oldest living organisms that rely on antibodies as part of their adaptive immune system. They produce the immunoglobulin new antigen receptor (IgNAR), a homodimeric heavy chain-only antibody, as a major part of their humoral adaptive immune response. Here, we report the atomic resolution structure of ...
30-May-2014
Angewandte Chemie, online article
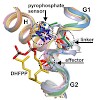
We present crystallographic and functional data of selina-4(15),7(11)-diene synthase (SdS) from Streptomyces pristinaespiralis in its open and closed (ligand-bound) conformation. We could identify an induced-fit mechanism by elucidating a rearrangement of the G1/2 helix-break motif upon substrate binding. This rearrangement highlights a novel effector triad ...
09-May-2014
J. Am. Chem. Soc., online article
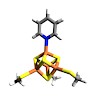
(E)-1-Hydroxy-2-methylbut-2-enyl 4-diphosphate reductase (IspH) is a [Fe4S4] cluster-containing enzyme involved in isoprenoid biosynthesis in many bacteria as well as in malaria parasites and is an important drug target. Several inhibitors including amino and thiol substrate analogues, as well as acetylene and pyridine diphosphates, have been reported. Here, we ...
08-May-2014
Cell, Volume 157, Issue 4, p922–934, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.038

The GroEL/ES chaperonin system functions as a protein folding cage. Many obligate substrates of GroEL share the (βα)8 TIM-barrel fold, but how the chaperonin promotes folding of these proteins is not known. Here, we analyzed the folding of DapA at peptide resolution using hydrogen/deuterium exchange and mass spectrometry. During spontaneous folding, all elements ...
31-Mar-2014
Molecular and Cellular Biology, online article
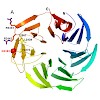
Mutations in the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 gene (LRRK2) are associated with familial and sporadic Parkinson's disease (PD). LRRK2 is a complex protein that consists of multiple domains, including predicted C-terminal WD40 repeats. In this study, we analyzed functional and molecular features conferred by the WD40 domain. Electron microscopic analysis of the ...
24-Mar-2014
Nature Communications, online article
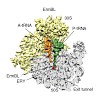
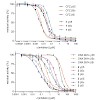
In bacteria, ribosome stalling during translation of ErmBL leader peptide occurs in the presence of the antibiotic erythromycin and leads to induction of expression of the downstream macrolide resistance methyltransferase ErmB. The lack of structures of drug-dependent stalled ribosome complexes (SRCs) has limited our mechanistic understanding of this regulatory ...
20-Mar-2014
Molecular Cell, online article
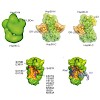
Hsp90 is the most abundant molecular chaperone in the eukaryotic cell. One of the most stringent clients is the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), whose in vivo function strictly depends on the interaction with the Hsp90 machinery. However, the molecular mechanism of this interaction has been elusive. Here we have reconstituted the interaction of Hsp90 with ...
03-Mar-2014
Angewandte Chemie, online article

Understanding and controlling proteolysis is an important goal in therapeutic chemistry. Among the natural products specifically inhibiting proteases microviridins are particularly noteworthy. Microviridins are ribosomally produced and posttranslationally modified peptides that are processed into a unique, cagelike architecture. Here, we report a combined ...
18-Feb-2014
Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, online article
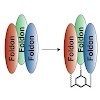
C 3-Symmetric trimesic acid scaffolds, functionalized with bromoacetyl, aminooxyacetyl and azidoacetyl moieties, respectively, were synthesized and compared regarding their utility for the trivalent presentation of peptides using three different chemoselective ligation reactions, i.e. thioether and oxime formation, as well as the “click” reaction. The latter ...
18-Feb-2014
PNAS, online article

Intracellular membrane trafficking requires correct and specific localization of Rab GTPases. The hypervariable C-terminal domain (HVD) of Rabs is posttranslationally modified by isoprenyl moieties that enable membrane association. A model asserting HVD-directed targeting has been contested in previous studies, but the role of the Rab HVD and the mechanism of Rab ...
17-Feb-2014
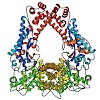
The Gram-negative bacterium Legionella pneumophila is the causative agent of Legionnaires’ disease. During infection of eukaryotic cells, the bacterium releases about 300 different bacterial effector molecules that aid in the establishment of the Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV) among which SidC is one of these secreted proteins. However, apart from membrane ...
11-Feb-2014
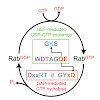
Ras superfamily GTPase activation and inactivation occur by canonical nucleotide exchange and GTP hydrolysis mechanisms. Despite conservation of active-site residues, the Ras-related Rab GTPase activation pathway differs from Ras and between different Rabs. Analysis of DENND1-Rab35, Rabex-Rab5, TRAPP-Rab1 and DrrA-Rab1 suggests Rabs have the potential for ...
10-Feb-2014
Current Opinion in Structural Biology, online article

A system for naming ribosomal proteins is described that the authors intend to use in the future. They urge others to adopt it. The objective is to eliminate the confusion caused by the assignment of identical names to ribosomal proteins from different species that are unrelated in structure and function. In the system proposed here, homologous ribosomal proteins ...
03-Feb-2014
Angewandte Chemie, online article
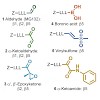
The ubiquitin–proteasome system (UPS) has been successfully targeted by both academia and the pharmaceutical industry for oncological and immunological applications. Typical proteasome inhibitors are based on a peptidic backbone endowed with an electrophilic C-terminus by which they react with the active proteolytic sites. Although the peptide moiety has ...
01-Feb-2014

Calcium is an important second messenger in eukaryotic cells that regulates many different cellular processes. To elucidate calcium regulation in chloroplasts, we identified the targets of calcium-dependent phosphorylation within the stromal proteome. A 73 kDa protein was identified as one of the most dominant proteins undergoing phosphorylation in a ...
31-Jan-2014

Kleine GTPasen fungieren als molekulare Schalter bei der Kontrolle zahlreicher essenzieller zellulärer Prozesse. Während eine fehlerhafte Funktion oder Regulierung von GTPasen in einer Vielzahl von humanen Erkrankungen eine wichtige Rolle spielt, hat es sich als schwierig erwiesen, diese Proteinklasse direkt zu adressieren, da ihre Regulierung und biologische ...
24-Jan-2014
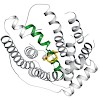
The biosynthesis of terpenes is catalysed by class I and II terpene cyclases. Here we present structural data from a class I hedycaryol synthase in complex with nerolidol, serving as a surrogate for the reaction intermediate nerolidyl diphosphate. This prefolded ligand allows mapping of the active site and hence the identification of a key carbonyl oxygen of ...
20-Jan-2014
Angewandte Chemie, online article
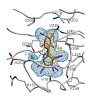
The enzymes of the non-mevalonate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis have been identified as attractive targets with novel modes of action for the development of herbicides for crop protection and agents against infectious diseases. This pathway is present in many pathogenic organisms and plants, but absent in mammals. By using high-throughput screening, we ...
20-Jan-2014
Angewandte Chemie, online article
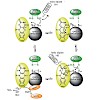
Nature provides a rich source of compounds with diverse chemical structures and biological activities, among them, sulfur-containing metabolites from bacteria and fungi. Some of these compounds bear a disulfide moiety that is indispensable for their bioactivity. Specialized oxidoreductases such as GliT, HlmI, and DepH catalyze the formation of this disulfide ...
07-Jan-2014
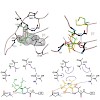
Despite their structural similarity, the natural products omuralide and vibralactone have different biological targets. While omuralide blocks the chymotryptic activity of the proteasome with an IC50 value of 47 nM, vibralactone does not have any effect at this protease up to a concentration of 1 mM. Activity-based protein profiling in HeLa cells revealed that ...
03-Jan-2014
Pathogenic bacteria have developed a variety of mechanisms with which to manipulate the functions of proteins in important cellular pathways of host organisms. Because of their pivotal role in the regulation of cell physiology, members of the family of G-proteins and cytoskeletal proteins are frequent targets for pathogens. They are modified both by noncovalent ...
01-Jan-2014

In eukaryotic cells, the ubiquitin–proteasome-system (UPS) is responsible for the non-lysosomal degradation of proteins and plays a pivotal role in such vital processes as protein homeostasis, antigen processing or cell proliferation. Therefore, it is an attractive drug target with various applications in cancer and immunosuppressive therapies. Being an ...