News 2012
14-Nov-2013

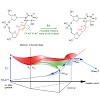
The general transcription factor (TF) IIB is required for RNA polymerase (Pol) II initiation and extends with its B-reader element into the Pol II active centre cleft. Low-resolution structures of the Pol II–TFIIB complex indicated how TFIIB functions in DNA recruitment, but they lacked nucleic acids and half of the B-reader, leaving other TFIIB functions ...
28-Dec-2012
Co-transcriptional pre-mRNA processing relies on reversible phosphorylation of the carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) of Rpb1, the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (RNAP II). In this study, we replaced in live cells the endogenous Rpb1 by S2A Rpb1, where the second serines (Ser2) in the CTD heptapeptide repeats were switched to alanines, to prevent ...
27-Dec-2012

Oligonucleotides used in gene therapy and silencing are fragile compounds that degrade easily in biological environments. Porous biocompatible carrier particles may provide a useful strategy to deliver these therapeutics to their target sites. Development of appropriate delivery vehicles, however, requires a better understanding of the oligonucleotide-host ...
27-Dec-2012
DNA methylation patterns change dynamically during mammalian development and lineage specification, yet scarce information is available about how DNA methylation affects gene expression profiles upon differentiation. Here we determine genome-wide transcription profiles during undirected differentiation of severely hypomethylated (Dnmt1−/−) embryonic stem cells ...
26-Dec-2012
Rab GTPases, key regulators of vesicular transport, hydrolyze GTP very slowly unless assisted by Rab GTPase-activating proteins (RabGAPs). Dysfunction of RabGAPs is involved in many diseases. By combining X-ray structure analysis and time-resolved FTIR spectroscopy we reveal here the detailed molecular reaction mechanism of a complex between human Rab and RabGAP ...
26-Dec-2012
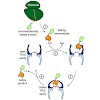
The eukaryotic chaperonin, TRiC/CCT (TRiC, TCP-1 ring complex; CCT, chaperonin containing TCP-1), uses a built-in lid to mediate protein folding in an enclosed central cavity. Recent structural data suggest an effective size limit for the TRiC folding chamber of ∼70 kDa, but numerous chaperonin substrates are substantially larger. Using artificial fusion ...
24-Dec-2012
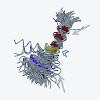
The etiology of Alzheimer’s disease depends on the relative abundance of different amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide species. These peptides are produced by sequential proteolytic cleavage within the transmembrane helix of the 99 residue C-terminal fragment of the amyloid precursor protein (C99) by the intramembrane protease γ-secretase. Intramembrane proteolysis is thought ...
23-Dec-2012

The Tel2 (also known as Telo2) and Tti1 proteins control the cellular abundance of mammalian PIKKs and are integral components of mTORC1 and mTORC2. Here we report that Tel2 and Tti1 are targeted for degradation within mTORC1 by the SCFFbxo9 ubiquitin ligase to adjust mTOR signalling to growth factor availability. This process is primed by CK2, which translocates ...
15-Dec-2012
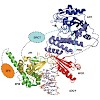
ADP-ribosylation is a post-translational modification of proteins that occurs mostly in response to cellular stress and is catalysed by members of the diverse poly-ADP-ribose (PAR) polymerase (PARP/ARTD) family. The founding member of the family, PARP1, is best recognized for its function as a sensor of DNA strand lesions, but ADP-ribosylation has been implicated ...
14-Dec-2012

We demonstrate that, at constant temperature, hundreds of DNA strands can cooperatively fold a long template DNA strand within minutes into complex nanoscale objects. Folding occurred out of equilibrium along nucleation-driven pathways at temperatures that could be influenced by the choice of sequences, strand lengths, and chain topology. Unfolding occurred in ...
13-Dec-2012
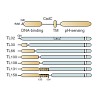
Translation elongation factor P (EF-P) is critical for virulence in bacteria. EF-P is present in all bacteria and orthologous to archaeal and eukaryotic initiation factor 5A, yet the biological function has so far remained enigmatic. Here, we demonstrate that EF-P is an elongation factor that enhances translation of polyproline-containing proteins: In the absence ...
12-Dec-2012
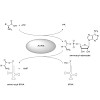
4-Hydroxyderricin is a heat labile bioactive chalcone isolated from the plant Angelica keiskei. It received attention due to its antibiotic potency against several strains of bacteria including pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus. Despite these promising pharmacological properties, the exact mode of action or the biological targets are still unknown. Here we ...
12-Dec-2012
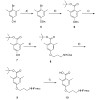
Investigating the different functions of distinct surface receptors is essential to understand the complex interactions between cells and their extracellular environment. Cells use specific transmembrane receptors of the integrin family to anchor and respond to extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. In doing so, integrins are capable of regulating cell migration, ...
11-Dec-2012
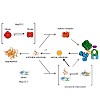
Small heat shock proteins (sHsps) are molecular chaperones that prevent the aggregation of nonnative proteins. The sHsps investigated to date mostly form large, oligomeric complexes. The typical bacterial scenario seemed to be a two-component sHsps system of two homologous sHsps, such as the Escherichia coli sHsps IbpA and IbpB. With a view to expand our ...
07-Dec-2012
Escherichia coli contains 30 two-component systems (TCSs), each consisting of a histidine kinase and a response regulator. Whereas most TCSs are well characterized in this model organism, little is known about the YpdA/YpdB system. To identify YpdB-regulated genes, we compared the transcriptomes of E. coli cells overproducing either YpdB or a control protein. ...
Promiscuous behaviour of archaeal ribosomal proteins: Implications for eukaryotic ribosome evolution
06-Dec-2012
In all living cells, protein synthesis occurs on ribonucleoprotein particles called ribosomes. Molecular models have been reported for complete bacterial 70S and eukaryotic 80S ribosomes; however, only molecular models of large 50S subunits have been reported for archaea. Here, we present a complete molecular model for the Pyrococcus furiosus 70S ribosome based ...
03-Dec-2012

In the mammalian retina, light signals generated in photoreceptors are passed to bipolar and horizontal cells via synaptic contacts. In various pathological conditions, these second-order neurons extend neurites into the outer nuclear layer (ONL). However, the molecular events associated with this neurite outgrowth are not known. Here, we characterized the ...
02-Dec-2012
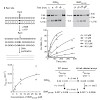
ISWI slides nucleosomes along DNA, enabling the structural changes of chromatin required for the regulated use of eukaryotic genomes. Prominent mechanistic models imply cooperation of the ISWI ATPase domain with a C-terminal DNA-binding function residing in the HAND-SANT-SLIDE (HSS) domain. Contrary to these models, we show by quantitative biochemical means that ...
28-Nov-2012
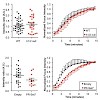
Recruitment of 53BP1 to chromatin flanking double strand breaks (DSBs) requires γH2AX/MDC1/RNF8-dependent ubiquitination of chromatin and interaction of 53BP1 with histone H4 methylated on lysine 20 (H4K20me). Several histone methyltransferases have been implicated in 53BP1 recruitment, but their quantitative contributions to the 53BP1 response are unclear. We ...
28-Nov-2012
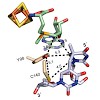
The spore photoproduct lyase is a radical SAM enzyme, which repairs 5-(α-thyminyl)-5,6-dihydrothymidine. Here we show that the enzyme establishes a complex radical transfer cascade and creates a cysteine and a tyrosyl radical dyade to establish repair. This allows the enzyme to solve topological and energetic problems associated with the radical based repair ...
28-Nov-2012
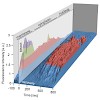
In basic and applied HIV research, reliable detection of viral components is crucial to monitor progression of infection. While it is routine to detect structural viral proteins in vitro for diagnostic purposes, it previously remained impossible to directly and dynamically visualize HIV in living cells without genetic modification of the virus. Here, we describe ...
27-Nov-2012
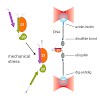
Mechanical forces are important signals for cell response and development, but detailed molecular mechanisms of force sensing are largely unexplored. The cytoskeletal protein filamin is a key connecting element between the cytoskeleton and transmembrane complexes such as integrins or the von Willebrand receptor glycoprotein Ib. Here, we show using single-molecule ...
21-Nov-2012
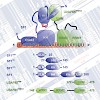
Recognition of the 30-splice site is a key step in premRNA splicing and accomplished by a dynamic complex comprising splicing factor 1 (SF1) and the U2 snRNP auxiliary factor 65-kDa subunit (U2AF65). Both proteins mediate protein–protein and protein–RNA interactions for cooperative RNA-binding during spliceosome assembly. Here, we report the solution structure of ...
21-Nov-2012
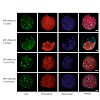
Members of the Alb3/Oxa1/YidC protein family function as insertases in chloroplasts, mitochondria, and bacteria. Due to independent gene duplications, all organisms possess two isoforms, Oxa1 and Oxa2 except gram-negative bacteria, which encode only for one YidC-like protein. The genome of Arabidopsis thaliana however, encodes for eight different isoforms. The ...
19-Nov-2012
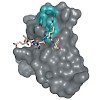
N-Methylation is one of the simplest chemical modifications often occurring in peptides and proteins of prokaryotes and higher eukaryotes. Over years of evolution, nature has employed N-methylation of peptides as an ingenious technique to modulate biological function, often as a mode of survival through the production of antibiotics. This small structural change ...
19-Nov-2012

A key goal for nanotechnology is to design synthetic objects that may ultimately achieve functionalities known today only from natural macromolecular complexes. Molecular self-assembly with DNA has shown potential for creating user-defined 3D scaffolds, but the level of attainable positional accuracy has been unclear. Here we report the cryo-EM structure and a ...
16-Nov-2012

We created nanometer-scale transmembrane channels in lipid bilayers by means of self-assembled DNA-based nanostructures. Scaffolded DNA origami was used to create a stem that penetrated and spanned a lipid membrane, as well as a barrel-shaped cap that adhered to the membrane, in part via 26 cholesterol moieties. In single-channel electrophysiological ...
15-Nov-2012

Recently new lysine modifications were detected in histones and other proteins. Using the pyrrolysine amber suppression system we genetically inserted three of the new amino acids ε-N-propionyl-, ε-N-butyryl-, and ε-N-crotonyl-lysine site specifically into histone H3. The lysine at position 9 (H3 K9), which is known to be highly modified in chromatin, was ...
14-Nov-2012
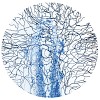
Mitochondria provide ATP, maintain calcium homeostasis, and regulate apoptosis. Neurons, due to their size and complex geometry, are particularly dependent on the proper functioning and distribution of mitochondria. Thus disruptions of these organelles and their transport play a central role in a broad range of neurodegenerative diseases. While in vitro studies ...
09-Nov-2012

Hybrid dendritic-linear block copolymers based on a 4-arm poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) core were synthesized using an accelerated AB2/CD2 dendritic growth approach through orthogonal amine/epoxy and thiol-yne chemistries. The biological activity of these 4-arm and the corresponding 2-arm hybrid dendrimers revealed an enhanced, dendritic effect with an exponential ...
30-Oct-2012

Calmodulin is the primary calcium binding protein in living cells. Its function and structure depend strongly on calcium concentration. We used single molecule force spectroscopy by optical tweezers to study the folding of calmodulin in the physiologically relevant range. We find that full-length calmodulin switches from a rich and complex folding behavior at ...
26-Oct-2012
Quorum sensing regulates cell density-dependent phenotypes and involves the synthesis, excretion and detection of so-called autoinducers. Vibrio harveyi strain ATCC BAA-1116 (recently reclassified as Vibrio campbellii), one of the best-characterized model organisms for the study of quorum sensing, produces and responds to three autoinducers. HAI-1, AI-2 and CAI-1 ...
24-Oct-2012
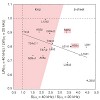
The 1H dipolar network, which is the major obstacle for applying proton detection in the solid-state, can be reduced by deuteration, employing the RAP (Reduced Adjoining Protonation) labeling scheme, which yields random protonation at non-exchangeable sites. We present here a systematic study on the optimal degree of random sidechain protonation in RAP samples as ...
22-Oct-2012
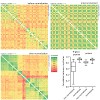
Cells secrete a large number of proteins to communicate with their surroundings. Furthermore, plasma membrane proteins and intracellular proteins can be released into the extracellular space by regulated or non-regulated processes. Here, we profiled the supernatant of 11 cell lines that are representative of different stages of breast cancer development by ...
18-Oct-2012
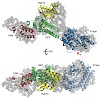
The process of dosage compensation (DC) in Drosophila counterbalances the monosomy of the X chromosome in male flies by increasing the transcription from this unique chromosome in the two-fold range. Upon exclusive expression of male-specific lethal 2 (MSL2) in males, the dosage compensation machinery assembles on active X-chromosomal genes. Overexpression of MSL ...
12-Oct-2012
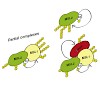
After the pathogenic bacterium Legionella pneumophila is phagocytosed, it injects more than 250 different proteins into the cytoplasm of host cells to evade lysosomal digestion and to replicate inside the host cell. Among these secreted proteins is the protein DrrA/SidM, which has been shown to modify Rab1b, a main regulator of vesicular trafficking in eukaryotic ...
11-Oct-2012
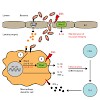
Background: Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is characterized by chronic intestinal inflammation due to dysregulation of the mucosal immune system. The cytokines IL-1β and IL-18 appear early in intestinal inflammation and their pro-forms are processed via the caspase-1-activating multiprotein complex, the Nlrp3 inflammasome. Previously, we reported that the ...
06-Oct-2012
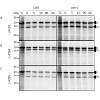
Chloroplast-located proteins which are encoded by the nuclear genome have to be imported from the cytosol into the organelle in a post-translational manner. Among these nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins are the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding proteins (LHCPs). After translation in the cytosol, precursor proteins of LHCPs are imported via the TOC/TIC ...
04-Oct-2012
Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are adapter molecules needed to translate genetic information into a peptide sequence. At the ribosome, the anticodon of each tRNA reads the corresponding codon of the messenger RNA. This anticodon– codon interaction allows the ribosome_s large subunit to catalyze amide-bond formation between the cognate amino acids present at the 3’ ...
02-Oct-2012

The vesicle-inducing protein in plastids 1 (Vipp1) is an essential component for thylakoid biogenesis in cyanobacteria and chloroplasts. Vipp1 proteins share significant structural similarity with their evolutionary ancestor PspA (bacterial phage shock protein A), namely a predominantly α-helical structure, the formation of oligomeric high molecular weight ...
02-Oct-2012

Molecular self-assembly with DNA offers a route for building user-defined nanoscale objects, but an apparent requirement for magnesium in solution has limited the range of conditions for which practical utility of such objects may be achieved. Here we report conditions for assembling templated multi-layer DNA objects in the presence of monovalent ions, showing ...
01-Oct-2012

ABPP, activity-based protein profiling; ABP, activity-based probe; Cat, Cathepsin; DIC, diisopropylcarbodiimide; DIEA, N,N-diisopropyl-N-ethylamine; DMEM, dulbecco's modified eagle medium; HBTU, 2-(1H-benzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate; HOBt, hydroxybenzotriazole; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; SB, sample buffer; SPPS, solid ...
01-Oct-2012
Ribosome protection proteins (RPPs) confer tetracycline resistance by binding to the ribosome and chasing the drug from its binding site. The current model for the mechanism of action of RPPs proposes that drug release is indirect and achieved via conformational changes within the drug-binding site induced upon binding of the RPP to the ribosome. Here we report a ...
24-Sep-2012

Look, no label! Microscale thermophoresis makes use of the intrinsic fluorescence of proteins to quantify the binding affinities of ligands and discriminate between binding sites. This method is suitable for studying binding interactions of very small amounts of protein in solution. The binding of ligands to iGluR membrane receptors, small-molecule inhibitorss to ...
21-Sep-2012
In eukaryotes, DNA is organized together with histones and non-histone proteins into a highly complex nucleoprotein structure called chromatin, with the nucleosome as its monomeric subunit. Various interconnected mechanisms regulate DNA accessibility, including replacement of canonical histones with specialized histone variants. Histone variant incorporation can ...
18-Sep-2012
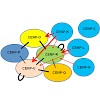
Kinetochores are multi-protein megadalton assemblies that are required for attachment of microtubules to centromeres and, in turn, the segregation of chromosomes in mitosis. Kinetochore assembly is a cell cycle regulated multi-step process. The initial step occurs during interphase and involves loading of the 15-subunit constitutive centromere associated complex ...
17-Sep-2012
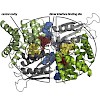
At acidic pH and in the presence of lysine, the pH sensor CadC activates transcription of the cadBA operon encoding the lysine/cadaverine antiporter CadB and the lysine decarboxylase CadA. In effect, these proteins contribute to acid stress adaptation in Escherichia coli. cadBA expression is feedback inhibited by cadaverine, and a cadaverine binding site is ...
13-Sep-2012

Neurons in the mammalian brain receive thousands of synaptic inputs on their dendrites. In many types of neurons, such as cortical pyramidal neurons, excitatory synapses are formed on fine dendritic protrusions called spines. Usually, an individual spine forms a single synaptic contact with an afferent axon. In this protocol, we describe a recently established ...
11-Sep-2012
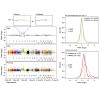
Extra chromosome copies markedly alter the physiology of eukaryotic cells, but the underlying reasons are not well understood. We created human trisomic and tetrasomic cell lines and determined the quantitative changes in their transcriptome and proteome in comparison with their diploid counterparts. We found that whereas transcription levels reflect the ...
11-Sep-2012
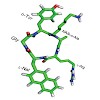
GABAA receptors are pentameric ligand-gated ion channels that are activated by the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian brain, g-aminobutyric acid (GABA).Binding of GABA results in the opening of a chloride ion selective pore, thus hyperpolarizing the postsynaptic neuron and decreasing the likelihood of action-potential firing. As such, GABAA ...
10-Sep-2012
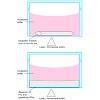
The pathways of interferon α2a release from a triglyceride based implant system were studied by single molecule fluorescence microscopy. The protein was labeled with a stable fluorescent dye ATTO647N, freeze-dried and embedded into the lipid matrix via twin-screw extrusion. The implant system consisted of a pore-forming agent (water soluble PEG 6000) and two ...
09-Sep-2012
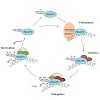
Eukaryotic RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) has evolved an array of heptad repeats with the consensus sequence Tyr1-Ser2-Pro3-Thr4-Ser5-Pro6-Ser7 at the carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of its largest subunit (Rpb1). Dynamic phosphorylation of Ser2, Ser5 and Ser7 residues orchestrates the binding of transcription and RNA processing factors to the transcription machinery. ...
06-Sep-2012

The eukaryotic RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) catalyzes the transcription of all protein encoding genes and is also responsible for the generation of small regulatory RNAs. RNAPII has evolved a unique domain composed of heptapeptide repeats with the consensus sequence Tyr1–Ser2–Pro3–Thr4–Ser5–Pro6–Ser7 at the C-terminus (CTD) of its largest subunit (Rpb1). Dynamic ...
03-Sep-2012
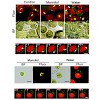
VESICLE-INDUCING PROTEIN IN PLASTIDS1 (VIPP1), proposed to play a role in thylakoid biogenesis, is conserved in photosynthetic organisms and is closely related to Phage Shock Protein A (PspA), which is involved in plasma membrane integrity in Escherichia coli. This study showed that chloroplasts/plastids in Arabidopsis thaliana vipp1 knockdown and knockout ...
30-Aug-2012
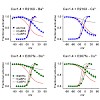
Cav1.4 L-type Ca2+ channels are crucial for synaptic transmission in retinal photoreceptors and bipolar neurons. Recent studies suggest that the activity of this channel is regulated by the Ca2+-binding protein 4 (CaBP4). In the present study, we explored this issue by examining functional effects of CaBP4 on heterologously expressed Cav1.4. We show that CaBP4 ...
30-Aug-2012
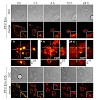
It is thought that foamy viruses (FVs) enter host cells via endocytosis because all FV glycoproteins examined display pH-dependent fusion activities. Only the prototype FV (PFV) glycoprotein has also significant fusion activity at neutral pH, suggesting that its uptake mechanism may deviate from other FVs. To gain new insights into the uptake processes of FV in ...
28-Aug-2012

Engineering efforts of genetically encoded calcium indicators predominantly focused on enhancing fluorescence changes, but how indicator expression affects the physiology of host organisms is often overlooked. Here, we demonstrate biocompatibility and widespread functional expression of the genetically encoded calcium indicator TN-XXL in a transgenic mouse model. ...
24-Aug-2012

The green tea compound epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) inhibits Alzheimer's disease β-amyloid peptide (Aβ) neurotoxicity. Solution-state NMR allows probing initial EGCG–Aβ interactions. We show that EGCG-induced Aβ oligomers adopt a well-defined structure and are amenable for magic angle spinning solid-state NMR investigations. We find that EGCG interferes with ...
16-Aug-2012

Chaperone-assisted sorting of post-translationally imported proteins is a general mechanism among all eukaryotic organisms. Interaction of some preproteins with the organellar membranes is mediated by chaperones, which are recognised by membrane-bound tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domain containing proteins. We have characterised AtTPR7 as an endoplasmic ...
13-Aug-2012
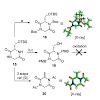
The variecolortides are a family of unusual natural products that combine motifs from a variety of biosynthetic streams. Herein, we present the gradual evolution of a convergent synthetic strategy that ultimately culminated in a reaction cascade featuring a hydrogen shift and a cycloaddition followed by a spontaneous air oxidation. Attempts to link an anthrone ...
06-Aug-2012
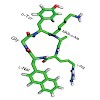
There can be only one: Using a peptoid motif obtained by shifting the arginine side chain of a pentapeptide previously developed by Fujii et al. to the neighboring nitrogen atom restricts the conformational freedom and yields a conformationally homogeneous peptide (see picture) with a 100-fold higher binding affinity to the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in the ...
06-Aug-2012
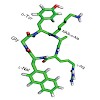
There can be only one: Using a peptoid motif obtained by shifting the arginine side chain of a pentapeptide previously developed by Fujii et al. to the neighboring nitrogen atom restricts the conformational freedom and yields a conformationally homogeneous peptide (see picture) with a 100-fold higher binding affinity to the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in the ...
26-Jul-2012

We are happy that Nature mentions CIPSMs' graduate educational program and quotes CIPSMs' CEO Oliver Baron in its highlight article about the German Excellence Initiative. pdf
24-Jul-2012
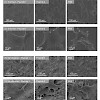
It is well known that functionalization of surfaces with cell adhesive peptides mimicking the integrin binding motif of extracellular matrix proteins is a feasible approach to improve osseointegration of implant materials. Also, modification of the surface properties of the material (e.g., roughness) strongly influences cell behavior. However, these two ...
16-Jul-2012

Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a group of genetically heterogeneous severe retinal diseases commonly leading to legal blindness. Mutations in the CNGB1a subunit of the rod cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channel have been found to cause RP in patients. Here, we demonstrate the efficacy of gene therapy as a potential treatment for RP by means of recombinant ...
13-Jul-2012
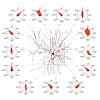
Dendritic spines arise as small protrusions from the dendritic shaft of various types of neuron and receive inputs from excitatory axons. Ever since dendritic spines were first described in the nineteenth century, questions about their function have spawned many hypotheses. In this review, we introduce understanding of the structural and biochemical properties of ...
13-Jul-2012

Light control of voltage-gated ion channels: We have developed red-shifted derivatives of QAQ, a powerful doubly charged photochromic blocker. These derivatives allow for remote control of Kv and Nav channel conductance with light and offer the opportunity to silence neuronal activity reversibly.
13-Jul-2012
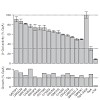
Formation of non-covalent functional complexes of integral membrane proteins is frequently supported by sequence-specific interaction of their transmembrane helices. Here, we aligned human single-span membrane proteins with orthologs from other eukaryotes. We find that almost half of the human single-span membrane proteins contain a transmembrane helix that ...
13-Jul-2012

Ribosomal RNA gene transcription, co-transcriptional processing, and ribosome biogenesis are highly coordinated processes that are tightly regulated during cell growth. In this study we discovered that Mybbp1a is associated with both the RNA polymerase I complex and the ribosome biogenesis machinery. Using a reporter assay that uncouples transcription and RNA ...
12-Jul-2012
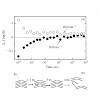
The light-driven disassembly process of amyloid-like structures formed by azobenzene model peptides is studied by time-resolved mid-IR spectroscopy from nanoseconds to minutes. The investigated peptide consists of two amino acid strands connected by the azobenzene switch. The peptides aggregate to amyloid-like structures when the azobenzene chromophore is in the ...
11-Jul-2012
Bacterial infections of skin and soft tissue represent a major health threat, especially if they are caused by multidrug-resistant strains such as MRSA. Novel treatment options for topical application are urgently needed, and even if new drug candidates are identified, their properties must match the specific physical requirements of the skin in order to ...
06-Jul-2012

ISWI is an evolutionarily conserved ATPase that catalyzes nucleosome remodeling in different macromolecular complexes. Two mammalian ISWI orthologs, SNF2H and SNF2L, are thought to have specialized functions despite their high sequence similarity. To date, the function of SNF2L in human cells has not been a focus of research. Newly established specific monoclonal ...
02-Jul-2012
Bacterial spores possess an enormous resistance to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This is largely due to a unique DNA repair enzyme, Spore Photoproduct Lyase (SP lyase) that repairs a specific UV-induced DNA lesion, the spore photoproduct (SP), through an unprecedented radical-based mechanism. Unlike DNA photolyases, SP lyase belongs to the emerging superfamily of ...
29-Jun-2012
In different phases of the transcription cycle, RNA polymerase (Pol) II recruits various factors via its C-terminal domain (CTD), which consists of conserved heptapeptide repeats with the sequence Tyr1-Ser2-Pro3-Thr4-Ser5-Pro6-Ser7. We show that the CTD of transcribing yeast Pol II is phosphorylated at Tyr1, in addition to Ser2, Thr4, Ser5, and Ser7. Tyr1 ...
28-Jun-2012

DNA and RNA contain, next to the four canonical nucleobases, a number of modified nucleosides that extend their chemical information content. RNA is particularly rich in modifications, which is obviously an adaptation to their highly complex and variable functions. In fact, the modified nucleosides and their chemical structures establish a second layer of ...
27-Jun-2012
Insufficient oral bioavailability is considered as a key limitation for the widespread development of peptides as therapeutics. While the oral bioavailability of small organic compounds is often estimated from simple rules, similar rules do not apply to peptides, and even the high oral bioavailability that is described for a small number of peptides is not well ...
25-Jun-2012
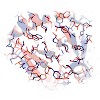
We have developed an approach for determining NMR structures of proteins over 20 kDa that utilizes sparse distance restraints obtained using transverse relaxation optimized spectroscopy experiments on perdeuterated samples to guide RASREC Rosetta NMR structure calculations. The method was tested on 11 proteins ranging from 15 to 40 kDa, seven of which were ...
22-Jun-2012

We provide here a molecular movie that captures key aspects of RNA polymerase II initiation and elongation. To create the movie, we combined structural snapshots of the initiation-elongation transition and of elongation, including nucleotide addition, translocation, pausing, proofreading, backtracking, arrest, reactivation, and inhibition. The movie reveals open ...
22-Jun-2012

Due to the biocompatibility and biodegradability as well as the mechanical properties of the fibers, spider silk has become an attractive material for researchers regarding biomedical applications. In this study, the engineered recombinant spider silk protein eADF4(C16) was modified with the integrin recognition sequence RGD by a genetic (fusing the amino acid ...
21-Jun-2012
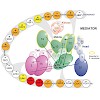
The Mediator is a highly conserved, large multiprotein complex that is involved essentially in the regulation of eukaryotic mRNA transcription. It acts as a general transcription factor by integrating regulatory signals from gene-specific activators or repressors to the RNA Polymerase II. The internal network of interactions between Mediator subunits that conveys ...
21-Jun-2012

Histone variants are non-allelic protein isoforms that play key roles in diversifying chromatin structure. The known number of such variants has greatly increased in recent years, but the lack of naming conventions for them has led to a variety of naming styles, multiple synonyms and misleading homographs that obscure variant relationships and complicate database ...
20-Jun-2012
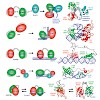
Protein–RNA interactions play essential roles in gene regulation and RNA metabolism. While high-resolution structures have revealed principles of RNA recognition by individual RNA binding domains (RBDs), the presence of multiple RBDs in many eukaryotic proteins suggests additional modes of RNA recognition by combination and cooperation of these interactions. ...
19-Jun-2012
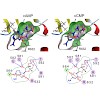
Activation of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels is facilitated in vivo by direct binding of the second messenger cAMP. This process plays a fundamental role in the fine-tuning of HCN channel activity and is critical for the modulation of cardiac and neuronal rhythmicity. Here, we identify the pyrimidine cyclic nucleotide cCMP as ...
17-Jun-2012
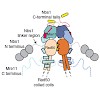
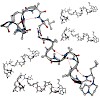
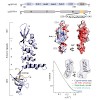
The Mre11–Rad50–Nbs1 (MRN) complex tethers, processes and signals DNA double-strand breaks, promoting genomic stability. To understand the functional architecture of MRN, we determined the crystal structures of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe Mre11 dimeric catalytic domain alone and in complex with a fragment of Nbs1. Two Nbs1 subunits stretch around the outside of ...
17-Jun-2012

Lys34 of the conserved translation elongation factor P (EF-P) is post-translationally lysinylated by YjeK and YjeA—a modification that is critical for bacterial virulence. Here we show that the currently accepted Escherichia coli EF-P modification pathway is incomplete and lacks a final hydroxylation step mediated by YfcM, an enzyme distinct from deoxyhypusine ...
15-Jun-2012

Thank you! CIPSM has once more been selected as a Cluster of Excellence in the German Excellence Initiative. In the next 5 years CIPSM will try to make sure, that it is here to stay. We thank all the people that helped to make that possible. More information can be found here
12-Jun-2012
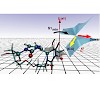
The photophysical and photochemical processes driving the formation of the ultraviolet (UV)-induced DNA Dewar lesion from the T(6-4)T dimer are investigated by time-resolved spectroscopy and quantum chemical modelling. Time-resolved absorption and emission spectroscopy in the UV revealed a biexponential decay of the electronically excited state (S1) with time ...
11-Jun-2012

The transmembrane domains of membrane fusogenic proteins are known to contribute to lipid bilayer mixing as indicated by mutational studies and functional reconstitution of peptide mimics. Here, we demonstrate that mutations of a GxxxG motif or of Ile residues, that were previously shown to compromise the fusogenicity of the Vesicular Stomatitis virus G-protein ...
08-Jun-2012
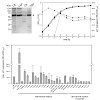
Two-component systems (TCSs) consisting of a membrane-anchored histidine kinase (HK) and a response regulator (RR) are major players in signal transduction in prokaryotes. Whereas most TCSs in Escherichia coli are well characterized, almost nothing is known about the LytS-like HK YehU and the corresponding LytTR-like RR YehT. To identify YehT-regulated genes, we ...
01-Jun-2012
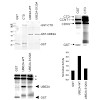
Cyclin-dependent kinase-9 (CDK9) plays a central role in transcriptional elongation and controls multiple cotranscriptional histone modifications, including histone H2B monoubiquitination (H2Bub1). Like other CDK9-dependent histone modifications, the role of CDK9 in maintaining H2Bub1 was shown to be partially dependent upon the phosphorylation status of Ser2 of ...
01-Jun-2012

Sesterterpenoids account for many bioactive natural products, often with unusual and complex structural features, which makes them attractive targets for synthetic chemists. This review surveys efforts undertaken toward the synthesis of sesterterpenoids, focusing on completed total syntheses and covering ca. 50 natural products in total.
01-Jun-2012

HSP90 is a central player in the folding and maturation of many proteins. More than two hundred HSP90 clients have been identified by classical biochemical techniques including important signaling proteins with high relevance to human cancer pathways. HSP90 inhibition has thus become an attractive therapeutic concept and multiple molecules are currently in ...
31-May-2012

A synthetic approach to several sesterterpenoids containing an isopropyl trans-hydrindane system is presented. Its most remarkable feature is the stereochemical diversification of a common precursor through the choice of different hydrogenation conditions.
Stereoselective Total Syntheses of Herbicidin C and Aureonuclemycin through Late-Stage Glycosylation
29-May-2012

Better late than never! Two herbicidins, members of an important family of nucleoside antibiotics, have been synthesized for the first time. The route integrates a stereoselective C-glycosylation with several reagent-controlled stereoselective transformations and a surprisingly facile and highly diastereoselective late-stage N-glycosylation.
29-May-2012
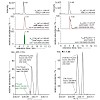
5-Methylcytosine (mC) is an important, well-known nucleobase modification that is involved in many biological processes, including gene expression, genomic imprinting, Xchromosome inactivation, and suppression of transposable elements.
28-May-2012

Therapeutic nanoparticles can be directed to cancer cells by incorporating selective targeting ligands. Here, we investigate the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mediated endocytosis of gene carriers (polyplexes) either targeted with natural EGF or GE11, a short synthetic EGFRbinding peptide. Highly sensitive live-cell fluorescence microcopy with single ...
25-May-2012

Non-adiabatic on-the-fly molecular dynamics (NA-O-MD) simulations require the electronic wavefunction, energy gradients, and derivative coupling vectors in every timestep. Thus, they are commonly restricted to the excited state dynamics of molecules with up to ≈20 atoms. We discuss an approximation that combines the ONIOM(QM:QM) method with NA-O-MD simulations to ...
24-May-2012
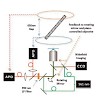
Three-dimensional tracking of single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNT) with an orbital tracking microscope is demonstrated. We determine the viscosity regime (above 250 cP) at which the rotational diffusion coefficient can be used for length estimation. We also demonstrate SWNT tracking within live HeLa cells and use these findings to spatially map corral volumes ...
18-May-2012

Microtubules (mt) are highly dynamic polymers composed of alpha- and beta-tubulin monomers that are present in all dividing and non-dividing cells. A broad variety of natural products exists that are known to interfere with the microtubule network, by either stabilizing or de-stabilizing these rope-like polymers. Among those tubulysins represent a new and potent ...
16-May-2012
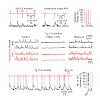
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by a progressive dysfunction of central neurons. Recent experimental evidence indicates that in the cortex, in addition to the silencing of a fraction of neurons, other neurons are hyperactive in amyloid-β (Aβ) plaque-enriched regions. However, it has remained unknown what comes first, neuronal silencing or hyperactivity, ...
11-May-2012

Fluorescent fusion proteins are widely used to study protein localization and interaction dynamics in living cells. However, to fully characterize proteins and to understand their function it is crucial to determine biochemical characteristics such as enzymatic activity and binding specificity. Here we demonstrate an easy, reliable and versatile ...
09-May-2012

The 3 life scientists Ulrike Gaul, Andreas Ladurner and Michael Sattler from CIPSM were today recognised by EMBO for their excellence in research. EMBO elects new members annually on the basis of scientific excellence. The selected researchers will help shape the direction of the life sciences in Europe and beyond by their involvement with the activities of the ...
08-May-2012
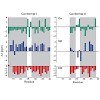
Aggregation of monomeric amyloid beta peptides (ABeta) into soluble oligomers and insoluble fibrils is one of the major pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer_s disease (AD). In the past few years, magic angle spinning (MAS) solid-state NMR spectroscopy has enabled considerable progress in the structural characterization of amyloid aggregates, and a number of ...
04-May-2012

Advances in fluorescence methodologies make it possible to investigate biological systems in unprecedented detail. Over the last few years, quantitative live-cell imaging has increasingly been used to study the dynamic interactions of viruses with cells and is expected to become even more indispensable in the future. Here, we describe different fluorescence ...
02-May-2012

Different bioactive molecules are released into living cells from lipid-covered mesoporous silica nanoparticles. The release is triggered by light, as the particles feature covalently attached photosensitizers as membrane-opening agents. It is demonstrated that the particles achieve endosomal escape and that they release their cargo into the cytosol.
01-May-2012
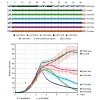
Eukaryotic RNA polymerase II (Pol II) has evolved an array of heptad repeats with the consensus sequence Tyr1-Ser2-Pro3-Thr4-Ser5-Pro6-Ser7 at the carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of the large subunit (Rpb1). Differential phosphorylation of Ser2, Ser5, and Ser7 in the 5′ and 3′ regions of genes coordinates the binding of transcription and RNA processing factors to ...
30-Apr-2012
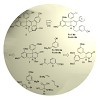
A concise asymmetric approach to the indeno-tetrahydropyridine core of the unusual alkaloid haouamine B allowed for an investigation of a biomimetic oxidative phenol coupling as a proposed biosynthetic step, and ultimately provided access to the published structure of the natural product. As a consequence of our synthetic studies, the structure of haouamine B has ...
27-Apr-2012
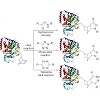
Methods for the site-specific chemical modification of proteins are currently of immense importance for the synthesis of protein–hybrid compounds for pharmaceutical and diagnostic purposes. Most of the methods rely on the reaction of free protein thiols with maleimides or the reaction of lysine side chains with activated esters. These methods provide only limited ...
26-Apr-2012

RNA synthesis and decay rates determine the steady-state levels of cellular RNAs. Metabolic tagging of newly transcribed RNA by 4-thiouridine (4sU) can reveal the relative contributions of RNA synthesis and decay rates. The kinetics of RNA processing, however, so far remained unresolved. Here, we show that ultra-short 4sU-tagging not only provides snap-shot ...
19-Apr-2012
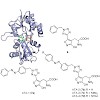
Light switch: A photochromic agonist ATA-3 (see scheme) of AMPA receptors, arguably the most important class of ionotropic glutamate receptors, is shown to be subtype selective, activates the AMPA receptor GluA2 in the dark, and is quickly turned off when irradiated with blue–green light. It can be used to effectively control neuronal activity in the mammalian brain.
19-Apr-2012
The transient receptor potential (TRP) channels TRPML1, TRPML2, and TRPML3 (also called mucolipins 1–3 or MCOLN1–3) are nonselective cation channels. Mutations in the Trpml1 gene cause mucolipidosis type IV in humans with clinical features including psychomotor retardation, corneal clouding, and retinal degeneration, whereas mutations in the Trpml3 gene cause ...
16-Apr-2012
Swi2/Snf2 (switch/sucrose non-fermentable) enzymes form a large and diverse class of proteins and multiprotein assemblies that remodel nucleic acid:protein complexes, using the energy of ATP hydrolysis. The core Swi2/Snf2 type ATPase domain belongs to the ‘helicase and NTP driven nucleic acid translocase’ superfamily 2 (SF2). It serves as a motor that ...
16-Apr-2012
The study of biologically active natural products has resulted in seminal contributions to our understanding of living systems. In the case of electrophilic natural products, the covalent nature of their interaction has largely facilitated the identification of their biological binding partners. In this review, we provide a comprehensive compilation of ...
13-Apr-2012
UV-induced cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) in the template DNA strand stall transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II (Pol II). If the nucleotide excision repair machinery does not promptly remove the CPDs, stalled Pol II creates a roadblock for DNA replication and subsequent rounds of transcription. Here we present evidence that Pol II has an intrinsic ...
10-Apr-2012
The accumulation of amyloid-β in the brain is an essential feature of Alzheimer’s disease. However, the impact of amyloid-β-accumulation on neuronal dysfunction on the single cell level in vivo is poorly understood. Here we investigate the progression of amyloid-β load in relation to neuronal dysfunction in the visual system of the APP23×PS45 mouse model of ...
10-Apr-2012
Intracellular vesicular trafficking is regulated by approximately 60 members of the Rab subfamily of small Ras-like GDP/GTP binding proteins. Rab proteins cycle between inactive and active states as well as between cytosolic and membrane bound forms. Membrane extraction/delivery and cytosolic distribution of Rabs is mediated by interaction with the protein GDP ...
09-Apr-2012

Cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channels play a pivotal role in phototransduction. Mutations in the cone CNG channel subunits CNGA3 and CNGB3 account for >70% of all known cases of achromatopsia. Cones degenerate in achromatopsia patients and in CNGA3−/− and CNGB3−/− mice. This work investigates the molecular basis of cone degeneration in CNG channel deficiency. As ...
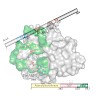
05-Apr-2012
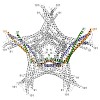
The Ska complex is an essential mitotic component required for accurate cell division in human cells. It is composed of three subunits that function together to establish stable kinetochore-microtubule interactions in concert with the Ndc80 network. We show that the structure of the Ska core complex is a W-shaped dimer of coiled coils, formed by intertwined ...
04-Apr-2012

Molecular self-assembly with DNA enables the construction of soluble objects with nanometer to micrometer scale absolute dimensions and custom chemical features, including crystals, patterns, bricks, boxes, and curved shapes, that can open novel paths to scientific discovery. Herein, we report on DNA nanoplates for nanopore-based sensing approaches. Nanopores in ...
30-Mar-2012
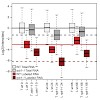
To monitor eukaryotic mRNA metabolism, we developed comparative Dynamic Transcriptome Analysis (cDTA). cDTA provides absolute rates of mRNA synthesis and decay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Sc) cells with the use of Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Sp) as internal standard. cDTA uses non-perturbing metabolic labeling that supersedes conventional methods for mRNA ...
29-Mar-2012
The histone variant H2A.Z has been implicated in many biological processes, such as gene regulation and genome stability. Here, we present the identification of H2A.Z.2.2 (Z.2.2), a novel alternatively spliced variant of histone H2A.Z and provide a comprehensive characterization of its expression and chromatin incorporation properties. Z.2.2 mRNA is found in all ...
26-Mar-2012

In a recent study we described the second periplasmic loop P2 of the transmembrane protein MalF (MalF-P2) of the maltose ATP-binding cassette transporter (MalFGK2-E) as an important element in the recognition of substrate by the maltose-binding protein MalE. In this study, we focus on MalE and find that MalE undergoes a structural rearrangement after addition of ...
16-Mar-2012
Two hemithioindigo–hemistilbene (HTI) derivatives, designed to operate as structural switches in peptides, as well as two HTI peptides are characterized by ultrafast spectroscopy in the visible and the infrared. The two HTI switches follow the reaction scheme published for other HTI compounds with a picosecond excited state reaction (τ1 ≈ 6 ps) and isomerization ...
16-Mar-2012

Arabidopsis thaliana contains two photosynthetically competent chloroplast-targeted ferredoxin-NADP+ oxidoreductase (FNR) isoforms that are largely redundant in their function. Nevertheless, the FNR isoforms also display distinct molecular phenotypes, as only the FNR1 is able to directly bind to the thylakoid membrane. We report the consequences of depletion of ...
15-Mar-2012
Hsp90 is a dimeric molecular chaperone required for the activation and stabilization of numerous client proteins many of which are involved in essential cellular processes like signal transduction pathways. This activation process is regulated by ATP-induced large conformational changes, co-chaperones and posttranslational modifications. For some co-chaperones, a ...
15-Mar-2012
The unusual cyclin-dependent protein kinase 5 (CDK5) was discovered based on its sequence homology to cell cycle regulating CDKs. CDK5 was found to be active in brain tissues, where it is not involved in cell cycle regulation but in the regulation of neuronal cell differentiation and neurocytoskeleton dynamics. An aberrant regulation of CDK5 leads to the ...
15-Mar-2012
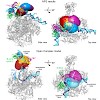
The open promoter complex (OC) is a central intermediate during transcription initiation that contains a DNA bubble. Here, we employ single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer experiments and Nano-Positioning System analysis to determine the three-dimensional architecture of a minimal OC consisting of promoter DNA, including a TATA box and an 11-nucleotide ...
14-Mar-2012

The diffusion dynamics of terrylene diimide (TDI) dye molecules and dye-labeled double-strand DNA were studied in micrometer long silica filaments containing collinear, oriented mesopores using single molecule fluorescence microscopy. TDI was used as a stable and hydrophobic probe molecule for single molecule structural analysis. We used template-free mesoporous ...
13-Mar-2012
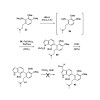
The evolution of a total synthesis of the exiguamines, two structurally unusual natural products that are highly active inhibitors of indolamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), is described. The ultimately successful strategy involves advanced cross-coupling methodology and features a potentially biosynthetic tautomerization/ electrocyclization cascade reaction that forms ...
08-Mar-2012
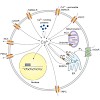
Calcium ions generate versatile intracellular signals that control key functions in all types of neurons. Imaging calcium in neurons is particularly important because calcium signals exert their highly specific functions in well-defined cellular subcompartments. In this Primer, we briefly review the general mechanisms of neuronal calcium signaling. We then ...
07-Mar-2012
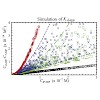
Fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy (FCCS) is used to determine interactions and dissociation constants (Kds) of biomolecules. The determination of a Kd depends on the accurate measurement of the auto- and cross-correlation function (ACF and CCF) amplitudes. In the case of complete binding, the ratio of the CCF/ACF amplitudes is expected to be 1. However, ...
07-Mar-2012

After elucidation of the atomic details of 20S proteasomes, current research focuses on the regulatory 19S particle. In this issue of Structure, He et al. present the crystal structure of Rpn2 and use electron microscopy to examine differences between Rpn2 and Rpn1.
06-Mar-2012

RNA polymerase (Pol) I contains a 10-subunit catalytic core that is related to the core of Pol II and includes subunit A12.2. In addition, Pol I contains the heterodimeric subcomplexes A14/43 and A49/34.5, which are related to the Pol II subcomplex Rpb4/7 and the Pol II initiation factor TFIIF, respectively. Here we used lysine-lysine crosslinking, mass ...
03-Mar-2012
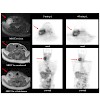
Imaging of angiogenesis has become increasingly important with the rising use of targeted antiangiogenic therapies like bevacizumab (Avastin). Non-invasive assessment of angiogenic activity is in this respect interesting, e.g. for response assessment of such targeted antiangiogenic therapies. One promising approach of angiogenesis imaging is imaging of specific ...
02-Mar-2012
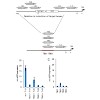
Specific control of gene activity is a valuable tool to study and engineer cellular functions. Recent studies uncovered the potential of transcription activator-like effector (TALE) proteins that can be tailored to activate user-defined target genes. It remains however unclear whether and how epigenetic modifications interfere with TALE-mediated transcriptional ...
01-Mar-2012

The histone variant macroH2A generally associates with transcriptionally inert chromatin; however, the factors that regulate its chromatin incorporation remain elusive. Here, we identify the SWI/SNF helicase ATRX (alpha-thalassemia/ MR, X-linked) as a novel macroH2A-interacting protein. Unlike its role in assisting H3.3 chromatin deposition, ATRX acts as a ...
01-Mar-2012

Single-pair Förster resonance energy transfer (spFRET) experiments using single-molecule burst analysis on a confocal microscope are an ideal tool to measure inter- and intramolecular distances and dynamics on the nanoscale. Different techniques have been developed to maximize the amount of information available in spFRET burst analysis experiments. ...
27-Feb-2012
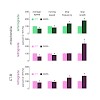
Axonal transport deficits have been reported in many neurodegenerative conditions and are widely assumed to be an immediate causative step of axon and synapse loss. By imaging changes in axonal morphology and organelle transport over time in several animal models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), we now find that deficits in axonal transport of organelles ...
24-Feb-2012

Hsp90 is an essential molecular chaperone in the eukaryotic cytosol. Its function is modulated by cochaperones and posttranslational modifications. Importantly, the phosphatase Ppt1 is a dedicated regulator of the Hsp90 chaperone system. Little is known about Ppt1-dependent phosphorylation sites and how these affect Hsp90 activity. Here, we identified the major ...
24-Feb-2012

Hypochlorite is a powerful oxidant produced by neutrophils to kill invading microorganisms. Despite this important physiological role of HOCl in fighting bacterial infections, no hypochlorite-specific stress response has been identified yet. Here, we identified a hypochlorite-responsive transcription factor, YjiE, which is conserved in proteobacteria and ...
23-Feb-2012
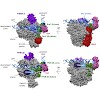
Recent studies of the three eukaryotic transcription machineries revealed that all initiation complexes share a conserved core. This core consists of the RNA polymerase (I, II, or III), the TATA box-binding protein (TBP), and transcription factors TFIIB, TFIIE, and TFIIF (for Pol II) or proteins structurally and functionally related to parts of these factors (for ...
23-Feb-2012
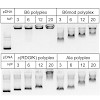
In the forthcoming era of cancer gene therapy, efforts will be devoted to the development of new efficient and non-toxic gene delivery vectors. In this regard, the use of Fmoc/Boc-protected oligo(ethane amino)acids as building blocks for solid-phase-supported assembly represents a novel promising approach towards fully controlled syntheses of effective gene ...
23-Feb-2012
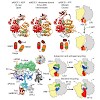
Ribosome-driven protein biosynthesis is comprised of four phases: initiation, elongation, termination and recycling. In bacteria, ribosome recycling requires ribosome recycling factor and elongation factor G, and several structures of bacterial recycling complexes have been determined. In the eukaryotic and archaeal kingdoms, however, recycling involves the ...
22-Feb-2012

The molecular conformation of proteins is sensitive to the nature of the aqueous environment. In particular, the presence of ions can stabilize or destabilize (denature) protein secondary structure. The underlying mechanisms of these actions are still not fully understood. Here, we combine circular dichroism (CD), single-molecule Förster resonance energy ...
21-Feb-2012
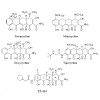
TP-434 is a novel, broad-spectrum fluorocycline antibiotic with activity against bacteria expressing major antibiotic resistance mechanisms, including tetracycline-specific efflux and ribosomal protection. The mechanism of action of TP-434 was assessed using both cell-based and in vitro assays. In Escherichia coli cells expressing recombinant tetracycline ...
19-Feb-2012
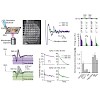
Local anesthetics effectively suppress pain sensation, but most of these compounds act nonselectively, inhibiting activity of all neurons. Moreover, their actions abate slowly, preventing precise spatial and temporal control of nociception. We developed a photoisomerizable molecule, quaternary ammonium–azobenzene–quaternary ammonium (QAQ), that enables rapid and ...
17-Feb-2012
Programmed cell death (PCD) in plants is a prerequisite for development as well as seed and fruit production. It also plays a significant role in pathogen defense. A unique group of papain-type cysteine endopeptidases, characterized by a C-terminal endoplasmic reticulum (ER) retention signal (KDEL CysEP), is involved in plant PCD. Genes for these endopeptidases ...
17-Feb-2012

Constitutive proteasomes and immunoproteasomes shape the peptide repertoire presented by major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) molecules by harboring different sets of catalytically active subunits. Here, we present the crystal structures of constitutive proteasomes and immunoproteasomes from mouse in the presence and absence of the epoxyketone ...
15-Feb-2012
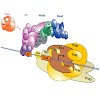
Gene transcription by RNA polymerase II requires the multiprotein coactivator complex Mediator. Mediator was identified two decades ago, but its molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood, because structural studies are hampered by its large size, modularity, and flexibility. Here we collect all available structural data on Mediator and discuss their ...
15-Feb-2012

The nucleus contains a plethora of different dynamic structures involved in the regulation and catalysis of nucleic acid metabolism and function. Over the past decades countless factors, molecular structures, interactions and posttranslational modifications have been described in this context. On the one side of the size scale X-ray crystallography delivers ...
14-Feb-2012
Active muscles generate substantial mechanical forces by the contraction/relaxation cycle, and, to maintain an ordered state, they require molecular structures of extraordinary stability. These forces are sensed and buffered by unusually long and elastic filament proteins with highly repetitive domain arrays. Members of the myomesin protein family function as ...
13-Feb-2012

Oxidative degradation of DNA is a major mutagenic process. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced in the course of oxidative phosphorylation or by exogenous factors are known to attack preferentially deoxyguanosine. The latter decomposes to give mutagenic lesions, which under physiological conditions are efficiently repaired by specialized maintenance systems in ...
12-Feb-2012

Analytical advantages of using multiple enzymes for sample digestion (MED), primarily an increase of sequence coverage, have been reported in several studies. However, this approach is only rarely used, mainly because it requires additional sample and mass spectrometric measurement time. We have previously described Filter Aided Sample Preparation (FASP), a type ...
10-Feb-2012

One of the earliest steps in metazoan pre-mRNA splicing involves binding of U2 snRNP auxiliary factor (U2AF) 65 KDa subunit to the polypyrimidine (Py) tract and of the 35 KDa subunit to the invariant AG dinucleotide at the intron 3′ end. Here we use in vitro and in vivo depletion, as well as reconstitution assays using purified components, to identify hnRNP A1 as ...
09-Feb-2012
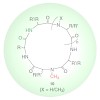
This protocol presents a detailed description of the synthesis of N-methylated cyclic peptides. N-methylation is a powerful technique to modulate the physicochemical properties of peptides by introducing one or more methyl groups into the peptidic amide bonds. Together with peptide cyclization, this procedure confers unprecedented pharmacokinetic properties to ...
09-Feb-2012

The action of cytosolic RIG-I–like helicases (RLHs) in the CNS during autoimmunity is largely unknown. Using a mouse model of multiple sclerosis, we found that mice lacking the RLH adaptor IPS-1 developed exacerbated disease that was accompanied by markedly higher inflammation, increased axonal damage and elevated demyelination with increased encephalitogenic ...
07-Feb-2012

Pyrrolysine is the 22nd amino acid that is encoded by the natural genetic code. In the archaebacterial family Methanosarcinaceae, its incorporation into three proteins (MtmB, MtbB, and MttB) involved in the methylamine catabolic pathway is specified by the amber stop codon UAG. The unusual amino acid was discovered in 2002 by crystallography and mass spectrometry ...
06-Feb-2012

Isoprenoids derive from two universal precursors, isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate, which in most human pathogens are synthesized in the deoxyxylulose phosphate pathway. The last step of this pathway is the conversion of (E)-1-hydroxy-methylbut-2-enyl-4-diphosphate into a mixture of isopentenyl diphosphate and dimethylallyl diphosphate ...
06-Feb-2012

Cancer is the No. 2 cause of death in the Western world and one of the most expensive diseases to treat. Thus, it is not surprising, that every major pharmaceutical and biotechnology company has a blockbuster oncology product. In 2003, Millennium Pharmaceuticals entered the race with Velcades, a first-in-class proteasome inhibitor that has been approved by the ...
03-Feb-2012

The Legionella pneumophila protein AnkX that is injected into infected cells by a Type IV secretion system transfers a phosphocholine group from CDP-choline to a serine in the Rab1 and Rab35 GTPase Switch II regions. We show here that the consequences of phosphocholination on the interaction of Rab1/Rab35 with various partner proteins are quite distinct. ...
03-Feb-2012
Polycomb repressor complexes (PRCs) are important chromatin modifiers fundamentally implicated in pluripotency and cancer. Polycomb silencing in embryonic stem cells (ESCs) can be accompanied by active chromatin and primed RNA polymerase II (RNAPII), but the relationship between PRCs and RNAPII remains unclear genome-wide. We mapped PRC repression markers and ...
01-Feb-2012
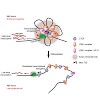
The key haematopoietic regulator Myb is essential for coordinating proliferation and differentiation. ChIPSequencing and Chromosome Conformation Capture (3C)-Sequencing were used to characterize the structural and protein-binding dynamics of the Myb locus during erythroid differentiation. In proliferating cells expressing Myb, enhancers within the Myb-Hbs1l ...
01-Feb-2012
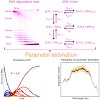
RNA exosomes are large multi-subunit protein complexes involved in controlled and processive 3' to 5' RNA degradation. Exosomes form large molecular chambers and harbor multiple nuclease sites as well as RNA binding regions. This makes a quantitative kinetic analysis of RNA degradation with reliable parameter and error estimates challenging. For instance, recent ...
01-Feb-2012
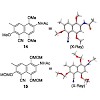
A robust and scalable synthesis of a novel, cyano-substituted Danishefsky-type diene and its use in the Diels-Alder reaction with various dienophiles is reported. The diene allows for the rapid construction of highly substituted aminonaphthoquinones that occur in numerous ansamycin antibiotics.
31-Jan-2012

Centromeres are important structural constituents of chromosomes that ensure proper chromosome segregation during mitosis by providing defined sites for kinetochore attachment. In higher eukaryotes, centromeres have no specific DNA sequence and thus, they are rather determined through epigenetic mechanisms. A fundamental process in centromere establishment is the ...
30-Jan-2012
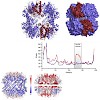
The barrel-shaped ClpP protease is a main virulence regulator in the bacterial pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. It consists of two heptameric rings forming a omo-tetradecamer with an inner chamber that houses the 14 active sites. We recently showed that SaClpP3 is able to adopt a compressed, inactive conformation. We here present the 2.3 Å resolution structure of ...
25-Jan-2012

In addition to redox regulation, protein phosphorylation has gained increasing importance as a regulatory principle in chloroplasts in recent years. However, only very few chloroplast-localized protein kinases have been identified to date. Protein phosphorylation regulates important chloroplast processes such as photosynthesis or transcription. In order to better ...
20-Jan-2012

Chromatin-modifying enzymes have long been proposed to be the authors of an epigenetic language, but the origin and meaning of the messages they write in chromatin are still mysterious. Recent studies suggesting that the effects of diet can be passed on epigenetically to offspring add weight to the idea that histones act as metabolic sensors, converting changes ...
15-Jan-2012
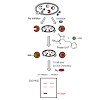
Here, we report the synthesis and in depth characterization of a second generation β-lactone derived virulence inhibitors. Based on initial results that emphasized the intriguing possibility to disarm bacteria in their virulence the present study develops this concept further and analyses the potential of this strategy for drug development. We were able to expand ...
12-Jan-2012
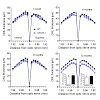
Purpose. To investigate rod function and survival after cone dysfunction and degeneration in a mouse model of cone cyclic nucleotide-gated (CNG) channel deficiency. Methods. Rod function and survival in mice with cone CNG channel subunit CNGA3 deficiency (CNGA3−/− mice) were evaluated by electroretinographic (ERG), morphometric, and Western blot analyses. The ...
10-Jan-2012

5-Methylcytosine (5 mC) in genomic DNA has important epigenetic functions in embryonic development and tumor biology. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine (5 hmC) is generated from 5 mC by the action of the TET (Ten-Eleven-Translocation) enzymes and may be an intermediate to further oxidation and finally demethylation of 5 mC. We have used immunohistochemistry (IHC) and ...
10-Jan-2012
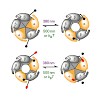
Advances in synthetic chemistry, structural biology, molecular modelling and molecular cloning have enabled the systematic functional manipulation of transmembrane proteins. By combining genetically manipulated proteins with lightsensitive ligands, innately ‘blind’ neurobiological receptors can be converted into photoreceptors, which allows them to be ...
09-Jan-2012
Living organisms exposed to sunlight are constantly challenged by the formation of UV-induced lesions in DNA, which induce cell death and cause mutations. UVirradiation of TpT and TpC sequences leads to the formation of two primary lesions, namely cyclobutane-pyrimidine dimers (CPD)and lesions, as depicted in Scheme 1. These lesions possess an additional ...
09-Jan-2012
The efrapeptin family of peptide antibiotics produced by the fungus Tolypocladium niveum, and the neo-efrapeptins from the fungus Geotrichum candidumare inhibitors of F1-ATPase with promising antitumor, antimalaria, and insecticidal activity. They are rich in Cα-dialkyl amino acids (Aib, Iva, Acc) and contain one β-alanine and several pipecolic acid residues. The ...
09-Jan-2012

Structural information is key for understanding biological processes. Insoluble proteins, like membrane proteins and amyloid fibrils, are a large class of proteins that are underrepresented in the protein data bank (PDB). As of today, only 7% of all entries in the PDB refer to either a membrane protein or an amyloid fibril structure (membrane protein: 4994 ...
08-Jan-2012
More than 70 years of studies have indicated that chloroplasts contain a significant amount of calcium, are a potential storage compartment for this ion, and might themselves be prone to calcium regulation. Many of these studies have been performed on the photosynthetic light reaction as well as CO2 fixation via the Calvin–Benson–Bassham cycle, and they showed ...
08-Jan-2012
Chromodomains typically recruit protein complexes to chromatin and read the epigenetic histone code by recognizing lysine methylation in histone tails. We report the crystal structure of the chloroplast signal recognition particle (cpSRP) core from Arabidopsis thaliana, with the cpSRP54 tail comprising an arginine-rich motif bound to the second chromodomain of ...
08-Jan-2012

A large part of higher eukaryotic genomes is transcribed into RNAs lacking any significant open reading frame. This “non-coding part” has been shown to actively contribute to regulating gene expression, but the mechanisms are largely unknown. Particularly instructive examples are provided by the dosage compensation systems, which assure that the single X ...
06-Jan-2012

Lamin B receptor (LBR) is a polytopic protein of the nuclear envelope thought to connect the inner nuclear membrane with the underlying nuclear lamina and peripheral heterochromatin. To better understand the function of this protein, we have examined in detail its nucleoplasmic region, which is predicted to harbor a Tudor domain (LBR-TD). Structural analysis by ...
06-Jan-2012

Sti1/Hop is a modular protein required for the transfer of client proteins from the Hsp70 to the Hsp90 chaperone system in eukaryotes. It binds Hsp70 and Hsp90 simultaneously via TPR (tetratricopeptide repeat) domains. Sti1/Hop contains three TPR domains (TPR1, TPR2A and TPR2B) and two domains of unknown structure (DP1 and DP2). We show that TPR2A is the high ...
06-Jan-2012

The human small heat-shock protein alphaB-crystallin (alphaB) rescues misfolded proteins from irreversible aggregation during cellular stress. Binding of Cu(II) was shown to modulate the oligomeric architecture and the chaperone activity of alphaB. However, the mechanistic basis of this stimulation is so far not understood. We provide here first structural ...
05-Jan-2012

High resolution proton spectra are obtained in MAS solid-state NMR in case samples are prepared using perdeuterated protein and D2O in the recrystallization buffer. Deuteration reduces drastically 1H, 1H dipolar interactions and allows to obtain amide proton line widths on the order of 20 Hz. Similarly, high-resolution proton spectra of aliphatic groups can be ...
04-Jan-2012
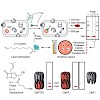
Activity-based protein profiling (ABPP) employs small molecule probes to profile their dedicated targets in complex proteomes. Unlike traditional proteomics which is limited on protein abundance, probes that selectively target the active site of certain proteins are a benign measure of protein activity and provide tools for functional analysis. ABPP probes have ...
03-Jan-2012

The molecular chaperone and heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) exists mainly as a homodimer in the cytoplasm. Each monomer has an ATPase in its N-terminal domain and undergoes large conformational changes during Hsp90’s mechanochemical cycle. The threecolor single-molecule assay and data analysis presented in the following allows one to observe at the same time ...
02-Jan-2012

Calcium has long been acknowledged as one of the most important signalling components in plants. Many abiotic and biotic stimuli are transduced into a cellular response by temporal and spatial changes in cellular calcium concentration and the calcium-sensitive protein aequorin has been exploited as a genetically encoded calcium indicator for the measurement of ...
01-Jan-2012
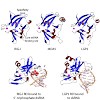
The innate immune system is a first layer of defense against infection by pathogens. It responds to pathogens by activating host defense mechanisms via interferon and inflammatory cytokine expression. Pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are sensed by specific pattern recognition receptors. Among those, the ATP dependent helicase related RIG-I like ...
01-Jan-2012

Tetraalkylcuprates are prototypical examples of organocopper(III) species, which remained elusive until their recent detection by NMR spectroscopy. In agreement with the NMR studies, the present electrospray ionization mass spectrometric experiments, as well as supporting electrical conductivity measurements, indicate that LiCuMe2·LiCN reacts with a series of ...
01-Jan-2012
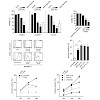
A key host response to limit microbial spread is the induction of cell death when foreign nucleic acids are sensed within infected cells. In mouse macrophages, transfected DNA or infection with modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) can trigger cell death via the absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) inflammasome. In this article, we show that nonmyeloid human cell types ...