News 2018
31-Dec-2018

Phosphorylation of the carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) governs stage-specific interactions with different cellular machines. The CTD consists of Y1S2P3T4S5P6S7 heptad repeats and sequential phosphorylations of Ser7, Ser5 and Ser2 occur universally at Pol II-transcribed genes. Phosphorylation of Thr4, however, ...
17-Dec-2018

It’s Christmas and we at CIPSM just wanted to say
Thank you and that it’s been a pleasure working with you this past year.
We wish you and your family wonderful holidays and a Happy New Year!
22-Nov-2018
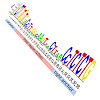
Mammalian-wide interspersed repeats (MIRs) are retrotransposed elements of mammalian genomes. Here, we report the specific binding of zinc finger protein ZNF768 to the sequence motif GCTGTGTG (N20) CCTCTCTG in the core region of MIRs. ZNF768 binding is preferentially associated with euchromatin and promoter regions of genes. Binding was observed for genes ...
21-Nov-2018
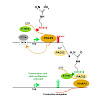
The post-translational modification of key residues at the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II (RNAP2-CTD) coordinates transcription, splicing, and RNA processing by modulating its capacity to act as a landing platform for a variety of protein complexes. Here, we identify a new modification at the CTD, the deimination of arginine and its conversion to ...
08-Nov-2018

The antibody light chain (LC) consists of two domains and is essential for antigen binding in mature immunoglobulins. The two domains are connected by a highly conserved linker that comprises the structurally important Arg108 residue. In antibody light chain (AL) amyloidosis, a severe protein amyloid disease, the LC and its N-terminal variable domain (VL) convert ...
07-Nov-2018
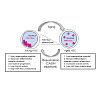
Background
The decline of hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) function upon aging contributes to aging-associated immune remodeling and leukemia pathogenesis. Aged HSCs show changes to their epigenome, such as alterations in DNA methylation and histone methylation and acetylation landscapes. We previously showed a correlation between high Cdc42 activity in aged HSCs ...
01-Nov-2018
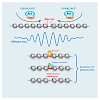
Regular successions of positioned nucleosomes, or phased nucleosome arrays (PNAs), are predominantly known from transcriptional start sites (TSSs). It is unclear whether PNAs occur elsewhere in the genome. To generate a comprehensive inventory of PNAs for Drosophila, we applied spectral analysis to nucleosome maps and identified thousands of PNAs throughout the ...
26-Oct-2018

The glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is a prominent nuclear receptor linked to a variety of diseases and an important drug target. Binding of hormone to its ligand binding domain (GR-LBD) is the key activation step to induce signaling. This process is tightly regulated by the molecular chaperones Hsp70 and Hsp90 in vivo. Despite its importance, little is known about ...
17-Oct-2018

Many evolutionarily distant pathogenic organisms have evolved similar survival strategies to evade the immune responses of their hosts. These include antigenic variation, through which an infecting organism prevents clearance by periodically altering the identity of proteins that are visible to the immune system of the host. Antigenic variation requires large ...
18-Sep-2018
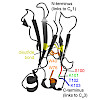
Despite their importance for antibody architecture and design, the principles governing antibody domain stability are still not understood in sufficient detail. Here, to address this question, we chose a domain from the invariant part of IgG, the CH2 domain. We found that compared with other Ig domains, the isolated CH2 domain is a surprisingly unstable monomer, ...
03-Sep-2018
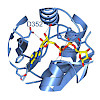
MacroH2A histone variants suppress tumor progression and act as epigenetic barriers to induced pluripotency. How they impart their influence on chromatin plasticity is not well understood. Here, we analyze how the different domains of macroH2A proteins contribute to chromatin structure and dynamics. By solving the crystal structure of the macrodomain of human ...
31-Aug-2018

Single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer (smFRET) is increasingly being used to determine distances, structures, and dynamics of biomolecules in vitro and in vivo. However, generalized protocols and FRET standards to ensure the reproducibility and accuracy of measurements of FRET efficiencies are currently lacking. Here we report the results of a ...
20-Aug-2018

The nature of chromatin as regular succession of nucleosomes has gained iconic status. However, since most nucleosomes in metazoans are poorly positioned it is unknown to which extent bulk genomic nucleosome repeat length reflects the regularity and spacing of nucleosome arrays at individual loci. We describe a new approach to map nucleosome array regularity and ...
25-Jul-2018

Background
Epigenome-wide association studies (EWAS) based on human brain samples allow a deep and direct understanding of epigenetic dysregulation in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, strong variation of cell-type proportions across brain tissue samples represents a significant source of data noise. Here, we report the first EWAS based on sorted neuronal and ...
18-Jul-2018
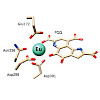
Interest in the bioinorganic chemistry of lanthanides is growing rapidly as more and more lanthanide-dependent bacteria are being discovered. Especially the earlier lanthanides have been shown to be preferentially utilized by bacteria that need these Lewis acids as cofactors in their alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes. Here, we investigate the impact of the lanthanide ...
18-Jul-2018
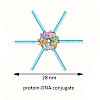
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) has been instrumental to determine the structure and dynamics of biomolecules but distances above 8 nanometer are not accessible. However, with the advent and rapid development of super-resolution (SR) microscopy, distances between two fluorescent dyes below 20 nanometer can be resolved, which hitherto has been ...
01-Jul-2018
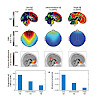
A major mystery of many types of neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), remains the underlying, disease-specific neuronal damage. Because of the strong interconnectivity of neurons in the brain, neuronal dysfunction necessarily disrupts neuronal circuits. In this article, we review evidence for the disruption of large-scale ...
28-Jun-2018
Photoisomerization reactions are quintessential processes driving molecular machines and motors, govern smart materials, catalytic processes, and photopharmacology, and lie at the heart of vision, phototaxis, or vitamin production. Despite this plethora of applications fundamental photoisomerization mechanisms are not well understood at present. The famous ...
28-Jun-2018
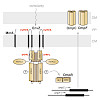
Although distinct amino acid motifs containing consecutive prolines (polyP) cause ribosome stalling, which necessitates recruitment of the translation elongation factor P (EF-P), they occur strikingly often in bacterial proteomes. For example, polyP motifs are found in more than half of all histidine kinases in Escherichia coli K-12, which raises the question of ...
27-Jun-2018
Constitutive NF-κB signaling represents a hallmark of chronic inflammation and autoimmune diseases. The E3 ligase TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) acts as a key regulator bridging innate immunity, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and antigen receptors to the canonical NF-κB pathway. Structural analysis and point mutations have unraveled the essential role of ...
26-Jun-2018
Post-transcriptional mechanisms play a predominant role in the control of microRNA (miRNA) production. Recognition of the terminal loop of precursor miRNAs by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) influences their processing; however, the mechanistic basis for how levels of individual or subsets of miRNAs are regulated is mostly unexplored. We previously showed that hnRNP ...
25-Jun-2018

The need for new pharmacological lead structures, especially against drug resistances, has led to a surge in natural product research and discovery. New biosynthetic gene cluster capturing methods to efficiently clone and heterologously express natural product pathways have thus been developed. Direct pathway cloning (DiPaC) is an emerging synthetic biology ...
22-Jun-2018

Molecular motors undergo repetitive directional motions upon external energy input. A profound challenge is the defined transfer of directional motor motions to remote entities at the molecular scale. Herein, we present a molecular setup that allows for the transfer of the directional rotation of a light‐powered motor unit onto a remote biaryl axis via an ...
14-Jun-2018
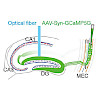
The ability to remember and to navigate to safe places is necessary for survival. Place navigation is known to involve medial entorhinal cortex (MEC)-hippocampal connections. However, learning-dependent changes in neuronal activity in the distinct circuits remain unknown. Here, by using optic fiber photometry in freely behaving mice, we discovered the ...
11-Jun-2018
Checkpoint molecules such as programmed death 1 (PD-1) dampen excessive T cell activation to preserve immune homeostasis. PD-1-specific monoclonal antibodies have revolutionized cancer therapy, as they reverse tumour-induced T cell exhaustion and restore CTL activity. Based on this success, deciphering underlying mechanisms of PD-1-mediated immune functions has ...
29-May-2018
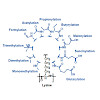
The analysis of the post-translational modification (PTM) state of proteins using mass spectrometry-based bottom-up proteomic workflows has evolved into a powerful tool for the study of cellular regulatory events that are not directly encoded at the genome level. Besides frequently detected modifications such as phosphorylation, acetylation and ubiquitination, ...
23-May-2018
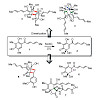
The sorbicillinoids are a large family of fungal natural products, many of which possess highly challenging molecular architectures. Depending on their individual structures they exhibit strong biological activities ranging from radical scavenging and anti‐infective properties to cytotoxicity. Despite the resulting strong biomedical potential of these natural ...
15-May-2018

Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (ssNMR) is a spectroscopic technique that is used for characterization of molecular properties in the solid phase at atomic resolution. In particular, using the approach of magic-angle spinning (MAS), ssNMR has seen widespread applications for topics ranging from material sciences to catalysis, metabolomics, and structural ...
11-May-2018
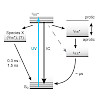
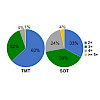
The decay of electronically excited states of thymine (Thy) and thymidine 5′-monophosphate (TMP) was studied by time-resolved UV/vis and IR spectroscopy. In addition to the well-established ultrafast internal conversion to the ground state, a so far unidentified UV-induced species is observed. In D2O, this species decays with a time constant of 300 ps for thymine ...
04-May-2018

Pore-forming toxins (PFT) are virulence factors that transform from soluble to membrane-bound states. The Yersinia YaxAB system represents a family of binary α-PFTs with orthologues in human, insect, and plant pathogens, with unknown structures. YaxAB was shown to be cytotoxic and likely involved in pathogenesis, though the molecular basis for its two-component ...
29-Apr-2018
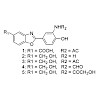
Actinomycetes are a relevant source of novel bioactive compounds. One of the pharmaceutically and biotechnologically important genera that attract natural products research is the genus Nocardiopsis, mainly for its ability to produce a wide variety of secondary metabolites accounting for its wide range of biological activities. This review covers the literature ...
25-Apr-2018
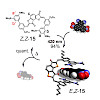
Indigoid photoswitches comprise a class of chromophores that are derived from the parent and well-known indigo dye. Different from most photoswitches their core structures absorb in the visible region of the spectrum in both isomeric states even without substitutions, which makes them especially interesting for applications not tolerant of high-energy UV light. ...
25-Apr-2018
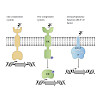
Every living cell possesses numerous transmembrane signalling systems that receive chemical and physical stimuli from the environment and transduce this information into an intracellular signal that triggers some form of cellular response. As unicellular organisms, bacteria require these systems for survival in rapidly changing environments. The receptors ...
24-Apr-2018
The Mongolian gerbil (Meriones unguiculatus) is widely used as a model organism for the human auditory system. Its hearing range is very similar to ours and it uses the same mechanisms for sound localization. The auditory circuits underlying these functions have been characterized. However, important mechanistic details are still under debate. To elucidate these ...
Von einer Helix zu einem kleinen Ring: Metadynamik‐inspirierte, selektive Liganden für αvβ6‐Integrin
16-Apr-2018
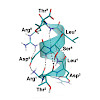
Das RGD‐erkennende Integrin αvβ6 trat in jüngster Zeit als vielbeachtete Zielstruktur für die Diagnostik und Therapie von Krebserkrankungen in Erscheinung. Infolgedessen besteht derzeit ein dringender Bedarf an niedermolekularen Liganden für diesen Rezeptor. Ein auf Metadynamik beruhender Ansatz ermöglichte die erfolgreiche Konvertierung eines helikalen ...
16-Apr-2018

Bearing in mind the often insufficient metabolic stability of carbohydrate antigens, which impairs both the bioavailability and immunogenicity of a given hapten, the development of chemically modified analogs with improved antigenicity is an important step towards effective glycoconjugate vaccines. Recently, strategic glycan fluorination has become an interesting ...
16-Apr-2018
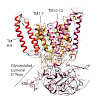
Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is a dimeric molecular chaperone that undergoes large conformational changes during its functional cycle. It has been established that conformational switch points exist in the N-terminal (Hsp90-N) and C-terminal (Hsp90-C) domains of Hsp90, however information for switch points in the large middle-domain (Hsp90-M) is scarce. Here we ...
14-Apr-2018
Substituted indigo derivatives undergo photoisomerization of the central double bond if both nitrogen atoms are functionalized. Indigo itself however does not photoisomerize because of a competing and highly efficient excited‐state proton transfer. In this work, we show that also mono‐arylated indigo undergoes photoisomerization despite still possessing one ...
13-Apr-2018

Remote control of complex molecular behavior and function is one key problem in modern chemistry. Using light signaling for this purpose has many advantages, however the integration of different photo processes into a wholesome yet complex system is highly challenging. Here we report an alternative approach to increase complexity of light control-simultaneous ...
13-Apr-2018

By N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU) mutagenesis, we generated the mutant mouse line TUB6 that is characterised by severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) and systemic sterile autoinflammation in homozygotes, and a selective T cell defect in heterozygotes. The causative missense point mutation results in the single amino acid exchange G170W in multicatalytic ...
13-Apr-2018
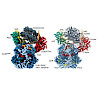
Protein synthesis, transport and N-glycosylation are coupled at the mammalian endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by complex formation between the ribosome, the Sec61 protein-conducting channel and the oligosaccharyltransferase (OST). Here, we used different cryo-electron microscopy approaches to determine structures of native and solubilized ribosome-Sec61-OST complexes. ...
12-Apr-2018

Wir freuen uns, dass der Bau unseres neuen CIPSM Gebäudes, das Institut für Chemische Epigenetik ICEM nun beginnt.
Damit Sie im Bilde sind und sich darauf einstellen können finden Sie hier die relevanten Eckdaten zur Baustelle Neubau ICEM:
1. Baustelleneinrichtung ab ca. 15.09.2017
2. Beginn Erdarbeiten/Spezialtiefbau ab ca. 30.09.2017
3. Beginn ...
11-Apr-2018
In the eukaryotic nucleus, DNA is packaged in the form of nucleosomes, each of which comprises about 147 base pairs of DNA wrapped around a histone protein octamer. The position and histone composition of nucleosomes is governed by ATP-dependent chromatin remodellers such as the 15-subunit INO80 complex. INO80 regulates gene expression, DNA repair and replication ...
PAM: A Framework for Integrated Analysis of Imaging, Single-Molecule, and Ensemble Fluorescence Data
10-Apr-2018
Fluorescence microscopy and spectroscopy data hold a wealth of information on the investigated molecules, structures, or organisms. Nowadays, the same fluorescence data set can be analyzed in many ways to extract different properties of the measured sample. Yet, doing so remains slow and cumbersome, often requiring incompatible software packages. Here, we present ...
01-Apr-2018

Alternative splicing generates distinct mRNA isoforms and is crucial for proteome diversity in eukaryotes. The RNA-binding protein (RBP) U2AF2 is central to splicing decisions, as it recognizes 3′ splice sites and recruits the spliceosome. We establish “in vitro iCLIP” experiments, in which recombinant RBPs are incubated with long transcripts, to study how U2AF2 ...
31-Mar-2018
Ultrastable cyclic peptide frameworks offer great potential for drug design due to their improved bioavailability compared to their linear analogues. Using the sunflower trypsin inhibitor-1 (SFTI-1) peptide scaffold in combination with systematic N-methylation of the grafted pharmacophore led to the identification of novel subtype selective melanocortin receptor ...
26-Mar-2018
Hemithioindigo-based molecular motors are powered by nondamaging visible light and provide very fast directional rotations at ambient conditions. Their ground state energy profile has been probed in detail, but the crucial excited state processes are completely unknown so far. In addition, very fast processes in the ground state are also still elusive to date and ...
21-Mar-2018
The recently discovered FeII/α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase AsqJ from Aspergillus nidulans stereoselectively catalyzes a multistep synthesis of quinolone alkaloids, natural products with significant biomedical applications. To probe molecular mechanisms of this elusive catalytic process, we combine here multi-scale quantum and classical molecular ...
19-Mar-2018
Many bacteria use extracellular signaling molecules to coordinate group behavior, a process referred to as quorum sensing (QS). However, some QS molecules are hydrophobic in character and are probably unable to diffuse across the bacterial cell envelope. How these molecules are disseminated between bacterial cells within a population is not yet fully understood. ...
13-Mar-2018
Specialized metabolites from bacteria are an important source of inspiration for drug development. The genes required for the biosynthesis of such metabolites in bacteria are usually organized in so-called biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs). Using modern bioinformatic tools, the wealth of genomic data can be scanned for such BGCs and the expected products can ...
08-Mar-2018

Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is associated with enhanced levels of the IL-1 family cytokines IL-1β and IL-18, which are activated by the Nlrp3 inflammasome. Here, we investigated the role of inflammasome-driven cytokine release on T cell polarization and DC differentiation in steady state and T cell transfer colitis. In vitro and in vivo data showed that ...
05-Mar-2018

NMR spectroscopy at ultra‐high magnetic fields requires improved radiofrequency (rf) pulses to cover the increased spectral bandwidth. Optimized 90° pulse pairs were introduced as Ramsey‐type cooperative (Ram‐COOP) pulses for biomolecular NMR applications. The Ram‐COOP element provides broadband excitation with enhanced sensitivity and reduced artifacts even at ...
28-Feb-2018
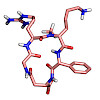
Specific targeting of the integrin subtype α5β1 possesses high potential in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Through sequential N-methylation, we successfully converted the biselective α5β1/αvβ6 peptide c(phg-isoDGR-k) into a potent peptidic RGD binding α5β1 subtype selective ligand c(phg-isoDGR-(NMe)k). Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and molecular modeling ...
28-Feb-2018
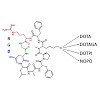
The epithelial integrin αvβ6 is expressed by many malignant carcinoma cell types, including pancreatic cancer, and thus represents a promising target for radionuclide therapy. The peptide cyclo(FRGDLAFp(NMe)K) was decorated with different chelators (DOTPI, DOTAGA, and DOTA). The Lu(III) complexes of these conjugates exhibited comparable αvβ6 integrin affinities ...
27-Feb-2018

Import of preproteins into chloroplasts is an essential process, requiring two major multisubunit protein complexes that are embedded in the outer and inner chloroplast envelope membrane. Both the translocon of the outer chloroplast membrane (Toc), as well as the translocon of the inner chloroplast membrane (Tic) have been studied intensively with respect to ...
26-Feb-2018

Solid-state NMR has been employed for characterization of a broad range of biomacromolecules and supramolecular assemblies. However, because of limitations in sensitivity and resolution, the size of the individual monomeric units has rarely exceeded 15 kDa. As such, enzymes, which are often more complex and comprise long peptide chains, have not been easily ...
24-Feb-2018
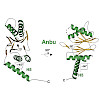
The 20S proteasome is a key player in eukaryotic and archaeal protein degradation, but its progenitor in eubacteria is unknown. Recently, the ancestral β-subunit protein (Anbu) was predicted to be the evolutionary precursor of the proteasome. We crystallized Anbu from Hyphomicrobium sp. strain MC1 in four different space groups and solved the structures by ...
24-Feb-2018

During the biogenesis of the mitochondrial inner membrane, most nuclear-encoded inner membrane proteins are laterally released into the membrane by the TIM23 and the TIM22 machinery during their import into mitochondria. A subset of nuclear-encoded mitochondrial inner membrane proteins and all the mitochondrial-encoded inner membrane proteins use the Oxa ...
22-Feb-2018
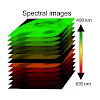
Raster image cross-correlation spectroscopy (ccRICS) can be used to quantify the interaction affinities between diffusing molecules by analyzing the fluctuations between two-color confocal images. Spectral crosstalk compromises the quantitative analysis of ccRICS experiments, limiting multicolor implementations to dyes with well-separated emission spectra. Here, ...
19-Feb-2018
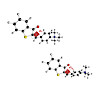
Hemithioindigo compounds are attractive two-way molecular photoswitches combining stilbene and thioindigo parts connected by a C–C double bond. In solution, these photoswitches have been well studied. This study presents the investigation of a hemithioindigo derivative in the gas phase. Visible absorption spectra, measured by standard (visPD) and helium-tagging ...
16-Feb-2018
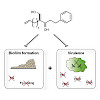
Staphylococcus aureus is a major bacterial pathogen that invades and damages host tissue by the expression of devastating toxins. We here performed a phenotypic screen of 35 molecules that were structurally inspired by previous hydroxyamide-based S. aureus virulence inhibitors compiled from commercial sources or designed and synthesized de novo. One of the most ...
14-Feb-2018
Expansion microscopy evolved as an interesting alternative in the field of super-resolution microscopy by physically expanding the target sample to increase its size by a multiple and to subsequently image the sample by conventional fluorescence microcopy. But the quantitative determination of the expansion factor remains challenging, since microscopic ...
12-Feb-2018

We explore the potential of DNA nanotechnology for developing novel optical voltage sensing nano-devices that convert a local change of electric potential into optical signals. As a proof-of-concept of the sensing mechanism, we assembled voltage responsive DNA origami structures labelled with a single pair of FRET dyes. The DNA structures were reversibly ...
09-Feb-2018
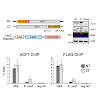
The chromatin remodeling complexes chromatin accessibility complex and ATP-utilizing chromatin assembly and remodeling factor (ACF) combine the ATPase ISWI with the signature subunit ACF1. These enzymes catalyze well-studied nucleosome sliding reactions in vitro, but how their actions affect physiological gene expression remains unclear. Here, we explored the ...
08-Feb-2018
All roads lead to Rome: The biosynthesis of the leporins in Aspergillus sp. involves an unprecedented pericyclic reaction cascade. The enzyme LepI directs the periselectivity of a [4+2] cycloaddition towards a hetero‐Diels–Alder reaction outcome to give the leporin molecular scaffold. The Diels–Alder side product is morphed into the leporin core structure by a ...
06-Feb-2018
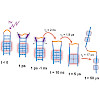
The light triggered unfolding reaction of the azobenzene peptide AzoTrpZip2 is investigated from 1 ps to 100 µs. Absorption changes show that the unfolding is a multistep process with the initial breaking of the hydrogen bonds in the vicinity of the AMPP chromophore on the 1 ns time scale followed by the disappearance of the remaining interstrand hydrogen bonds ...
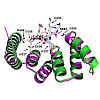
02-Feb-2018
Human cells are complex entities in which molecular recognition and selection are critical for cellular processes often driven by structural changes and dynamic interactions. Biomolecules appear in different chemical states and modifications like phosphorylation affect their function. Hence, using proteins in their chemically native state in biochemical and ...
01-Feb-2018
Translation of consecutive prolines causes ribosome stalling, which is alleviated but cannot be fully compensated by the elongation factor P. However, the presence of polyproline motifs in about one third of the E. coli proteins underlines their potential functional importance, which remains largely unexplored. We conducted an evolutionary analysis of polyproline ...
31-Jan-2018
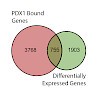
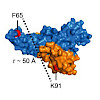
Objective: Homozygous loss-of-function mutations in the gene coding for the homeobox transcription factor (TF) PDX1 leads to pancreatic agenesis, whereas heterozygous mutations can cause Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young 4 (MODY4). Although the function of Pdx1 is well studied in pre-clinical models during insulin-producing β-cell development and homeostasis, ...
31-Jan-2018
Mitochondrial localized proteins are mostly synthesized in the cytosol and translocated across the outer mitochondrial membrane via the translocase of the outer membrane (TOM) complex. Although the channel protein is conserved among eukaryotes, the receptor proteins are more divergent and show features specific to the plant lineage. OM64, which is a paralogue of ...
19-Jan-2018

Classical structural biology can only provide static snapshots of biomacromolecules. Single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer (smFRET) paved the way for studying dynamics in macromolecular structures under biologically relevant conditions. Since its first implementation in 1996, smFRET experiments have confirmed previously hypothesized mechanisms and ...
19-Jan-2018
The use of dynamic, self-assembled DNA nanostructures in the context of nanorobotics requires fast and reliable actuation mechanisms. We therefore created a 55-nanometer–by–55-nanometer DNA-based molecular platform with an integrated robotic arm of length 25 nanometers, which can be extended to more than 400 nanometers and actuated with externally applied ...
19-Jan-2018

The ubiquitously expressed RNA-binding proteins Roquin-1 and Roquin-2 are essential for appropriate immune cell function and postnatal survival of mice. Roquin proteins repress target mRNAs by recognizing secondary structures in their 3′-UTRs and by inducing mRNA decay. However, it is unknown if other cellular proteins contribute to target control. To identify ...
16-Jan-2018

Understanding the activation and internalization of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) using conditional approaches is paramount to developing new therapeutic strategies. Here, we describe the design, synthesis, and testing of ExONatide, a benzylguanine-linked peptide agonist of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R), a class B GPCR required for ...
15-Jan-2018
The entatic state denotes a distorted coordination geometry of a complex from its typical arrangement that generates an improvement to its function. The entatic-state principle has been observed to apply to copper electron-transfer proteins and it results in a lowering of the reorganization energy of the electron-transfer process. It is thus crucial for a ...
11-Jan-2018
The molecules of life were created by a continuous physicochemical process on an early Earth. In this hadean environment, chemical transformations were driven by fluctuations of the naturally given physical parameters established for example by wet–dry cycles. These conditions might have allowed for the formation of (self)-replicating RNA as the fundamental ...
09-Jan-2018

The transcription factor c-Myc amplifies the transcription of many growth-related genes in cancer cells, but its role as an oncogene is not fully understood.
09-Jan-2018

Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels (HCNs) in the nervous system are implicated in a variety of neuronal functions including learning and memory, regulation of vigilance states and pain. Dysfunctions or genetic loss of these channels have been shown to cause human diseases such as epilepsy, depression, schizophrenia, and Parkinson's ...
08-Jan-2018
Modern proteomics requires reagents for exact quantification of peptides in complex mixtures. Peptide labelling is most typically achieved with isobaric tags that consist of a balancer and a reporter part that separate in the gas phase. An ingenious distribution of stable isotopes provides multiple reagents with identical molecular weight but a different mass of ...
08-Jan-2018
During cytokinesis, a signal from the central spindle that forms between the separating anaphase chromosomes promotes the accumulation of contractile ring components at the cell equator, while a signal from the centrosomal microtubule asters inhibits accumulation of contractile ring components at the cell poles. However, the molecular identity of the inhibitory ...
05-Jan-2018
Conformational changes of proteins and other biomolecules play a fundamental role in their functional mechanism. Single pair Förster resonance energy transfer (spFRET) offers the possibility to detect these conformational changes and dynamics, and to characterize their underlying kinetics. Using spFRET on microscopes with different modes of detection, dynamic ...
05-Jan-2018
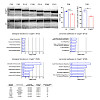
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) denotes a family of inherited blinding eye diseases characterized by progressive degeneration of rod and cone photoreceptors in the retina. In most cases, a rod-specific genetic defect results in early functional loss and degeneration of rods, which is followed by degeneration of cones and loss of daylight vision at later stages. ...
04-Jan-2018
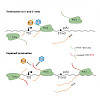
The carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase (Pol) II is composed of a repetition of YSPTSPS heptads and functions as a loading platform for protein complexes that regulate transcription, splicing, and maturation of RNAs. Here, we studied mammalian CTD mutants to analyze the function of tyrosine1 residues in the transcription cycle. Mutation of 3/4 of the ...
04-Jan-2018
Natural products have served as an inspiration to scientists both for their complex three-dimensional architecture and exquisite biological activity. Promysalin is one such Pseudomonad secondary metabolite that exhibits narrow-spectrum antibacterial activity, originally isolated from the rhizosphere. We herein utilize affinity-based protein profiling (AfBPP) to ...
03-Jan-2018

Salmonella infections require the delivery of bacterial effectors into the host cell that alter the regulation of host defense mechanisms. The secreted cysteine protease GtgE from S. Typhimurium manipulates vesicular trafficking by modifying the Rab32 subfamily via cleaving the regulatory switch I region. Here we present a comprehensive biochemical, structural, ...
17-Sep-2017
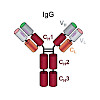
Nanobodies can be seen as next‐generation tools for the recognition and modulation of antigens that are inaccessible to conventional antibodies. Due to their compact structure and high stability, nanobodies see frequent usage in basic research, and their chemical functionalization opens the way towards promising diagnostic and therapeutic applications. In this ...
01-Jan-1970
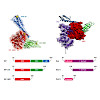
BiP is the endoplasmic member of the Hsp70 family. BiP is regulated by several co-chaperones including the nucleotide-exchange factor (NEF) Bap (Sil1 in yeast). Bap is a two-domain protein. The interaction of the Bap C-terminal domain with the BiP ATPase domain is sufficient for its weak NEF activity. However, stimulation of the BiP ATPase activity requires ...